11th Hour EOG Spotlight - Public Schools of Robeson County
advertisement

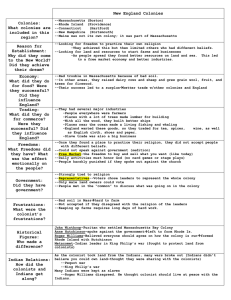
The Three Discoveries of America I. Native Americans: 1. Ice Age - ocean level dropped 2. Land-bridge formed connecting Asia to North America 3. Nomads from Asia crossed to North America by land bridge 4. Types of Nomads: A. Hunters and Gathers B. Herdsman (sheep/reindeer) 5. Gradually they overspread North and South America 6. Their life-style developed according to the land on which they settled. II. Vikings/Norsemen: 1. Lived in Norway 2. Hated Europeans 3. Made raids in Europe 4. Excellent Seamen 5. Their history is passed down by Sagas (tales of their travels) 6. Lief Erickson heard tales, or sagas, of travels to North America 7. He eventually made this trip and started a settlement there 8. This settlement (called Vineland) was found in Newfoundland 9. Vineland means “Vine Land” 10. The settlement failed and he returned to Norway III. Columbus: 1. An Italian sea captain 2. Studied wind and ocean currents from the Canary Islands 3. Believed the Earth was round and he could reach the Indies by sailing west. 4. Tried to get funding to find a short route to the Indies 5. He was turned down in Italy and Portugal 6. Queen Isabella financed the voyage from Spain 7. Columbus’s demands: A. The title Admiral of the Ocean Sea B. A percent of profits from all goods shipped on his route 8. Columbus’s ships: A. Nina B. Pinta C. Santa Maria 9. Landed on and named San Salvador in North America - also landed on Hispaniola Spanish Conquistadors I . Ponce de Leon: 1. Landed in & conquered Cuba (was the first governor of Cuba) 2. Landed on & claimed Florida for Spain 3. Gave Florida its name - which means Full of Flowers II. Balboa: 1. Landed on & claimed Panama in 1513 (small country in Central America) 2. Crossed the isthmus & discovered the Pacific Ocean (name means Peaceful waters) 3. The Pacific Ocean was called Balboa's Ocean III. Magellan: 1. He was a Portuguese sailor 2. He sailed in 1519 with: a. 5 ships b. 237 men 3. Purpose of voyage ..... to continue to look for passage to the East Indies (he had to find a way through or around North and South America) 4. By 1521 he reached Guam. From there he reached the Philippines where he died. 5. The group returned home in 1522 with only 17 survivors. 6. He is given credit for the first person to sail around the world. IV. de Soto: 1. Explored part of the mainland of North America 2. Came into South Carolina. 3. Traveled across South Carolina and first European to discover the Mississippi River. 4. Died in 1542 during the expedition and was buried in the Mississippi River. V. Cortes: 1. His mission: fact gathering in Mexico 2. His expedition consisted of: a. 11 ships b. 508 soldiers c. 16 horses d. Cannons 3. He landed in the Yucatan Peninsula and founded Veracruz 4. He was attacked by Aztec warriors on shore a. Aztecs - native Americans that lived in Mexico b. War-like tribe that controlled large amounts of Mexico c. Montezuma was king of the Aztecs 5. They lived in Present day Mexico. 6. Their capital was named Tenochtilaine a. was located on present location of Mexico City b. had great temples and shrines 7. Montezuma thought Cortes was the god Questzalcoatl a. he sent gifts to entice Cortes to turn back b. sent a very large gold medallion (big mistake) 8. After that Cortes' mission changed from explore to conquer 9. Montezuma, thinking Cortes was a god, invited him into the capitol city. 10. Montezuma died and eventually Cortes took over the Aztec empire 11. He took gold and silver from them and shipped it back to Spain 12. Cortes made the Aztecs' slaves and forced them to mine the gold 13. The period of time which Spain received this gold was called Spain's Golden Era VI. Pizzaor: 1. Conquered the Incas in South America 2 Was looking for gold and silver - found silver English Colonies in America I. England Challenges Spain 1. John Cabot sent to America in 1497 2. Claimed northern regions of America for England 3. English Sea Dogs were captains of English ships that robbed Spanish gold ships 4. Sir Frances Drake was the most famous Sea Dog AKA: Drake the dragon 5. King Philip II of Spain built a large fleet of warships to attack England: a. 130 ships b. 30,000 men c. 2,400 cannons 6. In 1588 Spain set sail to attack England with this Spanish Armada II. False Starts in America 1. Sir Humphrey Gilbert a. Received a charter to establish a colony b. Attempted a colony at Newfoundland c. He drowned and the colony failed 2. Sir Walter Raleigh 1. First Attempt to start a colony: a. Sent 7 ships to new world to establish a colony b. Spent first winter on Roanoke Island off the coast of North Carolina c. They were to establish a colony and look for gold d. They found no gold e. Fought with the Indians f. Gave up and went home 2. Second attempt: a. Sent another 100 colonists in 1587 headed by John White b. Landed on Roanoke Island c. Life was very hard d. White returned to England for supplies e. When he returned, the colony was gone (known as The Lost Colony) III. Motives of the Colonizers: 1. Reasons to go to America a. Queen and political leaders sent people to: (1). Find gold (2). Weaken Spain b. Upper-class gentlemen: (1). Adventure (2). Honor (3). Fame c. Ordinary people: (1). Chance to own their own property (2). Become useful workers (3). Religious freedom d. Enclosure Movement: (1). Big demand for wool cloth (2). Farmers enclosed their farms and started raising sheep. (3). Put many farmers out of work (4). Caused many problems in cities IV. Merchant Adventures 1. Very costly to found a colony 2. Business men were very cautious 3. They formed Joint Stock Companies A. Owned by stockholders B. Shareholders share in the profits and losses C. Virginia Company and London Company - examples of Joint Stock Companies 4. In 1606, London Company was given the right to develop a large track of land in Am. V. Jamestown: The First Permanent English Colony History Channel Video: http://www.history.com/topics/jamestown 1. London Company sent three ships to America in 1606 A. Discovery B. Godspeed C. Susan Constant 2. Life in Jamestown was an endless series of tousles. A. Site was swampy 1. Mosquitoes 2. Poor drinking water B. Many dead (½ dead by end of summer) C. Did not get food planted before growing season ended. D. Short of food before winter was over. E. Poor leadership. 1. Spent too much time looking for gold. 2. No real authority. 3. Settlers quarreled among themselves. 3. John Smith took control. A. Stopped searching for gold. B. Put people to work. VI. Headrights and Indentured Servants 1. Attempts by the English government to attract settlers to the new world. They offered: A. Headright - paid his own way to America or paid the way for others. He would in tern receive 50 acres of land for each head he transported. B. Guaranteed settlers that they would have the same rights as English citizens. C. Guaranteed settlers that they would have a voice in local government. (1). They could elect representatives to the House of Burgesses (2). This was thefirst elected government body in America D.Indentured Servants - people who agreed to work 7 years to pay for their passage to the new world. VII. Pilgrims 1. A very religious group from England 2. They left England in 1608 to escape religious persecution 3. They separated themselves from the accepted Anglican Church - the official Church of England. (They wanted Religious Freedom) 4. They moved to the Netherlands with the Dutch. 5. Became afraid their culture would be lost - they wanted to live in a place where their children could grow up English and at the same time have religious freedom. 6. They came to America on a ship called the Mayflower 7. Drew up a document which provided a legal basis for governing themselves and the area – it was called the Mayflower Compact (it was the first formal government in America.) 8. They settled at Plymouth, Mass. 9. Celebrated success with the Indians on Thanksgiving Day. VIII. The French in America 1. French sent Jacques Cartier to America to claim land 2. Set sail in 1534 3. Claimed land along the Saint Lawrence River for France 4. In 1608 Samuel de Champlain started the first permanent French colony – Quebec 5. In 1679, Robert de la Salle sailed through the Great Lakes, down the Mississippi River, and into the Gulf of Mexico claiming all land drained by the Mississippi River for France. 6. This land was named Louisiana after King Louie of France IX. Dutch and Swedish 1. The Dutch claimed the region drained by the Hudson River. 2. Henry Hudson claimed this region for the Dutch in 1609. 3. Swedish found New Sweden on the Delaware River near Wilmington 4. Swedish built the first log cabins X. Puritans 1. Sought to reform the Church of England from within 2. Met strong resistors. 3. Moved to America to create the perfect church & perfect community 4. Obtained a grant & organized the Massachusetts Bay Company 5. John Winthrop was the first governor 6. The tried to create a common wealth for the good of all 7. Boston was their chief town 8. During the next 10 years, 15-20 thousand people came 9. From there, Thomas Hooker lead settlers & formed Connecticut (Chief town was Hartford) XI. Rhode Island 1. Was formed when Roger Williams & Anne Hutchinson were driven out of Boston. 