water-use-and-water-treatment
advertisement

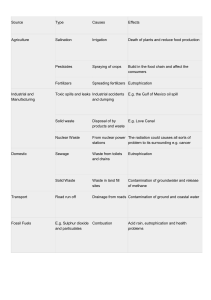
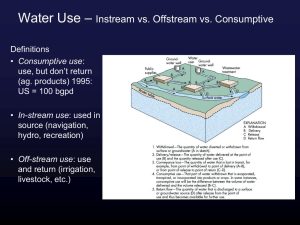
Water Use What is the hydrologic cycle? The water cycle Precipitation Evaporation transpiration What is ground water? Groundwater is water that is below the water table (level where the ground is saturated). Aquifer= from zone where groundwater can be obtained What is surface water? Surface water is water found above the water table/at the surface of the earth. Why do we have groundwater use problems? ½ the people in the US use ground water as a primary source of drinking water, sometimes at a rate of overdraft. Amount of water withdrawn is greater than inflow into the well. What is the difference between instream and off stream use? Off stream use = water removed from its source for use Some water is returned to the source (i.e. industrial cooling water) Consumptive use = water taken in (not returned to source) by humans, plants or animals In stream use = the use of water NOT removed from its source/ in rivers, dams, fish and wildlife habitats…etc. How can we conserve water through agricultural use? Agriculture accounts for 65% of total freshwater withdrawls of water between 1950-2005. (in reading) How can we reduce our public supply and domestic use (at home)? Think ecological footprint (in reading) Water Use 2 What is water pollution? The degradation of water quality, so that it harms living organisms or is not fit for human use. What is Biochemical oxygen demand? The amount of oxygen required for biochemical decomposition processes. When BOD increases, dissolved oxygen decreases What is water borne disease and how is it most commonly detected? Illness caused by bacteria or viruses in the water, whose symptom vary from a stomach ache to death. How do we monitor disease carrying organisms? Fecal coliform What nutrients most commonly cause water pollution? Nitrogen and phosphorus What is Eutrophication? The process by which a body of water develops a high concentration of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus (in the forms of nitrates and phosphates). What are the effects of Eutrophication? 1. Increased aquatic plant and algae growth 2. Blockage of sunlight by algae 3. plants and good bacteria die, and start to decompose 4. Decomposition increases BOD as the number of decomposers increase 5. Dissolved oxygen decreases 6. Fish die/ecosystem starts falling apart What is cultural Eutrophication Eutrophication? accelerated by humans Urban = sewage Rural = agricultural run off What are some causes of water pollution? Oil Sediment Acid mine drainage Agricultural Run off