GHW#8-Questions&Slides
advertisement

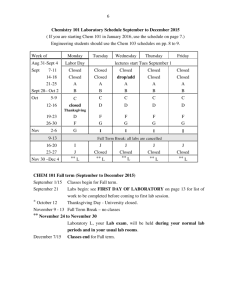
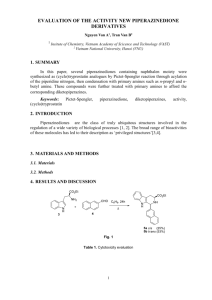
Chemistry 121(001) Winter 2015 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941; Office Hours: MTW 8:00 - 10:00 am; Th, F 9:00 - 10:00 am 1:00 - 2:00 pm. December 19, 2014: Test 1 (Chapters 12-13) January 26 , 2015: Test 2 (Chapters 14-16) February 13, 2015: Test 3 (Chapters 17-19) March 2, 2015: Test 4 (Chapters 20-22) March 3 , 2015: Make Up Exam: Chapters 12-22) Bring Scantron Sheet 882-E CHEM 121 Winter 2015 1 Chapter 18 and GHW#8 Questions & Slides Carbohydrates CHEM 121 Winter 2013 2 Chapter 18: Carbohydrates 18.1 Biochemistry-An Overview, 593 18.2 Occurrence and Functions of Carbohydrates, 593 18.3 Classification of Carbohydrates, 594 18.4 Chirality: Handedness in Molecules, 595 18.5 Stereoisomerism: Enantiomers and Diastereomers, 599 18.6 Designating Handedness Using Fischer Projection Formulas, 600 18.7 Properties of Enantiomers, 604 18.8 Classification of Monosaccharides, 607 18.9 Biochemically Important Monosaccharides, 609 18.10 Cyclic Forms of Monosaccharides, 612 18.11 Haworth Projection Formulas, 615 18.12 Reactions of Monosaccharides, 618 18.13 Disaccharides, 621 18.14 Oligosaccharides, 631 18.15 General Characteristics of Polysaccharides, 634 18.16 Storage Polysaccharides, 635 18.17 Structural Polysaccharides, 637 18.18 Acidic Polysaccharides, 640 18.19 Dietary Considerations and Carbohydrates, 641 CHEM 121 Winter 2013 33 3 Carbohydrates Organic compounds containing many -OH groups (polyhydroxy), and aldehydes or ketones functional groups. They are called sugars. Aldoses: Aldehyde sugars are called aldoses. Ketoses: Ketone sugars are called ketoses. Formula for Cabohydrates: CnH2nOn or Cn(H2O)n (hydrates of C) n= number of atoms Monosaccharides They consist of one sugar containing 3,4,5,6 and 7 carbon atoms Disaccharides Polysaccharides CHEM 121 Winter 2013 4 Drawing Sugar Molecules Linear structure-Fischer projection CHO Aldehyde H HO OH H CH2 OH O HO Ketone H H OH H OH H OH H OH CH2 OH Glucose Polyhydroxy aldehyde CHEM 121 Winter 2013 hydroxy CH2 OH Fructose Polyhydroxy ketone 5 Types of sugars Number fo carbon atoms • Triose sugar units containing three carbon atoms • Tetroses sugar units containing four carbon tomsa • Pentoses sugar units containing five carbon atoms • Hexoses sugar units containing six carbon atoms CHEM 121 Winter 2013 6 CHEM 121 Winter 2013 7 Chirality: Handedness in Molecules Most monosaccharaides exist in two forms: a “left handed” and “right handed” form due to chiral carbon atoms CHO CHO HO H H OH C C D isomers L isomers CH2OH CH2OH CHO CHO HO H CH2OH H OH CH2OH CHEM 121 Winter 2013 8 Chirality and Optical Activity D L L isomers D isomers Polarimeter assigns D and L isomers CHEM 121 Winter 2013 D-rotated to right L-rotates to left9 Cyclic anomeric forms: a- and b- forms Fischer structure Haworth structures ALDEHYDE sugar or aldoses + alcohol --- hemiacetal (cyclic ring) CHEM 121 Winter 2013 10 1) Give names of the following carbohydrates. Identify the chiral carbon atoms with * CHEM 121 Winter 2013 11 2) Circle the correct classifications that apply to the following carbohydrates. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 12 2) Circle the correct classifications that apply to the following carbohydrates. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 13 2) Complete the names, circle carbon atom numbers of the OH group which is on the left and the structure for following aldohexoses. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 14 2) Complete the names, circle carbon atom numbers of the OH group which is on the left and the structure for following aldohexoses. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 15 2) Complete the names, circle carbon atom numbers of the OH group which is on the left and the structure for following aldohexoses. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 16 2) Complete the names, circle carbon atom numbers of the OH group which is on the left and the structure for following aldohexoses. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 17 How you get cyclic hemiacetal form of the ketohexose sugar Dfructofuranose with b-anomeric. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 18 How you get cyclic hemiacetal form of the ketohexose sugar D-glucopyranose with banomeric. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 19 4) a) Complete the following diagram to get the cyclic hemiacetal form of the aldohexose sugar Dglucopyranose with b-anomeric configuration. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 20 4) b) Draw the structure of b-D-mannopyranose CHEM 121 Winter 2013 21 4) c) What is the difference between pynanose and furanose types of sugars? d) What is the difference between a and b forms of cyclic hemiacetal forms of sugars? CHEM 121 Winter 2013 22 5) Convert the hemiacetal cyclic structures (Haworth Projections) for following carbohydrates to Fischer Projections. a) Use the procedure we used in problem 4 to get linear form of the hexoketose sugar from cyclic D-fructofuranose with a-anomeric CHEM 121 Winter 2013 23 5) b) Use the procedure we used in problem 4 to get linear form of the hexoaldose sugar from cyclic D-sugarpyranose with b-anomeric CHEM 121 Winter 2013 24 Glycosidic bonds • Glycosidic bond- covalent bond between a hemiacetal or hemiketal and an alcohol. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 25 6) What are the following? What is/are glucosidic linkage found in them? a) Starch: b) Amylopectin: c) Glycogen: d) Cellulose CHEM 121 Winter 2013 26 7) Answer following question about glycosidic bond of the di-, oligo- and polysaccharides. a) Name of the following o-glucoside CHEM 121 Winter 2013 27 8) b) Name of the following N-Glycoside c) Name of the following glucoside. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 28 8) d) The following is a part of a cellulose polymeric chain. What is the type of glucosidic linkage? CHEM 121 Winter 2013 29 Nucleic Acids phosphate-group+pentose-sugar+Base D-Ribose D-deoxyribose • Deoxysugar or D-deoxyribose: ribose-derivative with an oxygen missing on C-2. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 30 Nucleic Acids Bases CHEM 121 Winter 2013 Purines pyrimidines 31 8) e) What is DNA? Describe the components. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 32 8) f) What is RNA? Describe the components. CHEM 121 Winter 2013 33