Photosynthesis
advertisement

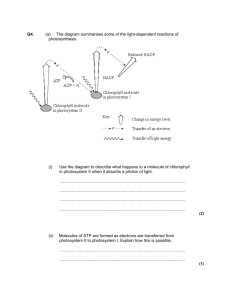
Photosynthesis Part I Photo (light)-synthesis (putting things together) Remember: - To make a large molecule (glucose) you need Energy - When you break down a large molecule (glucose) you generate Energy 2 Steps of Photosynthesis 1. Light-dependent reactions: convert the sun's energy into chemical energy - generate the energy needed for the next step 2. Light-independent reactions: use the energy from step 1. and Carbon dioxide to make glucose (food) 2 Steps Step 1 • Occurs in two different areas of the thylakoid – Photosystem I and Photosystem II • Photosystem – light collecting unit of the chloroplast • Photosystem has Chlorophyll and Electron Transport System ( a chain of Carrier Proteins) Light electrons - The more Energy an electron has , the further away from the protons it can get; - Given enough energy it can escape altogether leaving behind a (+) charged particle – ion - When an electron falls closer to protons, it releases energy - When Hydrogen (picture) looses 1 electron, it becomes a H+ ion Step 1 – getting that energy from the sun • Light-dependent – reactions need light • Requires water and sunlight • Chlorophyll absorbs the energy from the sun – (high energy particles called photons) – with enough energy 2 electrons will pop off from chlorophyll • To replace these lost electrons, Chlorophyll using photons will split water into oxygen, hydrogen ions and electrons – O2 H+ e- Step 1 – Photosystem II • The 2 electrons from Chlorophyll will travel down the electron transport chain (ETC) – a chain of carrier proteins that will use the energy form the electrons to transport H+ across the membrane – result high concentration of H+ inside the thylakoid • H+ ions build up inside the thylakoid from the break down of water and the ETC ATP formation • H+ wants to move from high to low concentration (Diffusion) but it needs help from a protein in the cell membrane called ATP synthetase • As H+ passes through, ATP synthetase is forced to turn and when it does it adds a phosphate group to ADP to make ATP Step 1 – Photosystem I The electrons from photosystem II lost energy when they pumped H+ across the membrane In photosystem I light gives electrons energy again Then they go through another ETC Here they are used to make NADPH which goes on to the next set of reactions Summary of Light dependent reactions • Require water and sunlight, have 2 parts: photosystem II and photosystem I • As light shines on Chlorophyll it looses 2 electrons, and replaces them with 2 electrons from water • As the plant uses the electrons from water H+ and O2 are left behind • Oxygen gas is given off in photosystem II and ATP is made • NADPH is made in photosystem I Step 2 – Light-independent reactions • • • • Also called Dark reactions or the Calvin cycle Takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast Need carbon dioxide to build carbohydrates Use ATP and NADPH (energy) from light dependent reactions and carbon dioxide to make carbohydrates/glucose Dark Side of Photosynthesis To be Continued.............