2. They attacked the religious beliefs of the Puritans XII. New York & New Jersey 1. When England took over colony name changed to New York 2. Duke of York was the Proprietor 3. He gave parts of it to his friends 4. New Jersey - given to George Carteret & Lord John Berkeley 5. To attract settlers the offered: a.. land on easy terms b. religious freedom 6. Berkely & Carteret eventually sold the land to the Quakers 7. In 1702 the Quakers re-united the land into one colony XIII. Pennsylvania and Deleware 1. King Charles II granted William Penn land in America to repay a debt 2. The land was named Pennsylvania in honor of Penn’s father 3. Philadelphia, the “City of Brotherly Love” was started by William Penn 4. Treated the Indians fairly 5. Penn lured settlers by: a. Offering them a voice in the government b. Religious freedom c. Telling how beautiful the land was 6. Settlers came from many lands 7. Delaware was granted to Penn as a port for Pennsylvania’s surplus 8. Delaware became a separate colony in 1704 XIV. Georgia 1. Last colony to be settled 2. Founded to provide a refuge for prisioners 3. Leader was James Oglethorpe 4. Founded Savanna with 100 settlers 5. Oglethorpe was very strict .....settlers didn’t like his rules, so he gave Georgia back to the king, therefore, it became a royal colony run by the king. 6. Vocabulary: (1). Patroon --------- Landowner like a feudal lord (ruled over a large estate) If anyone brought 50 settlers, they would be granted a very large estate. (2). Squanto --------- An Indian who helped the pilgrims survive in America. He taught them to plant corn and how to fish. (3). Peter Minuet ----Bought Manhattan Island from Indians for some beeds, trinkets, and knives. A very good real estate deal. (4). Roanoke Island - Same place as the Lost Colony was located. (5). Carolina ----------- colony named after King Charles I. Original 13 Colonies Game: http://www.softschools.com/social_studies/13_colonies_map/ Life in Colonial America I. Land and People 1. America was a very large land with very few people 2. Lots of work to be done 3. Plenty of food: a. Land to farm b. Game in the woods c. Fish in the streams II. Rivers Shape Life 1. Rivers became the first roads 2. The first communities grew up around the rivers 3. Building roads was expensive 4. Trade was conducted along rivers III. Women in Colonial America 1. First settlers were men 2. Married women could not own land 3. Women had more opportunities in America than in England 4. Some women ran large farms in America IV. The Right To Vote 1. Women could not vote 2. Only white men that owned land could vote 3. The English and Americans held the same opinion V. Origins of Slavery 1. Indentured servants eventually acquired land 2. Blacks from Africa were used cruelly 3. Indians were also used, but did not make good workers a. They were not accustomed to doing that kind of work b. Would be rescued by their friends or would run away 4. Spaniards brought blacks to America before Jamestown was founded 5. The English got the idea of enslaving blacks from the Spanish 6. The word “negro” is Spanish for black. 7. The first Africans were brought to the English Colonies by the Dutch. 8. They were sold to settlers in Jamestown in 1619. VI. Comparative Chart of Slaves to Indentured Servants Slaves Advantages Disadvantages 1. Yours for life 1. Could not speak English 2. Children your also 2. Expensive 3. Could sell them 3. Lacked farming skills 4. Won’t compete against former 4. Morally Wrong owners for markets 5. Must teach them all skills 5. Won’t have to pay them 6. Didn’t have immunities to 6. Population will increase as children European diseases are born Indentured Servants Advantages Disadvantages 1. Spoke English 1. They would compete against their 2. Cost less former owners for markets 3. Had farming skills 2. Must free them after 7 years 4. Morally accepted 3. Must be paid 4. Markets eventually flooded as more people planted same crops VII. Slave Life India’s Song: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DGY-3M-Bp24 1. Slavery was called the peculiar institution 2. Slaves were rarely beaten - too valuable to be treated badly (unless they refused to work or tried to run away) 3. Slaves got adequate food and clothing 4. Slaves got adequate shelter 5. Slaves could not vote or own property 6. Slave families could be separate 7. Slaves were considered as living property 8. Slaves were auctioned to the highest bidders 9. Slaves came to America in chains 10. They had no immunities to European diseases 11. The trip across the Atlantic Ocean was called the Middle Passage 12. Slave ships were inhumane VII. Southern Agriculture 1. Looked for cash crops a. Sugar b. Tobacco c. Rice d. Indigo e. Naval stores (1). Trees (2). Sap (3). Tar (4). Resin VIII. Northern Products 1. Fur trade 2. Fishing 3. Ship building 4. Lumber 5. Shipping industry (example: grain and fish to sugar islands and sugar back to colonies) (horses and barrels also profitable) IX. The Great Awakening 1. A religious movement in America 2. Started by George Whitefield 3. Preached across the colonies 4. Many were swept by religious excitement X. The Enlightenment 1. Also called the “Age of Reason” 2. Belief that in an orderly universe, human reason would prevail 3. Benjamin Franklin became famous in the Enlightenment period XI. Benjamin Franklin 1. Greatest American of the Enlightenment Period 2. Wrote Poor Richard’s Almanac 3. He invented: a. Cast iron stove b. Bifocal eyeglasses c. Discovered electricity 4. He was an outstanding citizen: a. Founded first library b. First fire department c. First hospital 5. He developed the first scheme for uniting the colonies a. Called “Albany Plan of Union” His slogan “Join or Die” Most did not like it XII. East-West Disputes 1. Most Americans lived comfortably 2. The land had been settled to the mountains 3. Travel was slow and difficult 4. Colonial governments were in dispute about boundaries which were vague 5. Most land-grants were made before the land was explored 6. This problem was settled in 1760's with the Mason-Dixon Line 7. Separated southern (agricultural) colonies from northern (industrial) colonies XIV. Bacon’s Rebellion 1. 1676 - Indians killed a shepherd 2. Settlers then killed 127 Indians 3. Indians then killed 36 settlers 4. One of these settlers worked for a tobacco farmer named Nathaniel Bacon 5. Bacon organized a large force to stop the Indians 6. Governor Berkeley tried to stop the violence 7. Bacon wiped out the wrong tribe of Indians 8. Said all Indians are alike 9. Oct. 6, 1676 Bacon died and the Rebellion ended Problems in America U.S Expansionism: http://www.animatedatlas.com/movie.html I. Attack on the sedition Acts p. 272 1. The Sedition Acts were attempts to frighten all critics of the Federalists Party into silence and help get Adams elected as President of the United States. 2. They violated the 1st Amendment - (Freedom of Speech & Press) 3. Jefferson began an attack on the Sedition Acts 4. He wrote (in secret) the Kentucky and Virginia resolution which were his statement against the Sedition Acts. 5. James Madison introduced these resolutions. II. Doctrine of Nullification p. 272, 338 1. According to Jefferson- any state could void or nullify any law pass by congress that if felt to violate the constitution. 2. Jefferson based the power of the states to do this on what he called States Rights. III. Election of 1800 p. 277 1. Hamilton again tried to sway the election. 2. The Federalists ran Adams for Pres. & Pinckney for V. President. 3. Hamilton disliked Adams so much that he published a pamphlet against him entitled "The Public Conduct and Character of John Adams." 4. In this pamphlet he said that Adams was a "jealous, vain and stubborn" man that was unfit to be President. 5. Once again (as in 1796) Hamilton tried to manage the electors in order to get Jefferson elected. 6. Jefferson ended up with 73 electoral votes but Burr only got 65. 7. Adams got 73 electoral votes also. 8. Since both were running for President- the tie had to be broken by a re- vote in the House of Representatives. (which had to break the tie). 9. They voted 35 times Without anyone changing a vote. 10. The vote was a state by state vote with each state getting only one vote. 11. Jefferson eventually won with Burr as V. pres. 12. After this everyone realize that because of the well organized political parties a new method of electing Pres. and V. Pres. was needed. 13. Therefore the 12th Amendment was added to the Constitution in which electors voted separately for pres. and V. pres. IV. The Louisiana Purchase p. 281 1. New Orleans was very important to the Americans. 2. Napoleon Bonaparte was a military genius. He overthrew the French Government and made himself dictator. 3. Napoleon told the Spanish that he wanted New Orleans back (he had an army in Santa Domingo - not far from the U.S.) 4. The Spanish gave it up - therefore, New Orleans became French Property again. 5. This frightened Americans because we did not know his intentions. (War with the U.S. ?? What about a RIGHT OF DEPOSIT??) 6. Jefferson sent Livingston and Monroe to France to try to buy New Orleans. 7. Napoleon's army in Santa Domingo was struck by Yellow Fever and many died. 8. Since Napoleon planned to resume the war with England, he needed money to rebuild his armies. 9. He, therefore, ordered Talleyrand to sell all of Louisiana to the United States. 10. President Jefferson had authorized Monroe and Livingston to spend up to $10 Million just for the city of New Orleans. 11. Napoleon instead offered to sell all of Louisiana for $15 Million. 12. The deal was made and we bought it. 13. The Federalist party was furious that Jefferson spent this money without even looking at the land. 14. Jefferson, therefore, sent Louis and Clark to explore this territory. V. Louis and Clark Expedition p. 283 Interactive Trail Map: http://www.pbs.org/lewisandclark/trailmap/index.html 1. Jefferson asked Congress for money to start an expedition. ($2,500) 2. On the expedition they had to examine plants, animals, and people and their languages. 3. 21 men in the expedition were from the military. 4. The entire group, called the Corps of Discovery, consisted of 45 people in all. 5. Sacajawea , an Indian girl whose name meant Bird Woman, joined the expedition as a guide and interperter. 