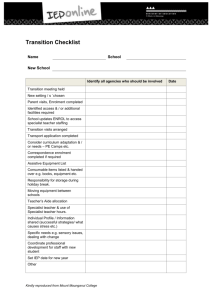
1 - Banbeis
advertisement

BANBEIS Publication No. 435 Bangladesh Education Statistics 2014 Bangladesh Bureau of Educational Information and Statistics (BANBEIS) Ministry of Education 1Sonargaon Road, Palashi-Nilkhet, Dhaka-1205 Website: www.banbeis.gov.bd, e-mail: info@banbeis.gov.bd Phone: 9665457, Fax: 9665457 March: 2015 1 2 Picture Message Nurul Islam Nahid M.P Minister Ministry of Education Government of the people’s Republic of Bangladesh In order to active the goal of vision 2012, effective education planning and management are very much essential. At the same time effective planning and management depend on updated ,authentic and accurate data. I am glade to know that Bangladesh bureau of Educational Information and statistics (BANBEIS) has completed Annual Education survey (on line) 2014 and Prepared a report and the basis of collected date which was focused on the education indicators and statistics. I believe this survey report will present a comprehensive picture of education of Bangladesh. I also believe that the report will provide valuable and authentic information related to education in Bangladesh and all the stakeholders in and outside the will be benefited from this report. I wish to express my thanks to the Director, BANBEIS and all his staffs for their sincere efforts to publish a quality report. (Nurul Islam Nahid M.P) 3 Picture Message Secretary Ministry of Education Government of the people’s Republic of Bangladesh Update and reliable education statistics are indispensible for effective planning, development and educational management in the education sector . Bangladesh bureau of Educational Information and statistics (BANBEIS) has completed Annual Education survey(on line) -2014 and prepared a report on the basis of data collected from this survey, focusing on the key education indicators , statistics and Time series data . Annual Education survey is routine but a difficult task . I think that in this report a comprehensive picture of the sector will be available. This report will also be helpful in determination of goals and strategies for the next Five year Plan keeping in view the vision 2021. I hope, this survey report will serve as a vital source of information to those who work in educational policy, standards and other aspects. I express my thanks and appreciation to all those who have significantly contributed to complete this report . (Md.Nazrul Islam Khan ) Preface 4 There has been a remarkable development in education in the last thirty years in Bangladesh. The rate of participation has increased steadily at all levels. The main responsibility of BANBEIS is to collect, analyze, compile data and publish educational statistics covering all levels in the postprimary sector. This organization also disseminates education data published by the Directorate of primary Education. Since various levels and areas of education are inter- related, it is necessary and prudent to publish all pertinent statistics on education in a single publication. The annual report entitled ‘Bangladesh Educational Statistics-2014’ is an attempt to publish educational statistics at all levels for the year 2014. This document comprises data collected from all post-primary educational institutions through on-line (self-responding). Every educational institute updated the respective database information on-line and sent it through internet. Quality Assurance(QA) process took place for validation. Databases have been developed in ORACLE 11g using ORACLE Developer 2010. We made all efforts to present the comprehensive and quality statistics, which will hopefully be useful for purposes of educational planning and management. This report can be used as a basis for educational planning and future investment by the Government, NGOs and private sectors as well as by the Donor Communities in Bangladesh. I would like to express my gratitude to the officers & staff concerned of this Bureau who have contributed in preparing this valuable report. The field officers (DEO and USEO) have provided significant inputs in the process. I express my gratitude to all of them. In spite of the best efforts some inadvertent errors may have crept into the report. Any Pragmatic Suggestion and/or Corrections pointed out will be highly appreciated and proper measure will be taken in preparing the next edition. BANBEIS February 2015 Md. Fashiullah Director 5 Editorial Board Chairman Md. Fashiullah Director, BANBEIS, Ministry of Education. Chief Editor Md. Shamsul Alam Chief, Statistics Division, BANBEIS. Members S.M. Morshed BipulChief, DLP division, BANBEIS. Sheikh Md. AlamgirSpecialist, Statistics, BANBEIS. Kazi Elias Uddin Ahmed- Specialist, Documentation Md. Khan Jahan AliStatistical officer S.M. Kamrul Hasan Khan- Statistical officer Muhammed Tariqul Islam- Assistant Statistical officer 6 CONTENTS List of Tables Acronym Data definition Executive Summary and survey findings Summary Statistics and key performance indicators Chapter 07 13 15 16 25 Page No. Contents 1 Introduction, Objectives, and survey methodology 36 2 Primary education 42 3 Secondary school Education 54 4 College Education 102 5 Madrasah Education 176 6 Professional and Teacher Education 208 7 Technical and Vocational Education 218 8 University Education 232 9 Education Finance 252 10 Output Statistics 260 11 English medium school 280 Annexure: Questionnaires 290 Data in the Web page (www.banbeis.gov.bd) 7 List of Tables No. of Table Table Head Table 3.1.0 Table: 3.1.1(a) Table 3.1.1(b) Table 3.1.1(c) Primary education : Number of Primary Education institution, teacher and student : Enrolment in Pre-Primary by Gender : Enrolment in Grade 1(All school) by Gender : New entrants in Grade 1 (all schools)by gender : Grade wise Enrolment by Gender (All school) : Enrolment by Type of School, Grade and Gender : Enrolment of Special Needs Children by Type of Disability :Enrolment of special needs children, 2005- 2014 : Enrolment of Special Needs Children (Disable) by Gender and Types of School (DPE controlled) : Gross and Net Intake Rate, 2005-2014 : Enrolment Rate in Primary Education, 2005-2014 : Dropout rate by Grade (%) : Dropout Rates, 2005-2014 : Dropout Rate by District and Gender : Repeaters by Grade and Gender : Repetition Rate by Grade and Gender :Repetition Rates by Gender, 2005-2014 : Year and Genderwise Survival Rate 2005-2014 : Yearwise Coefficient of efficiency, 2005-2014 : Yearswise Input per Graduate, 2005-2014 : Internal Efficiencies : Average Student Absenteeism by gender 2005-2014 : Primary Education Completion Examination Pass Rate by Year 2009-2014 : Number of C-in-Ed Trained Teacher by Gender and Division in GPS, RNGPS and NRNGPS : Number of C-in-Ed Trained Teacher by Division and Gender in Experimental and Community School Secondary Education : Number of Secondary School, Teacher And Enrolment by Gender, 1995-2014 :Number of institution, student and teacher by type :Number of Attached Primary Section, Student, and Teacher :Number of Attached Pre-Primary Section, Student, and Teacher Table 3.1.1(d) : Number of institution, student and teacher by location (Urban-Rural) Table 3.1.1(e) Table 3.1.2 (a) Table 3.1.2 (b) Table 3.1.2(c) Table 3.1.2(d) Table 3.1.3(a) Table 3.1.3 (b) Table 3.1.4 Table 3.1.5 Table 3.1.6 Number of Institution, Student and Teacher in Metropolitan Areas :Secondary Cycle Completion Rate, Dropout Rate and Coefficient of Efficiency by Sex : Dropout rate by grade and sex in secondary education :Gross and Net Enrolment Rate by Sex in Secondary Schools :Enrolment Rate at Secondary Level in School :Number of School, Teacher and student by Division and management : Number of School, Teacher and Student by Division and Location :Number of School, Teacher, Student and some indicators by District and management :Number of School , Teacher and Student by Area Status :Comparison of Districts with different Performance Indicators Table: 2.1 Table: 2.2 Table 2.3 Table 2.4 Table 2.5 Table 2.6 Table 2.7 Table 2.8 Table 2.9 Table 2.10 Table 2.11 Table 2.12 Table 2.13 Table 2.14 Table 2.15 Table 2.16 Table 2.17 Table 2.18 Table 2.19 Table 2.20 Table 2.21 Table 2.22 Table 2.23 Table 2.24 Table 2.25 8 Page number 43 44 44 44 44 44 45 45 45 46 46 47 47 48 49 49 49 50 51 51 51 52 52 53 53 55 55 56 56 57 58 59 60 60 60 61 63 63 77 78 Table 3.2.1 Table 3.2.2 Table:3.2.3 Table 3.2.4 Table-3.2.5 Table 3.2.6 Table 3.3.1 Table 3.3.2 Table 3.3.3 Table 3.3.4 Table 3.3.5 Table 3.3.6 Table 3.3.7 Table 3.3.8 Table 3.4.1 Table 3.4.2 Table 3.4.3 Table 3.4.4 Table 3.4.5 Table 3.4.6(a) Table 3.4.6(b) Table 3.4.7(a) Table 3.4.7(b) Table 3.4.8: Table 3.4.9 Table 3. 