Trapezoid - forgettingalzheimers
advertisement

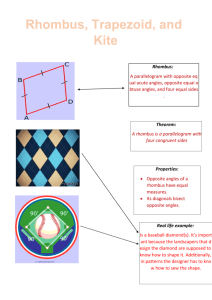
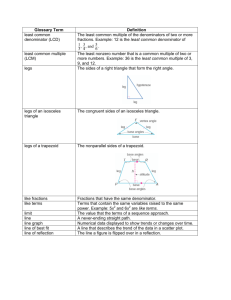
Lizzy Butler Kaitlyn Smeraldo Krisitn Donadio Definitions Trapezoid: quadrilateral that has only two parallel sides Isosceles Trapezoid: A trapezoid in which the non-parallel sides are congruent Scalene Trapezoid: A trapezoid in which the non-parallel sides are not congruent Right Trapezoid: A trapezoid in which one of the non-parallel sides is perpendicular to the two parallel sides (forming two right angles) Sides of trapezoids • The two parallel sides are called bases. • The two non-parallel sides (regardless if congruent) are called legs. •AB and CD are bases A B •AC and BC are legs C D Properties of Isosceles Trapezoids • Angles: – The angles on either side of the bases are congruent – Adjacent angles along the legs are supplementary …Continued Isosceles • Diagonals: – The diagonals are congruent only for isosceles trapezoids …Continued Isosceles • Sides: – The bases are parallel, as in all trapezoids – By definition, the opposite sides are congruent Lines of Symmetry • In an isosceles trapezoid, a line of symmetry can be drawn from the midpoint of Base 1 to the midpoint of Base 2. – Is perpendicular to the midsegment of a trapezoid • There are no lines of symmetry present in a scalene trapezoid and a right trapezoid. – Scalene: all sides are different lengths and therefore cannot be symmetrical on any sides – Right: one side of a trapezoid is straight and the other is on a diagonal, so a symmetrical line can not be constructed Coordinate Geometry • The Bases will exhibit the same slope • Legs – Isosceles trapezoid: legs will have same distance (length) – Right trapezoid: one leg will have an undefined slope and the other leg will be an oblique line; distances are different – Scalene trapezoid: both legs will have different slope and distance http://www.mathopen%ref.com/coordtrapezoid.html Coordinate Geometry • If you know the coordinates of the four vertices, you can find different properties of the trapezoid, including area and perimeter. The Median • Joins the midpoints of its legs • Special relationship to bases – Theorem: The median of a trapezoid is parallel to both bases, and its measure is one-half the sum of the measures of the bases (average of bases) • M= ½ (b1 + b2) • Length of median can be used to find the area even if you don’t know the length of the bases http://www.mathopenref.com/trapezoidmedian.html Formulas • Area of Trapezoid – A= ½ h (b1 + b2) – A= Altitude x median – Originates from parallelogram (2 trapezoids, one right side up, one down) • Area of Parallelogram= b x h • Perimeter of Regular Trapezoid – P= a + b1 + c + b2 Trapezoid Crossword Helpful Websites • http://www.mathopenref.com/coordtrapezoid.html • http://www.coolmath.com/reference/trapezoids.html • http://www.cliffsnotes.com/study_guide/Trapezoids.to picArticleId-18851,articleId-18804.html • http://www.mathwarehouse.com/geometry/quadrilate rals/trapezoid.php