6. Their first objective was to explore the Louisiana Territory. 7. A second objective was to find a water route to the Pacific. 8. The Continental Divide separate the continent. It's part of the Rocky Mountain Chain. 9. The expedition traveled up the Missouri River - crossed the Continental Divide, then down the Snake River to the Columbia River to the west coast. 10. There they built Fort Clatsop at the mouth of the Columbia River. VI. Jefferson and the Navy p. 297 1. During the previous administration, 3 American war ships were built: (under Adams) a. Constitution b. Constellation c. United States 2. When Jefferson became president, he saw no need to expand the Navy. 3. He decided to build cheaper ($10,000) gun-boats instead of the more expensive frigates. 5. Jefferson, therefore, stopped the building of the American Navy. VII. Trouble on the High Seas p. 291 1. The Milan Decree of 1807 (by Napoleon) stated that: - any neutral country that allowed its ships to be inspected on the high seas by a British war ship became English property. Since France was at war with England - Napoleon ordered his captains to capture those American ships. 2. To stop this from happening - America passed the Embargo Act . This Act prohibited all exports from the U.S. 3. The Embargo Act crippled the American economy. 4. Another cause of concern for the Americans was Impressment. 5. English ship captains would impress Americans into the English navy. This meant that the Americans would be forced into the English Navy against their will. VIII. America of the Eve of War 1. Madison was elected as the fourth President of the U.S. 2. In 1809 the Embargo Act was repealed 3. The Non-Intercourse Act was passed. (This law said that no English or French ships could enter an American harbor) This did not work either. 4. Macon's Bill #2 was passed next: (This law removed all restrictions on trade with England and France. It also provided that if either nation stopped attacking American merchant ships, the President would cut off all trade with the rival nation unless it also stopped its attacks.) This law failed also. 5. Since all efforts to stop the attack on American ships had failed, many Americans felt that WAR was the only solution. Building America I. The turn toward Manufacturing: p 310 1. Alexander Hamilton favored a diversified economy, one in which manufacturing existed side by side with agriculture. 2. America needed to be free from European suppliers of manufactured goods and produce their own products. 3. After the Revolutionary War the British began selling all kinds of manufactured products in America at discount prices in order to win back American customers. 4. American producers lost business as a result. 5. They wanted Protective Tariffs (high taxes on imported products) to keep British products from being sold cheaply in America. 6. After the War of 1812 Congress passed the Tariff Act of 1816 which placed a duty of 20 to 30 per cent on many manufactured products. 7. The purpose of these duties was not to collect money but to make foreign goods cost more than American made goods. 8. To further aid manufacturing, Congress created a new Bank of the United States. II. Mass Production: p 306-7 p 385-6 1. America had an enormous amount of natural resources. 2. America did not know how to mass produce products (produce in large quantity). 3. America’s Industrial Technology (tools, machines, and other things used to produce things) was very inefficient. 4. Eli Whitney was one of the first to improve our industrial technology. 5. He manufactured muskets made from Interchangeable Parts. (All parts of the guns Were exactly alike) 6. This new idea changed the way factories built products. 7. Using interchangeable parts allowed mass production of a product. III. The Industrial Revolution: p 306 1. The shift from hand tools to power driven tools is called the Industrial Revolution. 2. This began in England in the 1700's. a. Spinning wheel & Loom. b. Spinning Jenny - (a mechanical spinning wheel) c. Water frame - (invented by Arkwright ----produced a much stronger cotton thread but required a mechanical force such as waterpower to run it.) IV. The Factory Comes to America: p. 307 1. Arkwright’s water frame proved successful in England. 2. England exported cloth all over the world. 3. England would not share the secrets of its Industrial Revolution with other countries. 4. Samuel Slater, an English mechanic, memorized the designs for the new cotton spinning machinery and brought them to America. 5. With the help of Moses Brown, a cotton-spinning machine powered by water was made. 6. This machine made only thread - but it was stronger and cheaper than homespun. 7. Putting-Out System: Slater’s thread was supplied to women at home to use in their looms to make cloth from the thread. 8. This system was called “putting out the thread.” 9. This system was used widely in America. V. Recruiting a Labor Force : p 307-8 1. Rhode Island System: made use of children to operate Slater’s spinning machinery. a. It took nine children to operate one machine b. Children were cheaper than adults c. Farm children were used to working anyway. d. Children were not required to go to school. e. Salary: ranged from 33 cents to 67 cents per week for children and $2 to $3 per week for adults. 2. Lowell System: Lowell’s plant not only made thread but wove it into cloth. He Made use of unmarried women from neighboring farms. They could save part of their wages before settling down and getting married. p 308 IV. Immigration from Europe : p 393-4 1. Many women walked out of factory jobs around 1834-6 in protest of lowering wages. 2. These jobs were filled by immigrants men and women. 3. Immigration was unlimited. 4. Nativist believed that too much immigration would destroy American institutions. 5. They forgot that they, too, were once immigrates. VII. City Life In America: p 585-6 1. Most immigrates that came to America lived in Cities. 2. These cities were mostly shipping centers. 3. Cities to the west were mostly commercial centers and made up the urban frontier. 4. Most cities had poor sanitation. 5. Rapid growth caused slums and overcrowding to occur. 6. Families crowed together in buildings called tenements which had low rent. 7. Tenements were usually unsafe and unsanitary. VIII. New Roads and Turnpikes: p 314 1. Cities grew- stagecoach invented to carry people around town (1827). 2. Most roads were dirt.(dusty or muddy) 3. Builders of roads collected tolls form travelers that used their roads. These roads were called turnpikes 4. Thomas Jefferson authorized the building of the Cumberland or National Road. 5. It ran from Maryland to West Virginia and still carries passengers today. IX. Canals: p 316 How Canals Work: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tfWyBz5bHj8 1. The easiest means of moving loads is by water. 2. Canals were dug. 3. They were expensive to build. 4. The Erie Canal was built. It ran from the Hudson River to Lake Erie. Erie Canal Song: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Koj5yGigFNU 5. It was completed in 1825 6. It was called Clinton’s “Big Ditch” 7. When others saw how successful it was, they began to build their own canals. 8. Animals such as mules were used to pull barges up and down the canals. X. Steamboats: p 315 1. Travel by canal was slow- it still depended on animal power. 2. In the 1760's, James Watt invented a practical steam engine. 3. If this engine could power factories, then why not a boat? 4. In 1807, Robert Fulton built the first practical steam driven boatThe Clermont. 5. Those who watched it built called it Fulton’s Folly. 6. Construction on new and improved models were then on the way. XI. Railroads: p 386 1. The first steam-driven locomotive, the Tom Thumb, was built by Peter Cooper in 1803. 2. It was built for the “Baltimore and Ohio Railroad” 3. Afterwards, improvement was made. XII. Transportation Revolution: p 313-315 1. Turnpikes, Canals, Roads, Steamboats, and Railroads were all being used and improved. 2. This was called the Transportation Revolution. Governing the American Colonies I. Royal Grants and Charters 1. All colonies belonged to the King 2. The King did not personally manage each colony a. Colonial policy was set by the Privy Council 1. The Lords of Trade was a subcommittee of the Privy Council 2. They handled problems as they happened b. Parliament also made laws that applied to the colonies c. The King also made laws for the colonies 3. The King could dispose of the colonies as he wished II. Enumerated Articles 1. Products that could be sold or bought only within the British Empire 2. They were products that England needed, but could not produce at home. 3. These products were Enumerated only to England: a. Sugar b. Tobacco c. Furs d. Naval stores e. Cotton f. Indigo 4. Wheat and Fish were not enumerated, therefore could be sold anywhere. III. English Colonial Government 1. Each colony would have an English Governor 2. Governors were assisted by Councils that acted as advisors to the Governors 3. Locally elected Assemblies were to handle daily matters IV. English Colonial Policy 1. Stated that “Colonies are supposed to be profitable” to England 2. These were laws passed regulating trade from 1651 - 1733 V. Navigation Acts: 1. All goods must be shipped on ships made in either England or the colonies 2. Owners of these ships must be English 3. The captain and crew must also be English 4. European goods could be brought into the colonies only after being taken to England 5. The Molasses Act was the last of the Navigation Acts to be passed. It placed a pence tax on all imported molasses. It was not designed to be collected, but to regulate trade. (Passed in 1733) 6. Certain products (enumerated articles) could only be sold to England. 