5.1 Table 3.5.2 Table 3.5.3 Table 3.5.4 Table 3.5.5 Table 3.5.6 Table 3.5.7 Table 3.5.8 Table 3.5.9 80 80 81 81 82 82 83 83 84 85 86 87 87 88 89 89 90 91 91 92 92 93 93 94 95 96 96 97 97 98 98 99 99 100 Table 4.1 .1 :Number of School by Year of Establishment and Management Number of School by Type of Enrolment : Number of School by Topography :Number of non-government school by type of management committee :Number of Institution by Division and Management : Number of non government school by type of management committee :Number of Student by Level of Education in the secondary School :Number of Student by grade and management of Education in the secondary School :Number of Student by stream and management in the secondary Schools :Number of student by subjects :Student in Secondary Schools by location, division and management Student in Secondary Schools by type of disability and by grade :Distribution of Student by their Guardians 's occupation :Distribution of Student by Age, Gender and Class :Number of Teacher, Assistant Librarian and Employee by Designation : Number of Teacher by Designation and Type of School :Number of Teacher in Non-Govt. School by Designation and Gender :Number of Teacher in Govt. School by Designation and Gender :Number and Percentage of Trained Teacher by Management and Gender :Distribution of English teacher by academic qualification and type of institution :Distribution of Math teacher by academic qualification and type of institution :Number of School and average number of teacher teaching English by management :Number of School and average number of teacher teaching Math by management :Percentage of regular and acting headmaster in schools :Number of Teacher by education level, management and area status :Number of Institution having electricity connection :Number of Institution having multimedia :Number of School having computer facility :Number of Institution using teaching materials : Number of Non-Govt. School by M.P.O Status (Survey Data) : Number of school with different activities : Institutions having computer teacher : Number of school having solar panel : Number of school having internet facility College Education :Number of College by Type, Management and Gender, 2005-2014 Table 4.1.2 : Number of Teacher in Colleges by Management and Gender, 2005-2014 104 Table 4.1.3 : Enrolment in College by Management and Gender, 2005-2014 :Number of College, Teacher and Enrolment by type :Teacher Student Ratio(TSR)Average Student and Teacher per college by Type :Dropout and Completion Rate in College (XI-XII) :Higher Secondary (College & Madrasah) Cycle Completion Rate, Dropout Rate and Coefficient of Efficiency by Gender : Higher Secondary (College & Madrasah) Cycle Completion Rate, dropout rate and coefficient of efficiency by gender( 11 & 12) :Gross and Net Enrolment Rate in College (11 & 12) class 105 Table 4.1.4 Table 4.1.5 Table 4.1.6 Table 4.1.7 Table 4.1.8(a) Table 4.1.8(b) 9 103 106 107 107 107 108 109 Table 4.1.9 Table 4.1.10 Table 4.1.11 Table 4.1.12 Table 4.1.13 Table 4.1.14 Table 4.1.15 Table 4.1.16 Table 4.1.17 Table 4.1.18 Table 4.1.19 Table 4.2 Table 4.2.1 Table 4.2.2: Table 4.2.3: Table 4.2.4 Table 4.2.5: Table 4.3.1: Table 4.3.2: Table 4.3.3: Table 4.3.4: Table 4.3.5 : Table 4.3.6 : Table 4.4.1 Table 4.4.2 Table 4.4.3 Table 4.4.4 Table 4.4.4(a) Table 4.4.4(b) Table 4.4.4(c) Table 4.4.5 Table 4.4.6 Table 4.4.7 Table 4.4.8 Table 4.5.1 Table 4.5.2 Table 4.5.3 Table 5.1.1 Table 5.1.2 Table 5.1.3 Table 5.1.4 Table 5.1.5 Table-5.1.6 Table 5.1.7 Table 5.1.8 :Gross and Net Enrolment Rate in College and Madrasah (11 & 12) class :Number of college, Teacher and Enrolment by type, management and Gender :Number of college, Teacher and Enrolment by type and division :Number of College , Teacher and Student by Area Status :Number of teacher and enrolment by location and management :Number of College, teacher and enrolment in metropolitan cities :Number of College, teacher and enrolment in Dhaka city, metropolitan, municipal and rural Area :Number of college, teacher and enrolment by division, type and management :Number of college, teacher, enrolment by location, district, management &Type :Number of college, teacher, enrolment by division, district and management :District wise Comparison on Population, enrolment and Performance Indicators :Number of college by Type, gender and management :Number of college by division :Number of college by geographical areas and management :Number of college by recognition status :Number of college by year of establishment and management :Number of college according to type of managing committee :Enrolment by Gender management and type :Enrolment in college by geographical areas and management :Enrolment by Gender, level and management : Age wise Enrolment : Enrolment by Gender, grade and management : Enrolment by management, location, division : Number of College and teacher by Gender : Number of teacher working and receiving MPO in private college by Gender (Survey data) : Number of teacher in College by designation : Number of teacher in private College by designation : Number of teacher in service and receiving MPO by designation in private college : Number of teacher in service by designation in govt. college : Number of teacher by Gender and management : Number of College, Teacher by division : Teacher in college by geographical areas and management : Number of teacher by management, division and location : Number of librarian, employee by gender by type of college : Number of College having electricity and multimedia : Number of College having computer, Internet connection and Solar panel by Mgt. : Number of college having pure drinking water, toilet facilities by type Madrasah Education : Number of Madrasah (Dakhil to Kamil) by Type and gender ,1996-2014 :Number of Teacher in Madrasah by Type and gender, 1998-2014 : Enrolment in Madrasah by Type of madrasah and gender, 1998-2014 : Number of Madrasah, Teacher and Enrolment (Post-Primary) by Type, Gender and Management : Enrolment and Teacher for Ibtedaye Section of Madrasah by Type : Enrolment by Type, grade and gender : Teacher-Student (Post-Primary) Ratio by Type of madrasah and management : Number of Madrasah, Enrolment and Teacher by Type, Area and Gender 10 109 109 110 112 116 117 118 119 122 145 147 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 157 158 160 163 163 164 164 165 165 165 167 168 169 170 171 172 172 177 177 178 179 179 179 180 180 Table 5.1.9 Table 5.1.10 Table 5.1.11 Table 5.2.1 Table 5.2.2 Table 5.2.3 Table 5.2.4 Table 5.2.5 Table 5.2.6 Table 5.2.7 Table 5.2.8 Table 5.2.9 Table 5.2.10 Table 5.2.11 Table 5.2.12 Table 5.3.1 Table 5.3.2 Table 5.3.3 Table 5.3.4 Table 5.3.5 Table 5.3.6 Table 5.3.7 Table 5.3.8 Table 5.3.8.1 Table 5.3.9 Table 5.3.10 Table 5.3.10.1 Table 5.3.11 Table 5.3.11.1 Table 5.3.12 Table 5.3.12.1 Table 5.4.1 Table 5.4.2 Table 5.4.3 Table 5.4.4 Table 5.4.5 Table 5.4.6 Table 5.4.7 Table 5.4.8 Table 5.4.9 Table 5.4.10 Table 6.1 Table 6.2 Table 6.3 : District wise Madrasah, Teacher and Enrolment by gender : City corporation wise institution, Teacher and enrolment by type and gender : Comparison among Districts with different Performance Indicators : Number of Madrasah (Post-Primary) by Category, Management and Type : Number and Percentage of Madrasah by Type and Management : Recognition Status of Non-Govt. Madrasah by Type and Management :Number of Madrasah by year of Establishment and Management : Number and Percentage of Madrasah (Post-Primary)by Type and Division : Number of Madrasah by Type, Division, Location and Management : Number of Madrasah by type of Management Committee : Number of Madrasah by Geographical Area, Management and Type : Number of Madrasah having computer, Internet connection and Solar panel by Type : Number of Madrasah having Electricity and Multimedia by Type : Number of Madrasah having Pure Drinking Water and Toilet by Type : Percentage of Madrasah with different activities : Enrolment in Madrasah (Post-Primary) by Gender and Management : Average Enrolment (Post-Primary) of Madrasah by Division and Gender : Enrolment in Madrasah (Post-Primary) by Type and Division : Enrolment (Post-Primary) by Type, Management, Location and Division : Grade wise Enrolment by Management, Type and Gender : Grade wise Enrolment (Grade 11-12) : Enrolment in Madrasah (Post-Primary) by Management, Type Gender and Level : Enrolment by age, grade and Gender : Enrolment (Alim_Kamil)by age, grade and Gender : Enrolment(Dakhil-Alim) by Type of disability, grade and Gender : Secondary cycle(Dakhil) completion, dropout rate and co-efficient of efficiency : Promotion, repetition and dropout rate by grade ( secondary level) : Higher secondary cycle completion rate, dropout rate and co-efficient of efficiency :Promotion, repetition and dropout rate(Alim level) by gender : Gross and Net Enrolment Rate (Dakhil level) in Madrasah : Gross and Net Enrolment Rate (Alim level) in Madrasah : Number of Teachers (post-Primary) by Type, Management and Gender : Number of madrasah, teacher receiving MPO by gender and type (survey data) : Average Teacher (Post-Primary) by Gender, Management and Type : Average Teacher (Post-Primary) by Location Management and type : Number and Percentage of Teachers (Post-Primary) by Type and Division : Number of Teacher (Post-Primary) by Type, Location and Division Number of Teacher Working at Present, receiving MPO and having NTRCA by designation and gender : Number and percentage of Trained Teacher (post-primary) by Division and gender : Number and percentage of appointed/acting Institution Heads by Type and Management : Number and Percentage of Non Teaching Staff in Madrasah by Type and Gender Professional & Teacher Education : Number of Professional Educational Institution, Teacher and Enrolment by Management and Gender 2000-2014 : Number of Professional Educational Institutions by Type, Gender and Management : Number of Teacher in professional Education Institution by Type, Gender and 11 181 188 189 191 191 191 192 192 193 194 194 195 195 195 196 197 197 197 198 199 199 200 200 200 201 201 201 202 202 202 202 203 203 203 204 204 204 205 206 206 208 209 210 211 Table 6.4 Table 6.5 Table 6.6 Table 6.7 Table 6.8 Table 6.9 Table 6.10 Table 7.1 Table 7.2 Table 7.3 Table 7.4 Table 7.5 Table 7.6 Table 7.7 Table 7.8 Table 7.9 Table 7.10 Table 7.11 Table 7.12 Table 8.1 Table 8.2 Table 8.3 Table 8.4 Table 8.5 Table 8.6 Table 8.6(a) Table 8.7 Table 8.8 Table 9.1 Table 9.2 Table 9.3 Table 9.4 Table 9.5 Table 9.6 Table 9.7 Table 9.8 Table 9.9 Management : Enrolment in Professional Educational Institution by Type, Gender and Management : Number Teacher of Professional Education Institute by Type and Division ; Number of Teachers Training Institute, Teachers and Enrolment by Management & Gender, 2000-2014 : Number of Teacher Education Institution by Type, Gender and Management : Number of Teacher in Teacher Educational Institutions by Type and Management : Enrolment in Teacher Educational Institution by Type, Gender and Management Number of Teacher Education Institutes by Types and Division Technical & Vocational Education : Number of Technical and Vocational Institution, Teachers and Enrolment by Management and Gender 2000-2014 : Technical Institution with respect to Establishment Period(Independent Institution) : Number of Institution, Teacher and Enrolment by Type : Number of Institution, Teacher and Enrolment by management (Attached) : Number of Institution, Teacher and Enrolment in Technical & Vocational Education : Number of Institution, Teacher and Enrolment by