PPT
advertisement

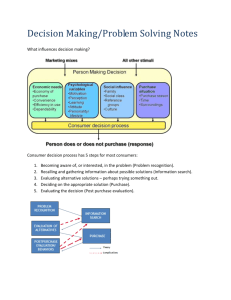
Chapter 22.1 Introduction to Business and Marketing Objectives Identify four decisions that consumers make when they buy goods and services. Compare brand-name and generic products. Identify choices that consumers must make about when to buy. List several choices that consumers have when selecting a store to make purchases. Describe tools that consumers can use to compare prices for goods and services. The Main Idea Consumers must make many buying decisions They must decide what, when, and where to buy goods and services, and how much to pay for them Buying Goods and Services A consumer must decide: What to buy When to buy Where to buy How much to pay Deciding What to Buy When deciding what products they want to buy, consumers decide what is a top priority for them. Buyers often associate quality with brand name products. Despite a difference in cost, generic products may be equal in quality to some brand-name products. Examples: Nike® Kellogg’s® Pepsi®. Deciding When to Buy Postponing or planning a purchase can sometimes save you money Buying AC units or bathing suits in the winter Buying coats or winter clothing in the summer Deciding When to Buy Stores often run specials promotions during and after the holidays, just before the school year begins, and at the end of the season When deciding when to buy, it often pays to wait until items go on sale Deciding Where to Buy There are three factors that affect a consumer’s decision where to shop: The kinds of goods and services sold Prices Convenience Department Stores Because department stores offer brand names and customer service, their prices may be higher than other types of stores. Examples: Sears JCPenny® Macy’s® Discount Stores Discount stores can sell for less because they offer fewer services and keep large quantities of goods. Examples: Wal-Mart® Kmart® Off-Price and Outlet Stores Off-price and outlet stores can offer big discounts because the items they sell may have flaws, may be out of season, or may be discontinued merchandise. Examples: T.J. Maxx® Stein Mart® Loehmann’s® Limited-Line Retailers Limited-line retailers, or specialty stores, have a variety of items and high levels of service and expertise. Examples: Foot Locker® PetSmart® Ace Hardware® Superstores Superstores sell groceries and a wide variety of items such as books, hardware, and clothing. Examples: Target® Wal-Mart® Convenience Stores Convenience stores offer limited lines of products, mostly grocery items. Example: 7-Eleven® Warehouse Stores Warehouse stores carry a huge selection of goods at low prices and in bulk quantities. Examples: Costco® Sam’s Club® Shopping at Home Consumers can shop at home through TV channels, catalogs, or the Internet. Many retail stores mail catalogs to consumers. Deciding How Much to Pay Comparison shopping is important for major purchases because the difference in cost can be significant. Deciding How Much to Pay Some people think the most expensive item is always the best product. Sometimes the least expensive item or the one in the middle might be the best buy for the money.