7. The Navigation Acts worked well for more than a 100 years - not really enforced. 8. Some smuggling took place by the colonists. They considered England their enemy. VI. French and English Wars 1. From the 1760's on, France and England were constantly at war 2. Whenever war broke out in Europe, the French and English colonists fought also 3. Several major conflicts occurred: a. King Williams War ------- 1689 - 1697 b. Queen Ann’s War -------- 1702 - 1713 c. King George’s War ------ 1744 - 1748 4. Even though few settlers were involved, tension increased between settlers of both nations. VII. French Menace 1. French Governor Marquis Duquesene de Menneville decided to construct a chain of forts from Lake Erie to the Ohio River. (Blocking the English from crossing the mts.) 2. Governor Dinwiddie of Virginia became upset, because he had planned to take land across the mountains and sell it to future settlers and therefore make millions of dollars for himself. 3. Dinwiddie sent George Washington to warn the French that they were trespassing on English Property. 4. The French rejected Dinwiddie’s message and continued to build the forts. 5. Dinwiddie then ordered the construction of a fort at the head of the Ohio River (this fort was to block the French from the Ohio Valley) This fort was latter named Fort Pitt. 6. George Washington was sent with 150 men to protect the fort from a French Attack. 7. Before Washington reached the fort, the French attacked the construction company and took the fort. The French then completed its construction and held the position. They renamed the fort Fort Duquesne. 8. Washington did not turn back. 9. He attacked a small French scout party and killed its leader on his way to the fort. 10. The main French army moved against Washington - he retreated as fast as he could and finally threw together a make shift fort to protect himself. This fort was called Fort Necessity. 11. After a severe French attack, Washington surrendered. 12. The French commander allowed Washington and his men to go free and return to Virginia. The disputed land now belonged to the French. VIII. French and Indian War French & Indian War Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VmoDHHwgiNc 1. Troops: French - 90,000 English - 1,500,000 2. British soldiers also took part in the struggle and did most of the fighting. 3. During the first 2 years of the war the French and Indians won most of the battles. 4. William Pitt took over the war effort for the English 5. He recaptured Fort Duquesne and changed its name to Fort Pitt 6. Gradually all the French forts fell into English hands 7. British general James Wolfe decided to attack Quebec, the French Capitol. 8. This battle was fought on The Plains of Abraham - just outside of Quebec. 9. The city surrendered to the British and the war was over. 10. By this time the “Seven Years War” had spread throughout the world. 11. The British were victorious everywhere. 12. The Colonists were delighted. a. The French threat was removed b. Spain was pushed back from the southern frontier c. The way to the west was open 13. The Royal treasury had paid most of the bills 14. The Colonists were never move loyal to England than in 1763. IX. Post War Problems 1. The new larger empire was more costly to maintain 2. Pontiac’s Rebellion - Indians in the Ohio Valley did not stop fighting. 3. British had to station 6,000 troops in the Ohio Valley to keep peace 4. Already established colonies quarreled over who would get this newly acquired land. 5. Proclamation of 1763 - “British law” which said the following: a. Only licensed fur traders could go into the Ohio Valley b. No one could buy Indian land c. This law closed off the Ohio Valley to all colonists. X. Sugar Act 1. The Proclamation of 1763 made peace with the Indians of the Ohio Valley 2. George Greenville became Prime Minister of England. 3. He viewed the colonies in terms of “money taken in - money spent’ 4. He found that: a. Running the colonies was expensive b. Most taxes collected in the colonies was spent in the colonies c. The colonies were no longer profitable d. Since English Colonial Policy said that colonies were suppose to be profitable, there was a problem. 5. Greenville imposed the Sugar Act a. Sugar and Coffee were to be taxed upon entry into any colonial port b. Import taxes were called duties c. The Molasses tax was reduced from 6 pence to 3 pence, but now it was to be collected. d. Greenville began strictly enforcing the Navigation Acts for the first time. 6. Molasses Act of 1733: a. Was the last of the Navigation Acts to be Passed b. Was designed to regulate trade - not to be collected. c. Placed a 6 pence tax on foreign molasses (so high no one could afford to pay it) d. The Sugar Act reduced the tax from 6 pence to 3 pence and now planned to collect the tax. (This was to make money for England) 7. American colonists complained about Taxation without Representation because England was now taxing the colonists but at the same time did not allow the colonists to have a Representative in the English Parliament to speak on their behalf. 8. Most colonists did little more than complain about the Sugar Act - they paid the tax. XI. Stamp Act 1. This is the second of Greenville’s tax laws. 2. This law taxed the following by requiring stamps to be placed on the following articles: a. Deeds to land b. Newspapers. c. Marriage licenses d. Diplomas e. Playing Cards f. Advertisements and Handbills 3. Colonists did NOT accept this law. 4. A Stamp Act Congress was formed a. Attended by representatives of 9 colonies b. They passed 14 resolutions (one of which said that this law “Subverted the rights and liberties of the colonists.” 5. Stamp Act Riots broke out - the largest of which was in New York City a. Windows were broken b. Stamp Masters were driven out of town c. Stamp offices were destroyed 6. Colonists organized a boycott (refusing to buy) all English products sold in the colonies. XII. Declaratory Act 1. Was only a statement of power over the colonies 2. It said that “Parliament could pass any law regarding the colonies that it desired. 3. At the same time this act was passed, Parliament repealed the Stamp Act. (Repeal means to do away with or take back a law) XIII. The Townshend Act of 1767 1. These were passed by Charles Townshend, the finance minister of England 2. These Acts placed Indirect Taxes on: a. Lead b. Paper * All common products used by colonists c. Paint d. Glass e. Tea 3. A board of Custom Commissioners were placed in Boston to enforce the Townshend Taxes. 4. Circular Letters were mailed throughout all the colonies making all colonists aware of the new taxes. 5. The colonists organized another boycott XIV. The Boston Massacre 1. Before the French and Indian War, English troops were not stationed in the colonies 2. Now, in peacetime, several thousand troops were suddenly quartered in Boston 3. Tension mounted 4. Soldiers were to guard the Custom House 5. A crowd gathered! 6. By mistake - the soldiers fired into the crowd - killing 3 Americans instantly and 2 others died later from their wounds. 7. This was called a “Massacre” by the Americans to gain support for the cause of freedom from England. (The Boston Massacre was used as a propaganda tool to turn American colonists against England) The Revolutionary War I. The Tea Act: 1. Passed in 1773 2. Designed to help the East India Tea Company a. Had always made money b. The company now was about to go bankrupt (because of the Townshend tax) c. Parliament passed the Tea Act to help it 3. The Tea Act allowed the company to sell tea directly to America 4. It actually lowered the price of tea in the colonies. 5. The colonists complained anyway because the Townshend tax was included in the new lower price. 6. This resulted in the organization of a second boycott by the American Colonists. 7. The Tea Act: a. Repealed the English tax on tea b. Only the Townshend tax remained c. It bypassed the English wholesalers d. It allowed tea to be sold directly to American Merchants. II. The Boston Tea Party: 1. When the tea (under the new Tea Act) arrived in the colonies, members of the Sons of Liberty in Boston dressed as Indians and threw the tea into the harbor. 2. The English Government was furious and decided that the colonies were in a state of rebellion. 3. As a result of the Boston Tea Party the English government passed the Coercive Acts. 4. 342 chest of tea were thrown overboard. In Boston Harbor. * 5. Christopher Gadsden from South Carolina founded and established the first chapter of the Sons of Liberty in Charles Town, South Carolina. * 6. Tea Parties were also held in Charles Town and Georgetown, South Carolina III. Coercive Acts: 1. They were passed by England in response to the Boston Tea Party 2. The Coercive Acts included the following: a. Boston Port Act - closed Boston’s harbor until the tea was paid for b. Administration of Justice Act - gave the governor power to transfer the trials of soldiers and royal officials accused of serious crimes to courts outside of Massachusetts. c. Massachusetts Government Act - gave Governor more power by placing him over town meetings and also replaced the elected colonial council with a council appointed by the king. d. Also, soldiers were to be placed in citizen’s homes e. Thomas Hutchinson, governor of Massachusetts, was replaced by the British General, Thomas Gage. 3. The Americans called the Coercive Acts the Intolerable Acts. Intolerable Acts Song Lyrics: Set to the tune of “Eye of the Tiger” Taxin' stamps, taxin' our tea Why so many taxes upon me Out in Britain they're taxin the colonies So many times we can hardly survive So many taxes, first it was papers Not any more we got angry They lost their grip and taxed all our goods I guess they can't just take a hint It's the tax of the tyrants They're tryin' to pay For the fight we fought against our rivals And they fought in our backyard So they're makin' us pay And we're makin' a stand on the tax of the tyrants Read my face I look really mad We said no we ain't payin' They said OK we'll just tax the tea Now we're here it is tea party time It's the tax of the tyrants They're tryin' to pay For the fight we fought against our rivals And they fought in our backyard So they're makin' us pay And we're makin' a stand on the tax of the tyrants Now its war Get ready to fight You got some guts taxin' the colonies Intolerable acts no we're not gonna stop This is war only one will survive All credit to the music goes to the respective copyright holders...duh. It's the tax of the tyrants They're tryin' to pay For the fight we fought against our rivals And they fought in our backyard So they're makin' us pay And we're makin' a stand on the tax of the tyrants Hyperlink: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvx7i8GXtPY IV. The First Continental Congress: (September 5. 