type, management and Gender : Number of Institution by Type, Management and Division : Number of Teacher by Type, Management and Division : Enrolment by Type, Management and Division : Number of Institution, Teacher and Enrolment by Location : Average teacher and Enrolment by Type : Teacher-Student Ratio by Type(independent) University education : Number of university, teacher and enrolment by type and Gender : Year of Establishment and the Number of Faculties, Department and Institutes of Public Universities : Year of Establishment and the Number of Faculties, Department and Institutes of Private Universities Number of Student, Teacher and Teacher Student Ratio of Public University Number of Student, Teacher and Teacher Student Ratio of Private University : Number of Teacher by Designation in Public University : Number of Teacher by Designation(regular) in Private University Student Enjoying Accommodation Facilities in Public Universities :Output Statistics of Degree (Pass), Degree (Hons) Masters and Equivalent Examinations conducted by public University Education Finance : The Share of Education Budget in National Budget,2011-12 to 2014-15 : The share of GDP and national budget in Education : Education Expenditure by level and Percentage share by type (Recurrent – Capital) : Education Expenditure by level and Percentage share by level : Recurrent expenditure on salary and non salary in percentage (only Non development budget and public institutions) : Per student expenditure (total, recurrent and capital) : Public Expenditure on Education by Nature of Spending : Number of Secondary and Higher Secondary Students Received stipend and Tuition subsidies under different Projects :Number of Non-govt. education institution getting salary subvention(MPO) from 12 211 213 214 215 215 216 217 219 220 221 222 222 224 225 226 227 229 230 231 233 233 235 238 24 243 245 248 250 253 253 254 254 255 255 255 256 257 Table 9.10 Table 9. 11 Table 10.1 Table 10.2 Table 10.3 Table 10.4 Table 10.5 Table 10.6 Table 10.7 Table 10.8 Table 10.9 Table 10.10 Table 10.11 Table 10.12 Table 10.13 Table 10.14 Table 10.15 Table 10.16 Table 10.17 Table 10.18 Table 10.19 Table 10.20 Table 10.21 Table 10.22 Table 11.1 Table 11.2 Table 11.3 Table 11.4 Table 11.5 Table 11.6 Table 11.7 Table 11.8 Table 11.9 Table 11.10 Table 11.11 Table 11.12 Table 11.13 Table 11.14 Table 11.15 government : Expenditure of the Govt. on Salary Subvention to Non-Govt. Education Institution 257 Percentage of Expenditure on Salary Subvention to the Non-govt. Education Institution as per budget of Secondary & Tertiary Education (MOE) Output Statistics : Result of Secondary School Certificate (S.S.C) Public Examination by gender : Result of Secondary School Certificate (S.S.C) Public Examination by Stream : Number and Percentage of Examinee by Steam for SSC : Number of SSC(Voc.) Examinee : Result of Higher Secondary School Certificate (H.S.C) Public Examination by Gender : Result of Higher Secondary School Certificate (H.S.C) Public Examination by Stream. : Number and Percentage of Examinee by Stream for HSC : Result of Higher Secondary Business Management (H.S.C BM) Public Examination by Sex : Result of Madrasah for Dakhil and Alim Public Examination : Result of Madrasah for Fazil and Kamil Public Examination :Result of SSC Graduate with grade point by gender : Result of Dakhil Graduate with grade point by gender : Result of SSC(Vocational) Graduate with grade point by gender : Result of HSC Graduate with grade point by gender : Result of Alim Graduate with grade point by gender : Result of HSC(BM) Graduate with grade point by gender : Result Statistics for Dakhil Examination by gender : Result Statistics for Alim Examination by gender : Result Statistics for Fazil Examination by gender : Result Statistics for Kamil Examination by gender and stream : Result of Degree (Pass) Examination published in 2002-2006 : Result of Degree (Pass) Examination published in 2007-2010 English Medium School 258 :No. of Schools by type of Enrolment :No. of Schools by type of Management :No. of Schools by Affiliation Status :No. of Schools by Affiliation Authority :No. of Schools by Area :No. of Schools by Division 281 281 282 282 282 282 282 283 283 283 284 284 284 284 285 : Number of Institution, Enrolment, Teacher, Average Enrolment per School : Enrolment by Gender : Number of Teacher by type of Gender : Number of Teacher by Designation : Number of officer and Staff by Designation : Enrolment by Division : Teacher by Division School Having Different Utilities : Number of enrolment and teacher by institution, 2013 13 261 262 263 264 264 265 266 266 267 267 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 277 278 279 Acronym AES AI AIUB ASTU ATI AUB B.A BBA B.Com B.Ed B.Sc BANBEIS BAU BBS BISE BMTTI BOU BSMMU BSMRAU BUET CU CWU DEO DG DIU DSHE DTE DU DPE EFA EMIS ESD EWU FCPS GER GIS GR HC HSC HSTTI IU IUB IUBAT Annual Education Survey Assistant Inspector American International University of Bangladesh Ahsanullah Science and Technology University Agriculture Training Institute Asian University of Bangladesh Bachelor of Arts Bachelor of Business Administration Bachelor of commerce Bachelor of Education Bachelor of Science Bangladesh Bureau of Educational Information and Statistics Bangladesh Agriculture University Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics Board of Intermediate and Secondary Education Bangladesh Madrasah Teachers Training Inatitute Bangladesh Open University Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agriculture University Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology Chittagong University Central Women’s University District Education Officer Director General Darul Ihasan University Directorate of Secondary and Higher Education Directorate of Technical Education Dhaka University Directorate of Primary Education Education for All Educational Management Information System Education for Sustainable Development East West University Fellow of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Gross Enrolment Rate Geographic Information System Growth Rate Homoeopathic College Higher Secondary Certificate Higher Secondary Teachers’ Training Institute Islamic University/Independent University Independent University of Bangladesh International University of Business, Agriculture and Technology 14 IUC JU KU LL.B M.A MBA M.Com MDGs M. Phil MOE-PC MOPME MS MSS NAEM NAPE NEP NER NGOs NTRCA NSU NU PEC Ph. D PPE PTI PUB QU RU SSC SUST SVR TTC UAP UC UIS UNESCO UGC USTC USEO VTTI Islamic University of Chittagong Jahangirnagar University Khulna University Bachelor of Law Master of Arts Master of Business Administration Master of Commerce Millennium Development Goals Master of Philosophy Ministry of Education-Planning Cell Ministry of Primary and Mass Education. Master of Science Master of Social Science National Academy for Educational Management National Academy for Primary Education National Education Policy Net Enrolment Rate Non Government Organization National Teachers Registration and Certification Authority North South University National University Post Enumeration Check Doctor of Philosophy Post-Primary Education Primary Training Institute People’s University of Bangladesh Queen’s University Rajshahi University Secondary School Certificate Shahjalal University of Science and Technology Sample Vital Registration Teachers Training College/Technical Training Centre University of Asia and the Pacific University of Comilla UNESCO Institute for Statistics United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization University Grants Commission University of Science and Technology, Chittagong Upazila Secondary Education Officer Vocational Teacher Training Institute 15 Data definition Enrolment: Number of students officially enrolled in a given grade or level of education regardless of age. Class Size : Average number of students together in a class enrolled. Teacher Student Ratio (TSR): Refers to the proportion of teachers in relation to the number of students in an institution. Calculated by dividing the total number of students in a school or group of schools by the total number of teachers teaching them. Urban Area: Refers to the area covered by municipalities, Upa-zila Head Quarters, District Head Quarters and City Corporations in the country. Cohort survival rate: percentage of students enrolled at the beginning grade/ year of the level of education who reached the final grade/year at the end of the required number of years of the level of education. Drop-out Rate: refers to the percentage of students for any reason leave educational institutions(in any given grade or level) and did not come back to finish the grade or level during that school year to the total number of students enrolled during the previous school year. Completion Rate: The percentage of students enrolled at the beginning grade/year of the level of education who finished or graduated from the final grade/year at the end of the required number of years of that level of education. Graduation rate: The percentage of pupils/students in the last grade/year of that level of education who completed and passed the academic requirements of that last grade/year. Gross Enrolment rate: Refers to the total enrolment of students in a grade or level of education, regardless of age, expressed as percentage of the corresponding eligible official age-group population in a given school year. Net Enrolment Rate: Refers to the number of students enrolled in the official specific-age group expressed as a percentage of the total population in that age group. School age Population: Population of the age group theoretically corresponding to a given level of education as indicated by theoretical entrance age and duration e.g the population from ages four to thirty inclusive regardless of the existing requirements of compulsory education or the period of education provided for in various types of schools. Co-efficient of efficiency: It is a ratio of expected student years required to complete the cycle by the graduates and the total years actually spent to produce those graduates expressed in percentage terms. The ideal (optimal) number of pupil-years required (i.e. in the absence of repetition and dropout) to produce a number of graduates from a given school-cohort for secondary education expressed as a percentage of the actual number of pupil-years spent to produce the same number of graduates. This is a synthetic indicator of the internal efficiency of an educational system. It summarises the consequences of repetition and dropout on the efficiency of the educational process in producing graduates. 