Photosynthesis with Mr. Anderson
advertisement

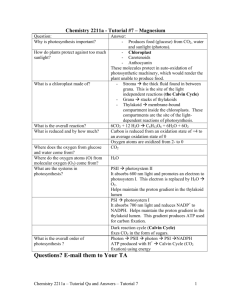
NOTES OUTLINE FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS and MR ANDERSON Mr. Anderson on Photosynthesis http://www.bozemanscience.com/photosynthesis 1. What are two things photosynthesis gives to “animals”. 2. Is it only found in plants? Is it predominantly found in plants? 2. Where in the cell does photosynthesis take place? 3. What are the key structures/regions of this organelle that we need to know about? Draw a diagram indicating a : thylakoid membrane, granum, stroma. 4. Identify which part of photosynthesis happens on the thylakoid membranes and what part occurs in the stroma. 5. If you grind up a leaf, there are several pigments. a. Chlorophyll A b. Chlorophyll B c. Xanthophylls d. Carotenes and Xanthophylls 6. What colors of light are ABSORBED by chlorophylls A and B 7. What color(s) are not absorbed? 8. What color light is generally reflected (and therefore not used) by plants? 9. Why are plants green? Why not black (to absorb everything)? 1 NOTES OUTLINE FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS and MR ANDERSON 10. What is the equation for photosynthesis? Underline the reactants. Identify where each is brought into the leaf. 11. What is the purpose of making glucose in the plant? 12. How does the plant utilize its own glucose (what process does it use). 13. Where does the photo part of photosynthesis take place? What are these reactions called? What reactant and what energy is used and what products are made? ? 14. Where does the synthesis part of photosynthesis of photosynthesis take place? What are the reactants and what are the products? 15. The light reactions take place in the thylakoid. Circle the two locations that energy enters the cell and and water that are the main “inputs” in the light reaction. Circle the products of the light reactions. Water is split inside the thylakoid (e- from water travel along the ETC and H+ accumulate in the thylakoid space). O2 is given off, what happens to the H+? What does the movement of e- do? Where do the electrons end up? What does the movement of H+ through ATP synthase produce? 2 NOTES OUTLINE FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS and MR ANDERSON Why is it important that ATP and NADPH are made in the stroma and not in the thylakoid space? What happens in the Calvin cycle? CO2 is added to RuBP (a 5 carbon compound) by an enzyme called RuBisCo. This is called FIXING carbon. This molecule is then REDUCED (electrons and hydrogen added) and a 2 3-carbon compounds (called G-3-P) are made. For every 6 CO2 that are put into the Calvin cycle 2 G3P carbon compounds are released to form glucose, fructose, maltose or be used to make other organic molecules and 10 are used to regenerate the RuBP compound (thus the cycle) So lets think about the Calvin cycle. It can’t take place without the _________ and ____________ that are made in during the light reactions. So, during a drought, even though there is lots of sun, a plant can’t make glucose. Additionally, when it is very hot, the stoma will remain closed to preserve water. If stoma are not opened, the ______________ cannot get into the leaf and _______________ cannot leave. This means that there will be more O2 trapped in the leaf than there is CO2. This can create a new problem called photorespiration. This only occurs (regularly) in very hot areas. There are two processes that plants have evolved to handle the extreme heat and/or low water. A C4 plant has an enzyme which allows CO2 to be incorporated into a 4-C compound (oxaloacetate) stored in bundle sheath cells. This storage allows stoma to remain closed. With plants in areas that are very warm with very low amounts of water (like cacti and pineapples) the plants store CO2 and create malic acid which is stored in vacuoles at night, and then converted to sugars during the day. Both processes requires more energy than C3 Calvin cycle, so it is only used or available in plants that have adaptations for hot climates (energy use is justified for survival). See the handout on Types of Photosynthesis for more information. 3