1774) 1. This was the first time the colonies came together as one group to stand together against England. (The Birth of the United States of America) 2. Resolutions they passed: a. They condemned the Coercive Acts and urged full support form the citizens of Boston. b. They demanded the repeal of all British taxes on colonists. c. They declared that only the colonial assemblies had the right to tax Americans. d. They denounced the British practice of maintaining a British Army in the colonies during peace time. e. They set up a Continental Association to enforce a ban on importing British products of all types. 3. Delegates from every colony, but Georgia, made up the First Continental Congress. * 4. Henry Middleton, of South Carolina was elected as the first President of the Continental Congress. 5. Most members of the congress wanted to avoid war at all costs. V. Lexington and Concord: Short History Channel Video: http://www.history.com/topics/americanrevolution/battles-of-lexington-and-concord 1. General Thomas Gage had to be present at all town meetings. 2. The Sons of Liberty’s leaders had to leave Boston and go to Concord to continue to meet. 3. The leaders were Samuel Adams and John Hancock. 4. They began to get as many men together as they possibly could. 5. They called the militia groups “Minute Men”, because they were supposed to be ready to fight at a minutes notice. 6. The men started an arsenal in nearby Concord. 7. They tried to get as much money, volunteers, guns, and ammo as they possibly could. 8. Gage sent out spies to find the leaders of the Sons of Liberty. 9. At the same time, Adams and Hancock set up a colonial spy system to watch the British soldiers in Boston. 10. If the soldiers were going to come by land, the signal would be one lantern, and if by water, it would be two lanterns. 11. Gage decided to go after Adams and Hancock on April 18, 1775. (By Water) 12. Paul Revere saw the signal and rode his horse to Lexington to warn them. 13. Adams and Hancock were able to escape before the British arrived. 14. Paul Revere was stopped by a British blockade, but a young doctor made it through and warned the citizens of Concord. 15. When the soldiers reached Lexington, shots were fired and a few minute-men were killed. This first shot is called the Shot That Was Heard Around The World. School House Rock: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y6ikO6LMxF4 16. When the soldiers reached Concord, the minute men had gathered on the North Bridge to stop them. 17. A fight took place and both British soldiers and minute men were killed. 18. The arsenal was moved and saved 19. The minute men chased the British soldiers all the way back to Boston, firing at them all the way. 20. Many British soldiers were killed and Gage was very angry. VI. Battle of Breed’s Hill 1. The war for American independence had begun 2. Within 48 hours, nearly 20,000 militia men had gathered across the Charles River from Boston. 3. In May, militia men from Connecticut & Massachusetts took Fort Ticonderoga & captured a heavy cannon. 4. Americans gained control of Breeds Hill on June 16 5. Worked all night digging a ditch around top of breeds Hill. 6. Gauge knew he couldn’t let American occupy Breeds Hill. 7. On June17, General Howe ferried 1500 Red-coats across the bay to Charleston. 8. Marched straight up Breeds Hill & attacked Americans. 9. American Commander was Colonel William Prescott. 10. When British were almost to the wall, Prescott gave the signal to fire. 11. British had to retreat back down Breeds Hill. 12. Came up a 2nd time & had to retreat again. 13. By this time, the Americans were low on ammo & had to use whatever they could find (rocks, nails, glass, ect.) 14. British went up for the 3 rd time & were able to clear the dirt wall 15. Attacked Americans with bayonets & won battle: a. 1000 British dead or wounded b. 100 Americans dead c. 300 Americans wounded or taken prisoner 16. Was known as Battle of Bunker Hill VII. Second Continental Congress (May 10, 1775) Declaration of Independence Song: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uZfRaWAtBVg 1. Formed American Army 2. Appointed George Washington as General: a. Washington looked like a General b. Had war experience c. From Virginia ( most powerful of southern colonies) d. Was very wealthy 3. Met at Independence Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in May 4. Sent Olive Branch Petition asking King to protect the colonists from Parliament 5. Next day, issued “ Declaration of the Causes & Necessity of Taking Up Arms” 6. Wrote Declaration of Independence * 7. Four signers of the Declaration from South Carolina were: 1) Edward Rutledge, 2) Thomas Heyward, 3) Thomas Lynch, & 4) Arthur Middleton. * 8. South Carolina and Pennsylvania voted AGAINST Independence. Revolutionary Battles Interactive Study Map: http://teachingamericanhistory.org/static/neh/interactives/americanrevolution/ VIII. Battle of Dorchester Heights 1. Washington found cannon expert, Colonel Henry Knox 2. Knox left to Fort Ticonderoga to get cannons 3. Washington placed cannons on Dorchester Heights 4. Battle of Dorchester Heights was worn by Washington, without firing a shot in March, 1776 IX. Battle of Long Island: 1. Declaration of Independence signedon July 4, 1776. 2. Howe to Halifaxin March, 1776. 3. Howe from Halifax to attack N.Y. in July, 1776. 4. Returned with 32,000 men & 400 warships. 5. By capturing New York, he could split New England colonies from the other colonies (Divide & conquer.) 6. Washington had to retreat across Delaware River into Pennsylvania (across the Hudson, also.) 7. One of the lowest points of moral & spirit during the war for Americans. X. Battle of Trenton: 1. About 1400 Hessians (German mercanaries) camped in Trenton. 2. Were paid by England to fight for England. 3. Hessians were hated by Americans. 4. Washington decided to attack the Hessian camp on Christmas night during a snowstorm (very strange) 5. At dawn, Washington overwhelmed the Hessians. 6. Only, 30 Hessians were killed, but 900 were taken prisoner, furthermore, no Americans were killed, & only 3 were wounded. 7. British camped at Princeton for winter. 8. British headquarters was camped at New York. 9. Americans were camped at Pennsylvania. 10. Washington wiped out British at Princeton. 11. After battle, Washington spent the first winter of war in Morristown, NJ. X1.The Battle Plans of 1777- 78 1.Howe sends Bergoin (“Gentleman Johnny”) to go down St.Lawrence to Montreal then to capture Fort Ticonderoga with 7,000 men & 138 cannons. 2. General Clinton stayed in NY & guarded Hudson River area with 10,000 men. 3. Howe stationed himself south of Philadelphia & was to take it over during the attack. 4. This led to the battle of Brandywine. X. The Battle of Brandywine: 1.In September, 1777 Howe took troops by sea to Chesapeake Bay in order To attack Philadelphia from the south. 2. Washington hurried south as soon as he learned where Howe was. 3. The two armies clashed at Brandywine Creek on September 11, 1777. 4. Washington was out maneuveredby Howe & the Americans were badly defeated. 5. On September 26, Howe marched into Philadelphia. XIII. The Battle of Saratoga: 1. Started on September19, 1777. 2. Bergoin came south to close loop (Battle Plans of 1776) 3. Trees were being cut down along trail to slow Bergoin’s travel. 4. While stalling Bergoin, malitia units formed army (Head-Horatio Gates, assistant-Daniel Morgan , Benedict Arnold) 5. Horatio was very slow to attack & was very cautious (biggest flaw) 6. The assistants were exactly the opposite (their biggest flaws) 7. Made attack on or around September 19 on Freeman’s Farm 8. Attacked again on October7 (finished the job) 9. Bergoin surrendered at Saratoga (Oct. 7) 10. Out of 6,500 British troops, 5,700 were taken prisoner 11. This was known as the turning point of the war 12. Because of this battle, French helped colonies fight England 13. Was the first victory againist a major sized British Army unit 14. This battle was also known as the Battle of Freeman’s Farm 15. While all this was going on Washington was recovering from Battle of Brandywine XIV. Battle of Germantown: 1. Washington has organized plan like the “Bull Horn” theory 2. In October, Howe marches out of Philadelphia 3. Fog sets in & mirror signals don’t work 4. Was considered a British victory, but was really about the same losses 5. During the battle, Washington made a decent showing againist Howe 6. Was not a smashing victory or defeat for either side 7. Led into the worst winter of the war for Washington and troops XV. Winter Camp at Valley Forge: 1.Washington and troops camped at Valley Forge after Battle of Germantown 2. Valley Forge was 18 miles from Philadelphia 3. Second winter of the war was lowest point of war 4. 