16 Executive Summary Introduction: In view of the importance of education in the development of the country, the government has been giving top most importance for the expansion of education. For the past decade Bangladesh has been investing heavily to achieve the education Millennium Development Goals. Besides reducing poverty, Bangladesh has made spectacular success in improving access to education. The gross enrolment ratio in primary education in 2014 has reached 108% and net enrolment rate 97.7%. The gross enrolment ratio in secondary education in 2014 reached 55.84% while net enrolment rate 50.27%. Bangladesh has achieved gender parity for educational access in both primary and secondary education (well in advance of their 2015 MDG). The number of out of school children has been continuously decreasing both in absolute and relative term. The Bangladesh education system is large, catering to over 37 million students (2014), involving many stakeholders (for example there are 14 types of providers in primary education, 10 examination broads at the secondary levels, about 98.33% secondary educations are privately managed). The education system of Bangladesh is comprised of a mix of heterogeneous providers. A variety of schools operate within the country; government run schools, privately run schools and madrasah, English medium schools, schools run by NGOs and kindergarten schools. Primary education spans grade 1-5; Junior secondary grades 6-8, secondary grade 9-10, higher secondary grade 11-12 and tertiary education grades 13 and above. Bangladesh has a centralized Education system administered by the Ministry of Education (MOE) and the Ministry of Primary and Mass Education (MOPME). The MOPME and DPE are responsible for planning and management of primary, mass and pre-primary education. The MOE, DSHE and DTE are responsible for post-primary education. The MOE and UGC look after the overall management of higher education. For the planning and development of the education sector, the ministries need a strong quality data base. With a view to up-dating the data base, BANBEIS regularly conducts post-primary education surveys. The base-line survey was conducted in 2008 after that the annual survey was conducted in 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014. The purpose of Bangladesh education survey is to provide up-dated educational information and key performance indicators to the policy makers and other stakeholders. The scope of annual survey-2014 was very broad. All the educational institutions imparting post primary education were covered. The present report based on educational survey 2014 data doesn’t fully address issues such as management, governance, equity and non-teaching staff. The socio-demographic characteristics of students and teachers were not considered. One limitation of the survey is the difficulty in obtaining data from English medium schools and Universities. The Survey methodology was similar to the one adopted in 2014 Survey (Details are given in the chapter one). The 2014 annual education Survey used 10 questionnaires, one for each type of institution. The questionnaires were pretested before finalization. 17 Questionnaires were up-loaded to Website viz; www.banbeis.gov.bd to fill up and sent to BANBEIS server through One-line. The data collection started on 01.10.2014 and continued up to30.12.2014. Editing was done at field (USEO office) and head office to ensure quality of data. Besides, Post Enumeration Check (PEC) was done for School, College and Madrasahs to minimize errors. In PEC a total of 620 Institutions were covered. Comparing the findings of the main Survey data with those of PEC it was found that the main survey data were reliable and valid. According to the Education Survey 2014, there were 146240 Educational institutions in the country. This number was 144124 in the year 2013. Primary Education: The Bangladesh primary education system is large, catering to 19.55 million students in 2014 through 14 types of providers. Among them the government primary school alone covered 14.67 million (75%) students. The number of girls students was 9913884(50.70%).The GPI was more than 1.00 (1.03%). In 2014, total teachers were 4.82 lacs. Female teachers were 60.11% of all teachers. Variation was observed between types of primary education institutions (Table 2.1) The Survey collected data on Pre-primary education enrolment from 7 types of institution (Table-2.2). The total pre-primary enrolment was 20.6 lacs, among them 10.06 lacs(49.7%) were girls. Drop-out was prevalent in every grade, the rate was higher in grade 2, 3 and 4 (Table 2.12) Apparent intake rate (AIR) and net intake rate (NIR) was 108.7% and 97.9% respectively. Small difference was observed between boys and girls. Gross enrolment Ratio (GER) and Net enrolment Rate (NER) in primary education have been increasing during the past decades. GER was 94% in 2005, and reached 108% in 2014. GER of girls(112.3%) was higher than that of boys. NER in primary education was 87% in 2005 and increased to 97.7% in 2014. The growth was spectacular and confirms continuous increase of access of school age children to education. Drop-out rates has been continuously decreasing from 47% in 2005 to 20.9% in 2014. Compared to boys, girls drop-out rate was lower (Table 2.11) District wise variation was remarkable. Repetition rate ranged between 2.8% and 10.2% between grades, highest in grade 4 (10.2%). Survival rates has shown a continuous growth trend (from 54% in 2005 to 81% in 2014) As a result of increasing growth of access, retention and survival of students the primary education coefficient of efficiency rate has been increasing from 63% in 2005 and rose to 80% in 2014. In 2009 pass rate in primary completion examination was 89% (88% for girls). The pass rate increased to nearly 99% (for both boys and girls) in 2014. Junior, Secondary and Higher Secondary Education: Total institutions offering Junior and Secondary education were 19684 in 2014. The number of institutions in this subsector was 12012 in 1995, has been smoothly increasing. Side by Side the enrolment and teachers also increased. In 2014, the total enrolment was 9.16 million among them 4.87 million (53%) were girls giving gender parity index 114%. Number of students per institution was 465 in 2014. Total teachers were 2.33 lac with 58969 female teachers. The percentage of 18 female teachers was 25% in 2014 and 20% in 2005. In 2014, teacher-student ratio (TSR) was 39 and average number of teachers per institution was only 11.8 Among all teachers 62.32% were trained. This percentage was 27.36% in junior schools 66.2% in Secondary and 75% in higher secondary institutions. In the total institution in 2014 the share of Junior Secondary institutions was 13%, Secondary institutions 83%, School and Colleges offering Higher Secondary 4%. Among all institutions (19684), more than 98% (98.4%) were privately managed and only 1.6% was publicly managed. Rural-Urban distribution reveals that in 2014, 77% institutions were located in rural areas, 69% teachers were working in the rural institutions, and 71% student was studying in rural institution. The distribution by division reveals unequal distribution. As regards number of institutions, Sylhet had only 5% while Dhaka had 26% of all institutions. As regards enrolment the share of Sylhet was 5.9% while Dhaka had 31.1% (Table 3.1.3/b). The 2013 Education Survey reveals that 81.4% of all institutions had electricity facility; the percentage was 45% in junior secondary schools, 86% in secondary schools and 97% in higher secondary institutions. Number of institutions having multimedia was 58%. This percentage was 8% in Junior Schools, 65% of secondary and 79% of higher secondary institution. Relatively more institutions had computer facility; 30% of junior secondary, 85% of secondary, 99% of higher secondary, 79% of all institutions. Table 3.5.4 gives an account for the use of teaching materials. It is seen that nearly 99% institutions reported use of teaching materials. The number and percentage of institutions receiving MPO is shown in Table 3.5.5. It is seen that 24.21% of Junior Schools, 90.98% of Secondary Schools and 83.65% of HSE institutions received MPO support. It is reported that 60% of all institutions offered computer education. This percentage was 19% for junior schools, 64% for secondary schools and 96% for higher secondary institutions. It is found that only 59% institution had computer teacher in 2013. It is found that some institutions offered computer education even without computer teacher. In 2014, the gross enrolment ratio in secondary schools rose to 55.84% from 43.1% in 2001, the gross enrolment rate for boys in 2014 was 50.89%, significantly lower compared to GER for girls 61.06%. In 2014, the NER in secondary schools was 50.21% (boys and girls together), 46.12% for boys and 50.52% for girls. In the total enrolment in grades vi-x of 9160365, boys were 4285281 (46.78%) and girls were 4875084 (53.21%). Gender parity index was 114% (Table 3.1.2d).Significant improvement took place in efficiency parameters. In 2014, the completion rate was 58.06% (55.6 in 2013), 65.98% for boys (58% in 2013), 51.62% for girls (50% in 2013). The drop-out rate reduced to 41.94% in 2014 from 44.4% in 2013. However the survival rate go up from 62% in 2013 to 63.83% in 2014. The coefficient of internal efficient index rose to 70.30% in 2014, from 65% in 2013. The co-efficient confirm improvement in the performance of secondary and higher secondary education during the past decade. 19 College Education: The institutions offering post higher secondary education are included in college education. The following types are recognized. Intermediate colleges, degree colleges, Honors Colleges and Masters Colleges. The total institution involved in college education have been increasing. The number was 3150 in 2005, 3324 in 2010, 3547 in 2012, 3793 in 2013 and 3985 in 2014. Majority (92.54%) was privately managed and 7.46% were government managed. There are two types of colleges; one is of coeducation type and the other is exclusively for girls students. In 2014, there were 679 colleges (17%) exclusively for girls. The share of intermediate college was 51.4%, degree colleges 34.32% and the remaining 14.29% were honors and masters College. The total enrolment in 2014 was 3.5 millions. Among them 1.06 millions (47.57%) were girls. Gender parity index was 89%.The share of intermediate colleges in total enrolment was 16.85% degree pass 31.32% degree honors’ 22.25% and masters 29.58%. In 2014 a college had on average 880 students, the highest 7682 in masters colleges and lowest in intermediate colleges. Total teachers in 3985 colleges are 105054. Among them 23% are female, Small variation in between types of colleges. The teacher-student ratio is 1:33 highest in masters colleges (1:101) and lowest in intermediate colleges. Number of colleges enjoying MPO was only 2737, 69% of the total. The drop-out and completion rate in colleges (xi-xii grades) in 2014 are presented in Table 4.1.6. The cohort drop-out rate was 41% in 2000, reduced to 23% in 2014. The survival rate increased to 97% in 2014. The coefficient of efficiency was 74.9%. Gross and Net Enrolment Rate in college in xi-xii grades are 41.68% and 28.66% respectively. The GER of girls is 46.63% in 2014 and of boys are 37.73%. The NER of girls (32.93%) was also higher than boys (25.24%). Number of colleges, teachers and enrolment was found to vary across divisions. The highest percentage of students was in Dhaka division (33%) followed by Chittagong (17.66%). The lowest was in Sylhet (5%). Rural and urban distributions reveal greater inequality between the two. In the overall distribution of population nearly 25% live in urban areas and 75% live in rural areas. Education survey 2014 reveals that only 53% institutions are located in rural areas, covering only 29% of all students. There were 3985 colleges in 2014. The survey shows that 3195 colleges (84%) have principal. Among them 7% were female. Vice principal was only in 953 (25%) colleges. Professors were 519 (0.13 professor /college). Associate professors were 2383 (0.63per institution). Assistant professors were 16826 (4.43 /institution), Lecturers were 66184 (17.4 per institution). All the institutions do not have the librarian and or assistant librarians. In 3985 institutions there were 3641 librarian or assistant librarian. i.e. 4% institution on average did not have any librarian. Among all institutions 96% had electricity, 74% had multimedia facility, 50% had desktop computers, 43% had laptop and only 90% had computer internet and 7.28% had solar panel. 20 Madrasah Education: Madrasah education is a subsector of education sector of Bangladesh. This subsector is also large, catering to over 3.78 million students including Ebtedayee. This is popularly known as religious stream quite distinct from general stream. This subsector has been continuously growing. The total institutions offering post-primary (Ebtedayee) madrasah education was 7279 in 2000 rose to 9341 in 2014. Ebtedayee madrasah offers primary equivalent while post-primary madrasah covers Dhakhil, Alim, Fazil and Kamil; Which are equivalent to secondary, Higher Secondary, Degree and Masters Education of general stream. The total institutions offering Ebtedayee madrasah in 2014 were 13570. Among them 9154 were attached Ebtedayee and 4416 were independent Ebtedayee. Total students in 13570 institutions were 2125306 in 2014. Average students per Ebtedayee was 157.The total girls students were 1075981, 50% of all students.The total teachers in 13570 Ebtedayee madrasah were 51167, on average 3.77 teachers per Ebtedayee. Women teachers constituted 14.1% of all teachers.Teacher-student ratio was 1:42. In 2014 a total of 9341 madrasah offered Dhakhil to Alim education. Madrasahs are absolutely privately managed. Dhakil, Alim and Fazil are privately managed. Out of 219 kamil madrasah only 3 were Government madrasahs . Among 9341 madrasahs 9338 (99.97%) were privately managed. Among 9341 madrasahs 70% were dakhil, 16% were Alim, 11% were Fazil and 2% were kamil. In 6582 Dakhil Madrasahs, total students were 1290014; more than 59% were girls. Average students per institution are 196. Total teachers were 65014, the average teacher per institution was 9.88. Teacher-student ration was 1:20. There were 1482 Alim Madrasah with 450534 students and 22160 teachers. Girls students were 54.6%. Female teachers were 11.65 percent. Average students per institution was 304 and average teacher per institution is 14.95 persons. Teacher student ratio was 1:20. In 2014 total Fazil madrasah was 1055 with 449329 students and 18758 teachers, Girls students were 46.6%. Female teachers were 10.48%. Average student per institutions was 426 and average teacher was 17.78, giving teacher-student ratio 1:24. There were 222 kamil madrasah in 2014 with 176495 students and 4860 teachers. Girls constituted 30.30% of total enrolment. Female teachers were 8.68% of total. Average students per institution was 795 and average teachers was 21.89, yielding teacherstudent ratio 1:36. The distribution of madrasahs by division reveals that 21% madrasahs were located in Dhaka, 16% in chittagong 17% in Rajshahi, 16% in Rangpur, 13% in Khulna, 13% in Barisal and 4% in Sylhet. Rural–Urban distribution shows that 87% of all madrasahs were located in rural areas. Variation between types of madrasahs and the rural share was as follows: Dhakil 90% Alim 83%, Fazil 80%, Kamil 40%.Most of the madrasahs (68%) prepare annual development plan, conduct co-curriculum activities, Madrasah (99%) run in one shift only, about 50% madrasahs use computer for academic purposes, 64% madrasahs have separate library. Only 22% madrasahs have science laboratories and 4.92% madrasahs have Ramp for special needs student. All madrasahs did not offered computer education as subject. On average 43% madrasahs offer computer education. Variation across the types of madrasahs is shown in Table 5.2.6. Among all teachers only 20% teachers were trained. This percentage varies between 15% in kamil and 21% in 21 Dakhil. Percentage of female trained teacher is 19% which is lower than percentage of male trained teacher. Nearly 95% Heads of madrasahs are appointed while 5% are acting heads variation between types of madrasahs was observed. Among all teachers 80% were receiving MPO in 2014. This percentage was 70% in case of female teachers. Number of teachers having NTRC was few. Among 110792 teachers only 15077 (14%) have NTRC. In Dakhil, Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) was 12.21 for both sex, 10.59 for boys and 13.92 for girls. The NER was very close to GER. NER was 10.89 boys 9.37 girls 12.48. It is to be mentioned that majority boys and girls of school age children go for secondary school. The Gross enrolment and NET enrolment ratio at Alim level was very low, this is 4.92% and.4.50% respectively. There was small difference between boys and girls GER and NER (Table 5.3.11). Estimates of internal efficiently parameters reveal that completion rate was 53% (Girls 45% only) in Dakhil, Drop-out rate was 47% (girls 57%) survival rate 70.79% (girls 61%) and co-efficient of efficiency was 61% (girls 52%). In Alim (Higher secondary level), the completion rate was 87% (girls 76%), dropout rate 13.22% (girls 30%) survival rate 94% (girls 93%) and coefficient of efficiency 89% (girls 71.60%).The above estimates reveal that girls lack behind the boys in participation in the education process. Professional Education: Professional institutions include 11 types of institutions. These are Medical College, Dental College, Nursing College, Homeopathic College, Unani/Ayurbedic, Nursing institute, Health Technology, Textile Technology, Leather Technology, law and Art Colleges. In 2014 there were 476 professional institutions in the country. This subsector has been growing. In 1995 total institutions were only 150. This number increased to 199 in 2003 and to 476 in 2014 (Table 6.1). Among 476 institutions 23% were public and 77% were private. The rate of growth has seen higher in private professional institutions. The total students in 11 type of institution were 122165 in 2014 and 51789 in 2003, showing a continuous growth in the past. Among all students 39% were girls in 2014. Gender parity index was only 63%.The number of students per institution was 256 in 2014, this number was 287 in public and 248 in private institutions. Among all students, percentage of students in medical college was 34%, 16% in Homeopathic College, 22% in health technology 15% in law college, 10% in nursing institutes and 3% in other 5 types of institutions. In 2014, there were 8185 teachers. Among them 1521 (18.6%) were female teachers. GPI was very low, only 23%, teacher-student ratio was 1:13.9. Percentage of female teachers was different in different institution, lowest (3%) in law college and highest (78%) in nursing college. Division wise distribution shows that 47% institutions were in Dhaka, 14% in Chittagong, 14% in Rajshahi, 9% in Khulna, 7% in Rangpur and 4% each in Sylhet and Barisal. 