2,000 died at Valley Forge 5. It was cold and there was hungar and diseases 6. No shoes on American’s feet (very bad condition) 7. Frozen rivers and roads prevented transportation of food etc. 8. Hospitals and log cabins were built 9. Continental Congress moved 80 miles away to York, Pennsylvania 10. Frederick Van Stuben helped army 11. Was hard on Washington’s men 12. Helped a lot XVI . The War in the South and the West 1. General Howe retired and went back to England 2. General Clinton took over and brought over General Cornwallis 3. British army regrouped 4. Clinton decided to take war down south XVII. The Battle of Monmoth Courthouse 1. Marching through New Jersey to New York, Clinton was attacked 2. Boosted Americans’ morale 3. Fought in June, 1778 XVIII. The Battle of Savannah 1. Clinton and troops to Savannah in 1778 2. Savannah was captured and there was no opposition XIX. The Fall of Charleston 1. Charleston was captured 2. Many prisoners taken (5-6 thousand) 3. Cornwallis unloaded major British army and started to march across XX. The Fall of Camden 1.Cornwallis vs. Gates 2. British won major battle at Camden, South Carolina 3. Was fought in August, 1780 4. Nathaniel Green took Gate’s place after he was discharged for not knowing wha he was doing 5. Cornwallis expected to pick up Tories while marching through SC 6. Instead, he fought against irregular soldiers called Partisans. a. Francis Marion (Swampfox) b. Thomas Sumpter (Gamecock) c. Andrew Pickens (Wizard Owl) 7. Swampfox had camp at Snow’s Island 8. Using hit-&-run tactics called Guerrilla warfare. 9. Partisans attacked unprepared British soldiers in the countryside of South Carolina. 10. Fergerson was a sharp-shooter and made a small army of loyalists in SC XXI. Battle of King’s Mountain 1. Mountain volunteers against Fergerson and Tories XXII. Battle of Cowpens 1. American army was divided into large flanks and used hit-&-run tatics by Nathaniel Green 2. Green met one of Cornwallis’s flanks at Cowpens 3. British flank was destroyed 4. Cornwallis retreated north 5. Nathaniel caught up with him in North Carolina 6. Was the Battle of Gilford Courthouse 7. Cornwallis ran towards Chesapeake Bay into Yorktown XXIII. Benadict Arnold 1. Benadict persuaded Washington, after Saratoga, to allow him to be commander of key Fort called Westpoint 2. Arnold made deal with British: A. Arnold gets large sum of money B. Became General in British Army C. British get Fort Westpoint 3. Arnold ran to New York & was shipped back to England XXIV. Battle of Yorktown 1. Cornwallis sent message to British to come rescue him 2. French army pulled into bay 3. Cornwallis was firing back at Green 4. Message sent to Washington to come finish Cornwallis 5. Everynight, decoys built fires around New York to fool Clinton into thinking Washington was still there 6. Washington came back to New York to attack Clinton 7. Clinton found out that Cornwallis was captured & retreated back to England 8. This was the end of the war 9. War lasted from 1776-1781 XXV. Extras 1. Thomas Payne called American soldiers “Sunshine Patriots” 2. James Wolfe called American soldiers “Cowardly Dogs” 3. This has ties with Battle of Bunker Hill... Gauge thought Wolfe wa FUN GAMES : http://www.history.org/kids/games/ Creating the Federal Government I. Legislative Branch ( Congress ) - Makes Laws 1. Make Laws 2. Raises money Congress: 3. Declare War I. House of Representatives 4. Raises and supports military a. Number per state is based 5. Approves treaties on population of state 6. May override president’s veto b. 2 year term - no limits 7. Can impeach president II. Senate a. Two per state II. Executive Branch ( President and his Cabinet ) b. 6 year term - no limits (Carries out the Laws) 1. Commander of Armed Forces 2. Carries out laws President and his Cabinet 3. Supervises domestic affairs 4 year term - 2 terms max. 4. Conducts foreign policy 5. Appoints high officials 6. Recommends legislation 7. Veto legislation III. Judicial Branch - Interpret the Laws - life term (Supreme Court, District Courts, and Appellate Courts) 1. Hears appeals involving: 1). The Constitution, 2). Laws of U.S. , 3) Treaties 2. Hears cases involving: 1). A state as a party, 2). High public officials Checks and Balance Legislative Branch 1. Has power over the Executive Branch by overriding President’s veto with 2/3 majority vote. 2. Has power over the Judicial Branch by approving the President’s appointments. Executive Branch 1. Has power over Legislative Branch by his veto 2. Has power over Judicial Branch by appointing Justices Judicial Branch 1. Has power over both branches by its ability to declare laws unconstitutional Articles of Confederation Quick review video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KsasRqBW0_A 1. Put into writing the powers of the Continental Congress 2. The states gave the new federal government very little power 3. Powers given to the Federal Government under the Articles of Confederation: a. Conduct foreign affairs b. Maintain armed forces c. Borrow money d. Issue currency 4. Under the Articles - the New Government could not: a. Levy taxes b. Regulate trade c. Force soldiers into the Army 5. Under the Articles of Confederation, there was no President. Land Ordinance of 1785 1. Provided a way to sell the land cheap in the Ohio Valley. Land Ordinance of 1787 ( Northwest Ordinance ) Provisions: 1. Divided the Northwest into units called Territories. 2. Congress appointed a governor and three judges to each territory 3. When the population of the territory reached 5,000 - they could elect a governor and govern their own affairs. 4. When the population of the territory reached 60,000 - they could draft a constitution. 5. If the constitution was approved by congress (democratic), then the territory would become a state equal to all other states. 6. The state could then elect representatives and 2 senators to go to congress. Trevett vs. Weeden 1. Rhode Island printed paper money - it did not have gold to back up the currency. 2. Weeden was a butcher. Trevett owed him money. Trevett tried to pay Mr. Weeden with this new paper money that was printed by the State of Rhode Island. 3. Weeden refused to accept the money as payment 4. There was a law that said Weeden would be fined or jailed for not taking the paper money. 5. Weeden sued in the state of Rhode Island. (He did not feel that the law was fair) 6. The case went to the U.S. Supreme Court. 7. The Rhode Island law was declared unconstitutional and thrown out. 8. This was the first law ever declared unconstitutional by the U.S. Supreme Court. Shay’s Rebellion 1. The state of Massachusetts was in debt. 2. They raised taxes to pay off their debts. 3. Many poor farmers could not afford the taxes. 4. The state of Massachusetts took their property (farms) and auctioned them off for the taxes. 5. A group of protestors was led by Daniel Shays. 6. The rebellion was finally stopped and Shays fled to Vermont. Amendments: 1. 13 th Amendment - freed the slaves 2. 14 th Amendment - made blacks citizens 3. 15 th Amendment - gave blacks the right to vote 4. 19 th Amendment 5. 26 - gave women the right to vote th Amendment - changed the voting age from 21 to 18 The Great Compromise: 1. The argument is based on how representatives to congress should be elected. A. Each state should get an equal number of representatives B. The number of representatives should be based on the population of the state 2. The final settlement was to do both - Congress was split into two houses: A. The House of Representatives - based on population B. The Senate - based on every state being equal Three-fifths Compromise: 1. The southern states wanted to count slaves as part of the population. 2. That would increase the number of representatives from the South. 3. The Northern states objected because slaves were not allowed to be citizens. 4. The compromise was that five slaves would count as three people in the population count. 5. This would qualify the southern states for more representatives in Congress. Federalists Papers: 1. A series of newspaper articles explaining and defending the United States Constitution The United States Government I. Establishing Precedents: p. 258 1. Precedent - a guide for later action 2. Congress departments: (departments started by our new government for the first time) a. State department b. War department c. Treasury department 3. Thomas Jefferson was first Secretary of State 4. Alexander Hamilton was the first Secretary of Treasury 5. Henry Knox was the first Secretary of War 6. Edmund Randolph was made Attorney General by George Washington as a legal advisor. II. Bill of Rights : p. 259 1. First ten amendments to the Constitution are called The Bill of Rights. 2. Citizens in America have two kinds of rights: a. Natural (human) rights b. Legal rights III. Hamilton and the National Debt: p. 259 1. The Tariff Act of 1789 placed a 5% import tax on all foreign goods entering America 2. Bonds of the U.S. were sold 3. Hamilton was arrogant and not many people liked him 4. Bonds were issued during the war 5. Hamilton was placed in charge of paying off the bonds 6. Spectators are investors buying bonds from poor people in hope of doubling their money. 7. The Elastic clause stretches the power of congress. IV. The French Revolution p. 264, 267 1. The French Revolution was held in 1789 2. American Revolution helped cause the French Revolution 3. French & English began war in 1793. 4. Americans signed a Treaty of Alliance in 1789 with France 5. France was in war with England during this time. 6. French Radicals executed King Louis XVI. 7. France sent Edmond Gente to seek help in America 8. We signed a Neutrality Proclamation (we refused to help France) V. Indian Confederacy : p. 263 1. 92 tribes joined together to fight Americans 2. Little turtle attacked and destroyed two armies 3. Little turtle did not attack Mad Anthony Wayne 4. Replaced by blue jacket 5. Blue jacket attacked and was destroyed by Wayne in the Battle of Falling Timbers 6. Signed treaty of Greenville VI . Jay’s Treaty: p. 264-5 1. Provisions of Jay’s Treaty A. The good Part. 1. English withdraw troops from America. 2. Americans could trade with English Colonies in America. 3. English paid damages to the ship who’s vessels were Illegally seized in the West Indies. B. The Bad part. 1. Refused to stop attacking American ships. 2. Wouldn’t allow American ships to trade with the British 3. Rejected the American view of trading rights of neutral nations during War time. 4. Wouldn’t pay for slaves who fled to English lines during the war. 2. Right of Deposit: the right for people in the Ohio valley to transfer their farm products form river craft to ocean going vessels in New Orleans VII. Pinckney’s’s Treaty P. 265 1. Gave Americans in the Ohio valley a tax free Right of Deposit in New Orleans. 2. Gave America free navigation rights on the Mississippi River 3. Fixed the Southern boundary of the US at 31 degrees N. Latitude VIII. Political Parties: p. 267 1. Federalists party candidates: A. President-----------------John Adams B. Vice Pres.----------------Charles Pinckney 2. Democratic-Republican Party candidates: A. President-------------------Thomas Jefferson B. Vice Pres.------------------Aaron Burr IX. XYZ Affair p. 270 1. Three (3) Americans visited France to get them to stop attacking our ships. 2. Because of the XYZ Affair, the army rose from 3,500 to 10,000. X. Alien and Sedition Acts: p. 271 1. Alien Acts: A. Increased from 5 to 14 years the length of time foreigners had to live in the United States before they could become a citizen. B. Gave the president power to jail or order out of the country, foreigners who he thought were dangerous to the “peace and safety of the U.S.” 2. Sedition Acts: A. Outlaws conspiracies against the Government and attempts to start riots or uprisings.’ B. Made it a crime for anyone to “write, print, or publish even merely scandalous statements critical of the government, of either house of congress, of the President.” This was an attempt to frighten Democratic/Republicans into silence XI. Vocabulary: 1. Bill of rights – the first 10 amendments to the Constitution of the United States. 2. Tariff Act of 1789 – first tax law passed in America 3. Speculators – rich investors that bought war bonds from the poor to make money. 4. Elastic Clause – stretches the power of Congress. “Necessary and Proper Clause” 5. Privateers – privately owned American warships 6. Confederacy – a group joined together for a cause 7. Right of Deposit – Americas right to transfer goods from river craft to ocean going vessels in another country’s seaport. 8. Neutrality - remaining neutral - not on either side - not taking sides - staying out of it. 9. Factions – political parties 10. Federalists – members of Congress who favored Hamilton’s financial plan for America. 11. Reactionary – one opposed to political or social change 12. Picaroons – French privateers 13. Frigates – powerful warships 14. “Unity and home - neutrality abroad” – Washington’s foreign policy War and Peace I. America declared war on England p. 292-3 1. People from the northeast opposed this war. 2. People from the west and south favored war - (they were called war hawks) II. Trouble on the Frontier p. 293 1. War hawks blamed the British for their troubles with the Indians. 2. They believed that if war broke out, the Indians would side with the British. 3. William Henry Harrison, governor of the Indian Territory, considered Indians as "Wretch savages" and drove them off their land. 4. Americans wanted the Indians to adopt our way of life. III. Tecumseh and the Prophet p. 293-4 1. Tecumseh, a Shawnee Indian chief, was against the sale of land. 2. He believed that land was for all people to use for homes and from which to gather food. 3. Harrison signed a treaty with a number of chiefs in 1809 in which he bought three million acres of land for $10,000. 4. Tecumseh was furious and threatened that if Harrison did not give the land back that he would organize the Indians into a Confederacy and side with the British if war should break out between the United States and England. 5. He did this and called the Indian Confederacy the Red Stick Confederacy. 6. Tecumseh's brother was called the "Prophet." 7. Harrison organized an army and marched over to Prophet Town - the headquarters of the Red Sticks. 8. The Prophet ordered an attack on Harrison. 9. This was called The Battle of Tippecanoe. 10. Harrison destroyed their town and became a hero. IV. The War of 1812 p. 296 Short Voting Game: http://home.nps.gov/fomc/castyourvote/explore.cfm 1. Congress declared war on England in June of 1812. 2. Reasons: a. Impressment of Americans into the British Navy b. British attacks on American ships V. The War at Sea p. 297 1. The first battles in the War of 1812 occurred at sea. 2. America had seven frigates. 3. Names of these ships included: a. "President" b. "Constitution" c. "Constellation" d. "United States" e. "Chesapeake" 4. The British fleet consisted of: a. 7 Ships - of - the - Line b. 34 Frigates c. Dozens of smaller ships 5. Maneuvers like "Crossing the T" were used. 6. The "Constitution" was nicknamed Old Ironsides. 7. American ships were very successful. VI. The Fight for Canada p. 296-7 1. Indians under command of Tecumseh caused the Americans to retreat to Detroit. 2. In 1813, William Henry Harrison took command of the army for Americans. 3. Before he could invade Canada, a fleet of British ships had to be cleared from Lake Erie. 4. Oliver Hazard Perry was given this job. 5. He built a fleet of ships right on the bank of Lake Erie. 6. Perry engaged the British fleet in September of 1813 in the Battle of Put-in-Bay where he defeated the British. 7. Harrison was then able to capture Detroit and advance into Canada. 8. In The Battle of the Thames America won back the Great Lakes Region for the United States. 9. The most significant results of the battle was the death of Tecumseh. VII. The Creek War p. 297 1. Indians in the South were also defeated. 2. The Creek Indians began attacking southern frontier outpost with the support of some British and Spanish agents. (1813) 3. Red Eagle, Chief of the Creek Indians, defeated the defenders of Fort Mims killing between 400-500 Americans including many women and children. 4. Andrew Jackson, with a force of Tennessee militiamen, marched into Creek country. 5. In a series of battles, Jackson smashed the Creek forces. 6. The last battle was the Battle of Horseshoe Bend in Alabama. 7. Jackson killed over 700 Indians losing only 26 of his men. 8. The Creeks surrendered 20 million acres to the Americans. VIII. The Burning of Washington p. 299 1. The British sent 14,000 troops to America. 2. They set out to destroy Washington. 3. The gunboats that Jefferson built fled when a fleet of British war ships entered the harbor at Washington. 4. British Troops were put ashore a few miles south of the city. 5. At Bladensburg, General Ross' troops attacked and the Americans fled in panic. 6. August 24, they marched into Washington and set fire to the city. 7. The Capitol was burned to the ground. IX. The Defense of Baltimore p. 299 1. The British attacked Fort McHenry which guarded the entrance to Baltimore harbor. 2. This assault was unsuccessful. 3. After a day and night firing on the fort, the American flag still flew. 4. The British could not get past the fort to the city of Baltimore. X. The Battle of New Orleans p. 299-300 SONG: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=50_iRIcxsz0&feature=kp 1. The British were planning a greater attack. 2. In 1814 the British gathered 11,000 veteran soldiers and a fleet of 60 ships to attack New Orleans. 3. The Redcoats landed east of the mouth of the Mississippi River and marched through the swampy country without being discovered until they were within 7 miles of the city. 4. Andrew Jackson was in command of the Americans in New Orleans. 5. As soon as Jackson received word that the British were near, he ordered an attack immediately ---- that night. 6. The battle began at 7:30 p.m. 7. Jackson was forced to retreat to a canal only 5 miles from the city. 8. The British delayed the attack, giving Jackson time to fortify his position. 9. The British finally attacked on January 8, 1815. 10. The British were mowed down by a hail of iron and lead when they walked into Jackson's trap. 11. The British suffered 2,000 casualties in an hour. 12. Only 71 Americans were killed. 13. The Battle of New Orleans restored American morale. 14. This battle took place after the war was officially ended. XI. The Peace of Ghent p. 299 1. After the Battle of New Orleans the British signed the Peace of Ghent. 2. Terms of the treaty: a. No land changed hands b. Peace was restored c. No promises were made d. (basically all that happened was they agreed to stop fighting.) 3. Federalists leaders in New England, who had opposed the war, met in 1814 to consider seceding from the union. This was called the Hartford Convention. 4. When the war ended, their plans fell through. XII. Solving Problems with England p. 322 1. The War of 1812 convinced England that the United States was here to stay. 2. The Rush-Bagot Agreement settled up with England. Its provisions were: a. Neither country would maintain a fleet of warships on the Great Lakes b. Each country could have four small vessels on the lakes to act as police force c. The border between the United States and Canada would remain forever unfortified. (1). A special commission decided the exact boundary between the United States and Canada (a). Northern boundary: fixed at 49 degrees North Latitude (b). Also, joint control of the Oregon Country was to be shared between the United States and Canada XIII. Jackson's Invasion of Florida p. 322-3 1. Florida remained in the hands of the Spanish at the end of the War of 1812. 