22 Teacher Education: Seven types of educational institutions comprise this sub-sector. These are: PTIs, TTC, TTTC, VTTI Physical Education College, HSTTI and Bangladesh Madrasahs Teacher training Institute (BMTTI). This sector has been growing slowly. Total number of institutions was 68 in 1995, 143 in 2003 and 215 in 2014. Among 215 institutions, 38% were government and 62% were privately managed. The percentage by type of institution was: 52% was TTC, 26% PTIs 14% was physical education college, and 8% was other institutions. More than 29% were located in Dhaka Division, 18% in Chittagong, 17% in Khulna 15% in Rajshahi and 20% in the rest 3 divisions.This confirms uneven distribution between divisions. There were only 1 TTTC and 1 VTTI in the country and both were in Dhaka. Total students in 215 institutions were 34644, average 162 per institutions. Among all students girls were 34% GPI was 55%, Percentage of girls was highest in PTIs, 40% and lowest (0%) in TTTC and VTTIs. Average enrolment per institution was 245 in PTIs, 164 in TTCs, 70 in TTTC, 122 in VTTI, 117 in Physical Education College. 437 in HSTTI and 1856 in BMTTI, showing large variation between types. The 2014 institutional survey found 2669 teachers in 215 institutions, average 12.4 teachers per institution. Among all teachers 21% were female. This percentages show variation between types of institutions. Gender parity index for all types of institution was only 26%. Teacher-student ratio was 1:16 in the teacher education sub-sector. Technical and Vocational Education: This subsector is diverse, catering to more than 689663 students, involving many stakeholders (for example 14 types of providers).Types of institutions involved were: Polytechnic, Technical school and college, Glass and ceramic. Graphic Arts, Survey Institutes, TTC Textile institutes, Textile vocational, Agricultural training institute, Marine Technology, SSC Vocational (independent) HSc Vocational (independent), HSC Vocational (attached) and HSC business management(BM).This is increasingly growing sub-sector: total institutions were 147 in 1995, 2314 in 2003, and 4014 in 2014; total students were 39650 in 1995, 45965 in 2003 and 689663 in 2014. Among 4014 institution, 60% were HSC vocational, 21% were SSC Vocational, 7% polytechnic 4% technical school and college and 8% were other institutions. Majority institutions (93%) were privately managed and only 7% were public managed. Division wise distribution shows that 25% were located in Dhaka division, 23% in Rajshahi 17% in Rangpur, 16% in Khulna, 9% in Chittagong, 8% in Barisal and 2% in Sylhet. Total enrolment in all 4014 institutions was 689663. On average 171.8 students per institution. Total girls students were 189174(27.43%) of total enrolment; Gender parity index was 39%, much behind the national target of 100%. Both percentage of girls and gender parity index were found to vary over long range between types of institutions (table 7.6). 23 Total teachers in 4014 institution were 28798 including 5901 (21%) female teachers. Average teacher per institution was 7.2. Gender parity index was 25%. Percentage of female teachers varied over a wide range between types of institution. Teacher-student ratio was 1:24 for all types of institutions. This ratio was highest (1:67) in glass and ceramic institutes and lowest (1:16) for textile vocational institutes. University Education: Annual Education Survey-2014 reveals that there were 112 Universities in Bangladesh, 34 (31%) were public and 78(69%) were private. Total number of students were 853712. Average number of students per University was 7622, the average number of student in public University was 13369 and private University was 5118. The difference is big. Among all students, 30.23% were girls. In Public University, this percentage was 37% and in private University this percentage was 27%. Gender parity index was 47.55% in both public and private University, 59% in public and 36% in private university. Table: 8.4 and 8.5 show that percentage of girls varies over a wide range between universities. Total teachers in 112 Universities were 24027. Among them only 25.6% were female. In public University this percentage was 20.66%, and in private University this percentage was 29.42%. Variation was large among the universities. Average number of teachers in 2014 was 338 in public, 160 in private and 214 in both public and private universities. Teacher-student ratio was 1:40 in public University, 1:32 in private and 1:36 in both public and private Universities .The number of teachers by designation shows that in 2014 there were 11505 teachers in public Universities. Among them 28.4% were professors 16.4% were associate professors, 29.31% were assistant professors and 25.36% were lectures. Among 34 public Universities, there were no residential facilities in 5 universities. These are: National University, Bangladesh Open University, Jagannath University, Begum Rokeya University, and Barisal University. Among total teachers of private Universities, 14% were professors 8.30% were associate professors, 20.48% were assistant professors and 57.18% were lectures. The total students of the remaining 30 Universities were 210602. Among them 66149 (31%) were resident students and 69% were non-resident students. Among 66149 resident students only 22301 girls (33.71%) were resident students. As against 36% girl students in the total enrolment in the in the public universities. This was the overall situation. University wise resident, non-resident students of 30 Universities are given in Table 8.7. It is seen that percent of resident students varies over a wide range from 4% in Jatya Kabi Kazi Nazrul Islam University to 100% in Sher-e-Bangla Agriculture University. In Dhaka University only 35.4% of all students were resident. Education Finance: An account of education finance is given in chapter 9. The total national budget for 2013-14 was 222491 million Taka and for 2014-2015 is 2505060 million Taka. The share of Education in the national budget was 11.28% in 2013-14 and set at 11.66% in 2014-15. In 2013-14, the share of primary was 5.36% while was 5.92% for post primary. Education expenditure in 2012-13 was 214241million Taka. More than 82% was recurrent expenditure and 18% was capital expenditure. The share of different level in the total expenditure was 46% in primary, 18% in junior secondary, 22% in secondary and 14% in tertiary level. The 24 amount which is received by the institutions at different level is spent mainly on salary head. A very small amount of the total budget was spent in non-salary head. The percentage varied by level, for example it was 1.4% in primary, 3.9-4.5% in secondary and 8.7% in tertiary education. Per-student expenditure in 2012-13 was Taka 5017 for primary, 4781 at junior secondary, 7794 at secondary and higher secondary and Tk 15186 at tertiary level. Out-put Statistics: Number of students appeared in SSC examination has been gradually increasing. Total students appeared in SSC was 433918 in 1990, 756387 in 2004 and 1087870 in 2014. The growth was more than 150% the growth of girls was higher than boys, 277% during 24 years. Spectacular growth occurred in pass rate. Percentage of pass was 32% (30% girls) in 1990, rose to 92.67% (92% girls) in 2014. The pass rate was higher in science group (96%) and lower in Humanities group. Participation in vocational examination (SSC) and percent of pass in examination showed a continuous increasing trend. The percentage of pass was 68% in 1999, increased to 82% in 2014. Girls’ performance (pass rate 84%) was higher. Statistics on number appeared in HSC and percentage of pass reveal a continuous growth. The number of students appeared increased almost three folds. Percentage of pass was 30% (31% girls) in 1990 and increased to75.78% (76.68% girls) In H Sc the performance of Business study group was better compared to Science and Humanities group. Participation in Dakhil, Alim, Fazil and Kamil examination of madrasah streams and their pass rate showed a continuous growth. The Current pass rate in all the above four examination was more than 90% (dakhil 89%, Alim 94%, Fazil 95% and Kamil 98%). Results of SSC and Dakhil graduates with grade point also reveal spectacular improvement over time. In 2004 a total of 8597 got GPA 5 (A+) in SSC. This number increased to 122313 in 2014, the growth was 14.23 times. Similarly in Dakhil GPA 5 score was obtained by 1111 students. This number increased by 12.61 times. Similar trend was seemed in SSC (Vocational) and HSC graduates with grade points (Table: 10.13 and 10.14). Results of Degree (Pass) examination for the period 2002-2011 were presented in Table 10.21 and 10.22. The trend analysis showed continuous growth of number appeared, number passed and pass rate. In 2002, the number appeared was 262805 and the number increased to 192448 in 2011. The pass rate was 31.2% in 2002 and rose to 75.23% in 2011. Female pass rate was higher in 2002 and also in 2011. English medium School Education: Annual Education Survey 2014 reveal that there are 159 English medium schools in Bangladesh. Among them 36 are ‘O’ level 98 are ‘A’ level and only 25 are Junior secondary level. Most of the Schools are located in Dhaka city(138) followed by Chittagong(11). Total number of Students in English medium Schools are 64507, among them 26785(46%) are girls’. Average number of student per school is 405. Average student per school by levels are: ‘O’ level 236, ‘A’ level 528 and junior secondary level 170. Total teacher in English medium schools are 5635, among them 3403(60%) are female. Average teacher per schools are; 21 in ‘O’ level, 44 in ‘A’ level and 22 in Junior secondary level. 