2. Seminole Indians, reinforced by Creek Indians from Alabama, were raiding American settlers in Georgia and South Carolina. 3. Slaves were running away into Florida to the Negro Fort. 4. In 1816 an American force marched into Florida and "blew up" the Negro Fort. 5. In 1818, General Andrew Jackson was sent to crush the Seminoles. 6. The Seminoles fell back into Florida to escape the battle. 7. Jackson followed them into Florida anyway. 8. Jackson believed the Indian conflicts were caused by foreign agents. 9. Jackson captured two British agents, put them on trial, found them guilty, and hanged them. 10. He also hanged two Indian chiefs. 11. Since Jackson could not find anyone else to fight, he returned through Pensacola - the capitol of Florida and captured it for America. 12. Jackson then wrote a letter to President Monroe telling him what he had done - and then he went home to Tennessee. XIV. The Transcontinental Treaty p. 323 1. Because of Jackson's invasion of Florida, Luis de Onis, the Spanish minister to the United States, bitterly protested. 2. President Monroe, however, did NOT want to give Florida back. 3. Monroe said Jackson had invaded Spanish land because of "Military Necessity." 4. Onis knew then that the United States did not intend to give Florida back. 5. Since Luis de Onis had already been negotiating with John Q. Adams over the boundary between the Louisiana Purchase and Spanish Mexico, he decided that he may get a better settlement on that boundary if he gave up Florida. 6. The U.S. said the boundary should be placed at the Rio-Grande river, which would give the U.S. Texas as part of the Louisiana Purchase. (We are cheating) 7 The final settlement was: a. Spain could keep Texas b. The U.S. boundary north of Texas would extend all the way to the Pacific at approximately 42 degrees North Latitude. c. The U.S. got Florida (paid 5 million for East Florida - took West Florida.) 8. The Transcontinental Treaty gave the United States a boundary from "Sea to Shining Sea." XV. Revolutions in Latin America p. 324 1. Spain's weakness caused them to give up Florida and part of the Southwest to the United States. 2. By 1822, all of Spain's colonies in South and Central America had revolted and declared their independence. XVI. The Monroe Doctrine p. 324 1. The U.S. would not interfere with any existing European colony in North or South America. 2. No more colonies could be founded in the Americas. 3. Any attempt to create a new colony in considered dangerous to the U.S.'s peace and safety. 4. The U.S. might be willing to go to war to prevent any new colonies from being formed. 5. The U.S. would not become involved in purely European affairs. Manifest Destiny U.S Expansion Interactive Map Quiz: http://www.eduplace.com/kids/socsci/books/applications/imaps /maps/g5s_u5/ I. Texas 1. Moses Austin discovered Texas 2. He got permission from Mexico to move into Texas with 300 families. 3. Moses died so his son Stephen moved into Texas instead. 4. Many families eventually moved into Texas. 5. Since Texas belonged to Mexico, they controlled how many people they let settle there. 6. Mexico became concerned that to many Americans were moving onto their land, so they came in, took over the land, and would not allow any more people to come there. 7. The Texans were forced to obey Mexican law and authority. 8. They finally revolted against the Mexican authority. 9. A Mexican army led by General Santa Anna came into Texas to bring them under control. 10. When the Mexican army approached San Antonio, the Texans held up in the “Alamo” Alamo Song: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3amU4FqKCqw 11. The Mexican army tried to get them out of the Alamo for 10 days. 12. Davey Crocket and Jim Bowie were among the Texans in the Alamo. 13. When the Mexican army finally got in, they killed everyone inside. 14. The Texans formed an army- which was led by Sam Houston. 15. Houston avoided battles for several weeks until they were ready. 16. Sam Houston led the Texans in a surprise attack against the Mexican army. 17. “Remember that Alamo” was their battle cry. 18. The Texans demanded the state of Texas from the Mexicans or threatened to kill them. 19. The Mexicans gave up the territory and Texas became an independent nation. 20. After they became free, the Texans applied to the United States for Statehood. 21. They needed protection from the Mexican army should they return and try to take Texas back. 22. Andrew Jackson, President of the U.S., rejected Texas’ application for statehood. 23. Texas applied as a slave state. 24. Finally Polk was elected. He promised to bring in Texas and the Oregon Country. 25. In December of 1845, Texas was admitted as a state. 26. The Oregon Country was brought into the U.S. in 1846. II. War with Mexico 1. War was to determine the boundary of Texas. 2. General Zachary Taylor was sent with an army to guard the border of the U.S.A. at the Rio Grande River. 3. American and Mexican armies met at the Rio Grande. 4. The Mexican patrol attacked the American Patrol. 5. General Taylor beat three major Mexican armies. 6. The last of these battles was called the Battle of Buena Vista. 7. President Polk sent General Winfield Scott to attack Mexico City- Mexico’s capitol. 8. General Scott easily captured Mexico’s capitol. 9. Nicholas P. Trist negotiated with the Mexicans. 10. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ended the war with Mexico. III. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo 1. Trist was authorized to spend up to $30 million dollars for California and the rest of the southwest. 2. Trist proved to be an excellent negotiator. 3. He persuaded the Mexicans to sell all the territory for $18 million. 4. President Polk became greedy and ordered Trist not to sign a treaty with the Mexicans. 5. President Polk ordered Trist to return to Washington immediately. 6. Trist ignored the order and completed negotiations with Mexico. 7. This resulted in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo being signed and sent back to the United States. 8. Polk was furious. He fired Trist and refused to pay him for his work, however the treaty was binding and Polk had to honor it. 9. Provisions: (1). Bought California and Southwest for $18 million. (2). Placed the southern border of Texas at the Rio Grande River. IV. The Mormons of Utah 1. The Mormons were organized by Joseph Smith. 2. Smith claimed that an angel named Moroni gave him golden tablets on which was written the “Book of Mormons.” 3. This book became the basis of the Mormon Church. 4. The Mormons adopted religious practices that were different and set them apart. 5. Polygamy- one of their practices- allowed a man to have more than one wife at a time. 6. The Mormons organized a private army. 7. Opposition to the Mormons finally led to Smith’s arrest. 8. He was dragged from jail and lynched. 9. Brigham Young became their leader. 10. He eventually led the Mormons to Utah to avoid any further persecution. 11. They settled at Salt Lake City, Utah. 12. Their trail to Utah became known as the Mormon Trail. V. Gold in California 1. John Sutter was granted a huge amount of land in California before the Americans took it from Mexico. 2. Sutter hired James Marshall to build a saw mill on this land. 3. Marshall found gold on Sutter’s ranch while trying to install the water wheel to the mill. 4. Word quickly spread that there was gold in California. 5. Thousands of people began to rush to California. 6. Only a few found any gold. 7. However, because of the 1849 Gold Rush, California’s population reached the 60,000 mark long before most other wester territories. 8. In 1850 California applied for statehood. 9. This created a problem because California applied to join the U.S. as a free state. VI. Controversy over new additions to America 1. There were two additions that caused particular problems: 1). Missouri 2). California Missouri: 1. Missouri applied to join the United States as a slave state in 1820. 2. At that time there were 11 slave states and 11 free states. 3. Missouri would upset the balance- (especially in the Senate) 4. Missouri could not get a majority vote in the Senate to approve its newly written constitution, so therefore could not be admitted as a state. 5. This was worked out in the Missouri Compromise of 1820. 6. Provisions: (1). Missouri could come in as a slave state (2). Maine was created and could come in as a free state. (3). Divide the rest of the Louisiana Territory into free and slave territories at 36 degrees 30 minutes North latitude. 7. This compromise would keep the balance of Senators even in Washington. California 1. California applied to join the United States as a free state in 1850. 2. This would upset the balance of Senators in Washington. 3. The Compromise of 1850 allowed California to enter the union as a state. 4. The Compromise was worked out by Henry Clay. 5. Provisions: (1). California could enter as a free state. (2). The rest of the former Mexican lands were organized into two large territories, Utah and New Mexico, without mention of slavery. (3). Texas was given 10 million dollars to pay off its debts. (4). Slave trade in Washington, D.C. was abolished. (5). A new Fugitive Slave Law was passed. 1) Officials in the North agreed to capture and return run-away slaves to their owners in the South. 2) Southerners could go (or send someone) into the North to capture and return with their escaped slaves.