25 Summary Statistics and Key Performance Indicators (KPI) Part 1: Summaries Table 01: Number of institution, student and teacher by type of education, 2014 Type of Education Manage ment Public Primary Education School Education College Education Madrasah Education Professional Teacher Education Technicalvocational University Total (Postprimary) Country (Primary +Postprimary) No. of Institu tion 63041 No. of Teacher No. of Student Total Female % Fem. 319112 191830 60.11 Total 14671914 Girl 7530261 Indicators % Girl TSR SPI TPI 51.32 46 233 5 Private 45496 163772 87275 53.29 4881065 2383623 48.83 30 107 4 Total 108537 482884 279105 57.8 19552979 9913884 50.7 40 180 4 Public 327 8210 2645 32.22 280634 136122 48.51 34 858 25.1 Private 19357 224784 56324 25.06 8879731 4738962 53.37 40 459 11.6 Total 19684 232994 58969 25.31 9160365 4875084 53.22 39 465 11.8 Public 297 12843 3410 27 1335291 597098 45 104 4496 26 Private 3688 92211 20741 22 2171092 1070741 49 24 589 25 Total 3985 105054 24151 23 3506383 1667839 48 33 880 26 Public 3 73 0 0 4992 365 7 68 1664 24 Private 9338 110719 13045 12 2361380 1269583 54 21 253 12 Total 9341 110792 13045 12 2366372 1269948 54 21 253 12 Public 111 3952 885 22 31829 13769 43 21 247 12 Private 365 4233 636 15 90336 33916 38 15 257 17 Total 476 8185 1521 19 122165 47685 39 16 231 14 Public 83 1202 323 27 19154 6407 33 11 117 11 Private 132 1467 236 16 15490 5344 35 13 161 12 Total 215 2669 559 21 34644 11751 34 15 192 12 Public 4945 23853 686 5215 14 22 177527 512136 29058 160116 16 31 36 715 7 Private 248 3766 21 133 6 Total 4014 28798 5901 20 689663 189174 27 24 172 7 Public 34 11505 2377 20.66 454530 168499 37.07 40 13368 338 Private 78 12522 3684 29.42 399182 106629 26.71 32 5118 161 Total 112 24027 6061 25.24 853712 275128 30.23 35 7622 215 Public 1103 42730 10326 24.17 2303957 951318 41.29 54 2089 39 36724 469789 99881 21.26 14429347 7385291 51.18 31 393 13 Private Total 37827 512519 110207 21.50 16733304 8336609 49.82 33 442 14 Public 64144 361842 202156 55.87 16975871 8481579 49.96 47 265 6 82220 633561 187156 29.54 19310412 9768914 50.59 30 235 8 146364 995403 389312 39.11 36286283 18250493 TPI-Teacher per Institution 50.30 36 248 7 Private Total TSR-Teacher Student Ratio, SPI- Students per Institution, 26 Table 02: Number of Student by level, management and gender, 2014 Country *University Technical and vocational Teacher Education Professional Madrasah College School Management Type of Education Level of Education Tertiary Junior Secondary ( 6 to 8) Secondary (9 to 10) Total Girls Total Girls Public 174421 86506 106213 49616 Private 6366950 3438098 2512781 1300864 Total 6541371 3524604 2618994 1350480 Higher Secondary (11 to 12) Post-Secondary non-tertiary Degree Total Total Girls Public 379401 186685 846197 365646 109693 44767 Private 1504289 749732 657316 316281 9487 4728 Total 1883690 936417 1503513 681927 119180 49495 0 Girls 0 Total Masters Girls Total Girls Public 383 43 284 26 854 79 1675 89 1796 128 Private 1368125 783451 635903 328487 221575 108945 103538 39816 32906 8953 Total 1368508 783494 636187 328513 222429 109024 105213 39905 34702 9081 0 0 Public 11464 5586 20365 8183 Private 62720 22403 83085 30586 27616 11513 Total 39080 17099 Public 7388 2885 11766 3522 Private 200 21 15290 5323 Total 7588 2906 27056 8845 Public 405388 142549 49142 25950 Private 273063 70075 126119 23554 Total 678451 212624 175261 49504 Public 28324 8631 40253 5465 108950 14962 Private 159698 59881 247792 88404 104646 11831 Total 188022 68512 288045 93869 213596 26793 Public 174804 86549 134821 58273 420508 192229 127802 23433 1285391 519989 160631 70845 Private 7735075 4221549 3308382 1689232 1973656 947081 132462 23365 1111927 453898 168512 37235 Total 7909879 4308098 3443203 1747505 2394164 1139310 260264 46798 2397318 973887 329143 108080 47.27 51.76 20.58 20.99 14.31 13.69 1.56 0.56 14.33 11.70 1.97 1.30 % Share to Total 27 Part 2: Primary Education Table: 2.1: Number of Primary Education Institution, Teacher and Student, 2014 Total Teachers No. of School Total Female Govt. Primary School New Nationalized PS Regd. NGPS Non-regd. NGPS Experimental School Ebtadaee Madrasah Kindergarten NGO School Community School 38033 25008 193 1744 55 2673 16170 2512 120 222652 96460 771 6649 282 11673 93799 5454 405 Attached to High Madrasah 5526 19764 Primary Sections of High School BRAC ROSC School Sishu Kollyan Primary School Other Schools 1511 8301 7779 3818 133 3262 7798 3591 410 4875 7277 2867 277 2967 108537 482884 279105 School type Grand Total: Total Students Total Girls % of Girls 144434 47396 464 4716 246 2300 54813 3764 322 % of Female 64.9 49.1 60.2 70.9 89.2 19.7 58.4 69.0 79.5 10188129 4483785 38282 256268 10652 372277 1988365 210170 16747 5252022 2278239 19611 127112 5250 181341 914016 107898 8679 51.6 50.8 51.2 49.6 49.3 48.7 46.0 51.3 51.8 2812 14.2 871047 427341 49.1 53.6 572751 295659 51.6 93.3 79.8 67.6 60.9 324438 106884 15665 97519 185873 53751 8284 48808 57.3 50.3 52.9 50.0 57.8 19552979 9913884 50.7 4450 Source: DPE Part 3: Secondary, Higher secondary & Tertiary Education Table 3.1: Number of School, student and teacher by type and management, 2014 Type Junior Secondary Secondary School School & College All School Manageme nt Number of Institution Girls Total Ins. Private 2412 Total Number of Teachers Indicator Number of Students Total Female % Female Total Girls % Girls TSR SPI TPI 559 18618 5099 27.39 367510 217990 59.32 20 152 7.7 2412 559 18618 5099 27.39 367510 217990 59.32 20 152 7.7 Private 16003 2431 186761 44544 23.85 7782235 4140815 53.21 42 486 11.7 Public 316 147 7675 2389 31.13 264131 131373 49.74 34 836 24.3 Total 16319 2578 194436 46933 24.14 8046366 4272188 53.09 41 493 11.9 Private 942 147 19405 6681 34.43 729986 380157 52.08 38 775 20.6 Public 11 3 535 256 47.85 16503 4749 28.78 31 1500 48.6 Total 953 150 19940 6937 34.79 746489 384906 80.86 37 783 20.9 Private 19357 3137 224784 56324 25.06 8879731 4738962 53.37 40 459 11.6 Public 327 150 8210 2645 32.22 280634 136122 48.51 34 858 25.1 Total 19684 3287 232994 58969 25.31 9160365 4875084 53.22 39 465 11.8 28 Table 3. 2: No. of College, teacher and student by type, Gender and management, 2014 Type of college Manag ement No. of college Teachers Total Female Enrolment % Female Total Girls % Teacher per college Student per college Teacher student ratio Girls School & College (College Section) Private 942 14442 3723 26 238097 126702 53 15 253 16 Public 11 38 21 55 3773 1592 42 3 343 99 Total 953 14480 3744 26 241870 128294 53 15 254 17 Higher Secondary College Private 1275 22460 5031 22 334426 174586 52 18 262 15 Public 26 294 95 32 14652 5393 37 11 564 50 Total 1301 22754 5126 23 349078 179979 52 17 268 15 Degree (Pass) College Private 1135 39693 7836 20 977197 495514 51 35 861 25 Public 79 1897 438 23 120832 60227 50 24 1530 64 Total 1214 41590 8274 20 1098029 555741 51 34 904 26 Degree (Honors) College Private 295 13089 3191 24 483499 211233 44 44 1639 37 Public 97 3419 804 24 296836 155109 52 35 3060 87 Total 392 16508 3995 24 780335 366342 47 42 1991 47 Private 41 2527 960 38 137873 62706 45 62 3363 55 Public 84 7195 2052 29 899198 374777 42 86 10705 125 8297 107 Masters College Grand Total Total 125 9722 3012 31 1037071 437483 42 78 Private 3688 92211 20741 22 2171092 1070741 49 25 589 24 Public 297 12843 3410 27 1335291 597098 45 43 4496 104 Total 3985 105054 24151 23 3506383 1667839 48 26 880 33 TSR SPI TPI 9.88 Table 3.3: No. of Madrasah, Teacher and Enrolment (Post-Primary) by Type, Gender and Management, 2014 Type of Madrasah Dakhil Alim Fazil Kamil Total Management No. of madrasah Total Teacher Female % Female Total Enrolment Girls % girls Private 6582 65014 8076 12.42 1290014 761090 59.00 1:20 196 Sub Total 6582 65014 8076 12.42 1290014 761090 59.00 1:20 196 9.88 Private 1482 22160 2582 11.65 450534 245976 54.60 1:20 304 14.95 Sub Total 1482 22160 2582 11.65 450534 245976 54.60 1:20 304 14.95 Private 1055 18758 1965 10.48 449329 209398 46.60 1:24 426 17.78 Sub Total 1055 18758 1965 10.48 449329 209398 46.60 1:24 426 17.78 Public 3 73 0 0.00 4992 365 7.31 1:68 1664 24.33 Private 219 4787 422 8.82 171503 53119 30.97 1:36 783 21.86 Sub total 222 4860 422 8.68 176495 53484 30.30 1:36 795 21.89 Public 3 73 0 0.00 4992 365 7.31 1:68 1664 24.33 Private 9338 110719 13045 11.78 2361380 1269583 53.76 1:21 253 11.86 Total 9341 110792 13045 11.77 2366372 1269948 53.67 1:21 253 11.86 29 Table 3.4: Number of Institution, Teacher and Enrolment in Technical & vocational education by type, management and gender, 2014 Type of Institute Polytechnic Institute Technical School & College Glass & Ceramic Institute Graphic Arts Institute Survey Institute Technical Training Centre Textile Institute Textile Vocational Institute Agriculture Training Institute Institute of Marine Technology S.S.C Vocational (Independent) HSC Voc/B. Management (Independent) Total(Independent Technical Education) S.S.C Vocational (Attached) HSC Voc/B. Management(Attached) Total(Technical Education) Management Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Public Private Total Teachers No. of Inst. 46 240 286 64 106 170 1 1 1 Total 1486 3179 4665 1140 1166 2306 13 Female 174 587 761 125 295 420 3 Students % of female 11.71 18.46 16.31 10.96 25.30 18.21 23.08 Total 90512 79557 170069 36418 28508 64926 1047 Girls 11007 8256 19263 4908 8844 13752 54 % of girls 12.16 10.38 11.33 13.48 31.02 21.18 5.16 3 4 23.08 26.67 1047 695 54 52 5.16 7.48 1 2 2 4 38 66 104 10 23 33 40 10 50 13 96 109 1 13 15 0 15 35 20 55 1124 176 1300 188 332 520 265 80 345 145 815 960 52 4 6 1 7 182 34 216 27 62 89 47 18 65 35 156 191 5 26.67 17.14 5.00 12.73 16.19 19.32 16.62 14.36 18.67 17.12 17.74 22.50 18.84 24.14 19.14 19.90 9.62 695 827 422 1249 21114 7655 28769 3585 6542 10127 4248 1270 5518 11368 18125 29493 916 52 32 35 67 7056 2943 9999 284 505 789 1078 237 1315 3427 3035 6462 106 7.48 3.87 8.29 5.36 33.42 38.45 34.76 7.92 7.72 7.79 25.38 18.66 23.83 30.15 16.74 21.91 11.57 1 11 158 169 10 665 675 237 1366 1603 52 267 1709 1976 144 5815 5959 4874 13292 18166 5 37 362 399 27 1254 1281 672 2769 3441 9.62 13.86 21.18 20.19 18.75 21.56 21.50 13.79 20.83 18.94 916 2962 21464 24426 3116 121145 124261 176808 284688 461496 106 497 6285 6782 166 41146 41312 28667 71286 99953 11.57 16.78 29.28 27.77 5.33 33.96 33.25 16.21 25.04 21.66 1456 1456 11 944 955 248 3766 4014 5710 5710 71 4851 4922 4945 23853 28798 1323 1323 14 1123 1137 686 5215 5901 23.17 23.17 19.72 23.15 23.10 13.87 21.86 20.49 129309 129309 719 98139 98858 177527 512136 689663 50416 50416 391 38414 38805 29058 160116 189174 38.99 38.99 54.38 39.14 39.25 16.37 31.26 27.43 30 Table-3. 5.1 : Number of English Medium School by type ,2014 Total School Type of School O level school 36 A level school Junior school Total: 98 Only for Boys Only for Girl Co Educationtogether Co Education separate 20 16 49 48 13 12 82 76 1 25 159 0 1 Table-3.5.2: Number of Institution, Enrolment, Teacher, Average Enrolment per school, Average, teacher per school and Teacher student ratio, 2014 Teacher Type Enrolment School Total Female Total TSR SPI TPI Girl O level school 36 752 444 8490 3632 1:11 235.83 20.90 A level school 98 4335 2601 51765 21193 1:12 528.21 44.23 Junior school 25 548 358 4252 1960 1:8 170.08 21.92 Total 159 5635 3403 64507 26785 1:11 405.70 35.44 Table 3.6: Number of university, teacher and enrolment by type and gender, 2014 Type of university No. of university Number of teacher Total Female % of Female Student Total Girls % of Girls Public 34 11505 2377 20.66 454530 168499 37.07 Private 78 12522 3684 29.42 399182 106629 26.71 Total 112 24027 6061 25.24 853712 275128 30.23 31 Part 4 : Key Performance Indicators 4.1: Participation Indicators Table 4.1.0: Year wise Gross and Net Enrolment Rate in Primary Education- 2005-2014 Year GER (%) NER (%) Boys Girls Total Boys Girls Total 2005 91.2 96.2 93.7 84.6 90.1 87.2 2006 92.9 103 97.7 87.6 94.5 90.9 2007 93.4 104.6 98.8 87.8 94.7 91.1 2008 92.8 102.9 97.6 87.9 90.4 90.8 2009 100.1 107.1 103.5 89.1 99.1 93.9 2010 103.2 112.4 107.7 92.2 97.6 94.8 2011 97.5 105.6 101.5 92.7 97.3 94.9 2013 101.3 107.6 104.4 95.4 98.1 96.7 2013 106.8 110.5 108.6 96.2 98.4 97.3 1014 104.6 112.3 108.4 96.6 98.8 97.7 Table 4.1.1: Dropout Rate by Grade in Primary Education- 2014 Sex Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Boys 2.0 3.5 7.4 9.4 2.4 Girls 0.4 5.7 2.3 6.8 2.2 All 1.2 4.6 4.8 8.1 2.3 Table 4.1.2: Gross and Net Enrolment Rate by gender in Secondary Level of Education, 2014 Sl. Indicators No Secondary level (Cycle-School+ Madrasah+Voc.) Both Boys Girls 1. Gross Enrolment Rate 69.23 62.94 75.88 2. Net Enrolment Rate 62.25 57.04 67.74 3. Adjusted Net Enrolment Rate 64.01 58.80 69.51 32 Figure-4.1.2.1: Student participation rate in secondary education 2014 Enrolment Rate in Secondary Education 2014 100 90 80 70 % 60 50 40 Gross Enrolment Rate 69.23 Net Enrolment Rate , 62.25 Adjusted Net Enrolment Rate, 64.01 1 2 3 30 20 10 0 0 4 Table 4.1.3: Completion Rate, Dropout Rate, Survival rates and Coefficient of Internal Efficiency by gender in Secondary Level 2014 (Rates in Percentage) Indicators Secondary level Madrasah School (Cycle-School,Madrasah&voc.) (Secondary level) Sl. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. Completion Rate Dropout Rate Survival Rate Coefficient of Internal Efficiency Both Boys Girls Both Boys Girls Both Boys Girls 58.41 65.48 52.33 52.86 62.15 42.85 58.06% 65.98% 51.62% 41.59 34.52 47.67 47.14 37.85 57.15 41.94% 34.02% 48.38% 71.10 84.89 66.26 70.79 77.29 61.91 63.83% 72.06% 57.10% 66.60 73.40 60.60 61.40 71.50 51.70 70.30% 75.90% 65.30% 33 Figure-4.1.3.1: Internal efficiency in secondary education 2014 Internal Efficiency in Secondary Education 2014 100 90 80 70 % 60 50 40 Completion Rate, 58.41 30 Survival Rate, 71.1 Coefficient of Internal Efficiency, 66.6 20 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 Table 4.1.4 : Promotion, Repetition, and Retention/Survival Rate by Grade and gender at Secondary level (School + Madrasah+ Voc.), 2014 (Rates in Percentage) Grade Promotion Both Boys Repetition Girls Both Boys Dropout rate Girls Both Boys Girls VI 93.41 92.32 93.84 1.11 0.80 1.19 5.48 6.88 4.97 VII 95.16 97.63 92.98 1.02 0.85 1.29 3.82 1.52 5.73 VIII 83.55 89.48 81.76 5.49 0.90 6.38 10.96 9.62 11.86 IX 89.70 91.99 87.52 .89 0.66 1.04 9.44 7.35 11.44 X 82.30 84.89 77.80 5.04 4.57 6.49 12.66 10.54 15.71 Table 4.1.5: Gross and Net Enrolment Rate in College and Madrasah (11 & 12 Class), 2014 Indicators Both Boys Girls Higher Secondary age population (16-17 years) 4518978 2510584 2008394 Enrolment of all ages Enrolment of (16-17years) Gross enrolment rate(GER) Net enrolment rate(NER) 2106119 1060678 1045441 1498575 739032 759543 46.61 42.29 52.05 33.16 29.44 37.82 34 Table 4.1.6: Completion Rate, Dropout Rate, Survival rates and Coefficient of Internal Efficiency by Sex in Higher Secondary Level of College and madrasah (11+12) 2014 (Rates in Percentage) Sl. No. Indicators Both Boys Girls 1. Completion Rate 78.63 74.68 82.95 2. Dropout Rate 3. Survival Rate 4. Coefficient of Internal Efficiency 21.37 97.43 77.3 25.32 97.55 73.6 17.05 97.29 81.4 Table 4.1.7: Dropout and Completion Rate, GER and NER (%) in Secondary level 2008-2014 Year Dropout Rate (%) Both Boy Girl Completion Rate (%) Both Boy Girl Both GER Boy Girl Both NER Boy Girl 2008 61.38 56.61 65.69 38.62 43.39 34.31 49.81 44.32 55.88 45.09 39.88 50.83 2009 55.31 42.15 64.93 44.69 57.85 35.07 53.94 49.52 58.80 49.13 44.79 54.01 2010 55.26 57.29 53.57 44.74 42.71 46.43 55.81 49.59 62.62 49.53 44.45 55.09 2011 53.28 46.73 56.43 46.72 53.27 43.57 61.89 57.04 66.91 56.50 51.94 59.94 2012 44.65 34.9 52.36 55.35 65.1 47.64 64.05 57.37 71.31 57.37 51.64 63.58 2013 43.18 34.18 48.89 56.82 65.82 51.11 65.58 59.63 71.86 58.97 54.05 64.16 2014 41.59 34.52 47.67 58.41 65.48 52.33 69.23 62.94 75.88 62.25 57.04 67.74 Figure 4.1.7.1: Drop out rate in Secondary Education 2008-2014 70 60 50 Dropout Rate (%) Both 40 Dropout Rate (%) Boy 30 Dropout Rate (%) Girl 20 10 0 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 35 2013 2014 Figure 4.1.7.2: Student Completion rate in Secondary Education 2008-2014 2008 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 2014 2009 Completion Rate (%) Both Completion Rate (%) Boy 2013 Completion Rate (%) Girl 2010 2012 2011 Figure 4.1.7.3- Gross Enrolment rate in Secondary Education 2008-2014 80 70 60 50 GER Both 40 GER Boy 30 GER Girl 20 10 0 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 36 2013 2014 Figure 4.1.7.4: Net Enrolment rate in Secondary Education 2008-2014 70 60 50 40 NER Both 30 NER Boy 20 NER Girl 10 0 2008 2009 2010 2011 NER Girl NER Boy NER Both 2012 2013 2014 4.1.8: Student Participation, Completion and Dropout rate in Higher secondary level 2008-2014 KPI 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 GER 38.33 39.71 41.09 42.47 43.85 45.23 46.61 NER 25.00 26.36 27.72 29.08 30.44 31.80 33.16 Completion rate 53.14 57.89 62.64 62.87 78.20 78.40 78.63 Drop out rate 46.86 42.11 37.36 37.13 21.80 21.60 21.37 Figure 4.1.8.1: Student Participation rate in Higher Secondary Education 2008-2014 50 45 40 38.33 39.71 41.09 35 30 25 26.36 27.72 43.85 42.47 29.08 30.44 45.23 31.8 46.61 33.16 GER 25 NER 20 15 10 5 0 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 37 2013 2014 Figure 4.1.8.2: Drop out rate in Higher secondary level 2008-2014 50 45 40 35 30 25 Drop out rate 20 15 10 5 0 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 4.1.9: Gender parity Index in Post-Primary Education Level of Education Junior Secondary level (6-8) Secondary level (9-10) Higher secondary level(11-12) Post secondary non-tertiary Tertiary Level: Degree Masters Management Public private Total Public private Total Public private Total Public private Total Public private Total Public private Total Student Boy 88255 3513526 3601781 76548 1619150 1695698 228279 976575 1254854 104369 109097 213466 765402 658029 1423431 89786 131277 221063 38 Girl 86549 4221549 43080987 58273 1689232 1747505 192229 947081 1139310 23433 23365 46798 519989 453898 973887 70845 37235 108080 Gender parity Index(boy to girl) .98 1.20 1.20 .76 1.04 1.03 .84 .97 .91 .22 .21 .22 .68 .69 .68 .79 .28 .49 4.1.10: Transition rate from Primary to secondary School Education 2014 Particulars Student Girl 1287353 15320 1272033 1344875 94.58 Boy 1112296 8898 1103398 1139477 96.83 Enrolled in Grade-VI Repeater in grade VI New entrance in grade VI Number of Passed in grade V on 2013 Transition Rate(%) Total 2399649 24218 2375431 2484352 95.61 4.2: Quality Indicators 4.2.1. Quality Indicators in Secondary Schools, 2014 Indicators of Quality 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 Projected 2015 Teacher Student Ratio Classroom size % of Trained Teachers in schools (Total) % of Trained teacher in schools(Female) % of schools having separate Toilet Facilities for Girls+ % of schools with Computer facilities % of schools with Internet Connection % of school with electricity connection 1: 34 1:30 1:36 1:37 1:39 1: 30 72 n.a - 44 68.53 75.36 72.7 73.8 62.32* 80.50 73.69 77.43 73.8 73.9 60.24 91.00 94.92 96.00 93.83 93.26 94.35 99.00 59.21 65.06 70.3 78.77 29.73 45.7 63.37 71.71 75.98 77.0 81.38 80.35 69.11 83.17 85.05 18.18 % of school having safe drinking water 85.00 87.00 94.51 95.93 96.57 91.00 % of school having multimedia facility % of School having solar system - - 10.10 57.92 66.22 7.52 80.00 7.71 *Minimum BEd , BPEd, MEd, BAgEd and Dip in Educatiobn 39 60 38.85 80.00 10.00 Part 5: Comparison of Statistics (South and West Asian Countries) Table 5.1: Secondary Education, 2012-13 Country Student(6-12) Total (000) % Girl % of TVE to total student in secondary (6-12) % Girl in TVE TSR in secondary and upper secondary (6-12) GER in Secondary and Higher secondary(612) NER in Secondary and Higher secondary( 6-12 School life expectancy(Prim ary and secondary)-in years GPI of School life expectancy Afghanistan 2416 35 1 12 1:32 54 … 9.48 0.66 Bangladesh Bhutan India Iran Maldives Nepal 12187 66 113727 7118 … 3014 52 51 46 48 … 50 4 1 11 - 33 25 34 - 1:32 1:20 1:26 1:30 54 74 69 86 66 48 57 82 … 59 9.26 12.19 10.40 11.30 11.65 1.10 1.03 0.98 0.96 1.06 Pakistan Sri Lanka Regional 10371 2590 152002 41 51 46 4 6 - 43 45 - 1:21 1:17 1:25 37 99 64 36 - 7.20 12.86 10.00 0.82 1.04 0.97 World 552443 48 - - 1:17 71 65 10.46 0.97 Source: UIS Table 5.2: Tertiary Education, 2012-13 Country Student(tertiary) (In thousand) Total %Girl % Private Afghanistan 98 2008 GER in tertiary GPI of GER in tertiary School life expectancy (tertiary)-in years 24 1.33 3 0.33 0.19 Bangladesh Bhutan India 7.4 28526 40 40 41 45 - 13 9.4 25 0.69 0.69 0.78 0.66 0.47 1.24 Iran Maldives Nepal Pakistan Sri Lanka 4404 385 1817 271 50 42 48 62 45 62 34 8 55 15 10 17 1.00 … 0.94 1.65 2.4 0.72 0.48 0.84 Regional World 37522 196077 43 51 - 23 32 0.81 1.08 1.12 1.60 Source: UIS Table 5.3: Public Expenditure on Education by Nature of Spending, 2012-13 Country Total public expenditure as a % of GDP as a % of total government expenditure Afghanistan Bangladesh Bhutan India 2.06 4.7 3.35 - 11.28 11.30 11.32 Iran Maldives 3.61 5.9 16.08 14.16 Nepal Pakistan 4.7 2.13 9.89 Sri Lanka 1.72 8.75 Source: UIS Source: Global Education Digest 2013 40