Articulation
advertisement

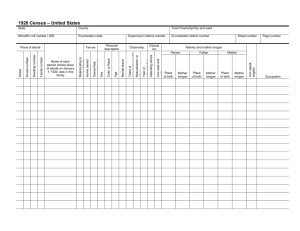
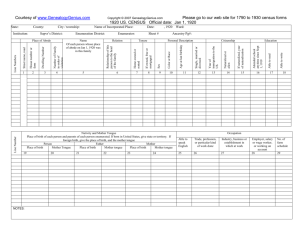
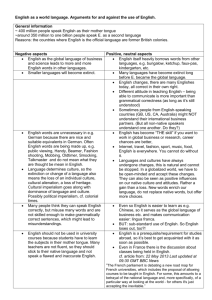
• • • • Lips Teeth Tongue Palate • Hard • Soft • Mandible Zemlin, pg 227. • Adults have 32 teeth • Many only have 28 • Anatomy of a tooth • Crown • Neck • Root Zemlin, pg 240. • • • • Lips Teeth Tongue Palate • Hard • Soft • Mandible Zemlin, pg 227. • “The tongue is without doubt the most important and the most active of the articulators”- Zemlin • Alveolar ridge • Just behind front teeth (top) Zemlin, pg 251. • 2 parts of the tongue • Blade • Root • 4 parts of the tongue • Tip • Blade: Alveolar ridge • Front: Hard palate • Back: Soft palate Zemlin, pg 251. • Intrinsic Muscles • Superior longitudinal: • • • • Most superficial Longitudinal, oblique fibers Course anteriorly from the root Contraction: shorten the tongue, turn tip upward Zemlin, pg 254. • Intrinsic Muscles • Inferior longitudinal: • • • • Muscle fibers on the underside of the tongue Fibers run between genioglossus and hyoglossus fibers Course anteriorly from the root Contraction: shorten the tongue, turn tip downward Zemlin, pg 254. • Intrinsic Muscles • Transverse: • Fibers course laterally • Contraction: narrow tongue, elongate tongue • Vertical: • Course downward (and laterally) throughout the body of the tongue • Contraction: flattens the tongue Hixon, T.J., et al. (2008). Preclinical Speech Science: Anatomy, Physiology, Acoustics, and Perception. • Extrinsic Muscles • Genioglossus: • Forms the bulk of tongue tissue • Strongest/largest extrinsic muscle • Lower fibers: connect to the body of the hyoid • Upper fibers: connect to the root and blade • Contraction: move tongue root forward so tip is against teeth; pull front backward; pull center down Hixon, T.J., et al. (2008). Preclinical Speech Science: Anatomy, Physiology, Acoustics, and Perception. • Extrinsic Muscles • Styloglossus: • Connects the styloid process with the tongue • Contraction: draws tongue up and back; can draw sides of tongue upward Hixon, T.J., et al. (2008). Preclinical Speech Science: Anatomy, Physiology, Acoustics, and Perception. http://antranik.org/geography-of-the-skull/ • Extrinsic Muscles • Hyoglossus: • Connects greater cornua with the posterior tongue • Contraction: retract/depress tongue; elevate hyoid (phonation) Hixon, T.J., et al. (2008). Preclinical Speech Science: Anatomy, Physiology, Acoustics, and Perception. • Extrinsic Muscles • Palatoglossus (glossopalatine): • Connects soft palate with the posterior tongue • Forms anterior faucial pillars • Contraction: lower soft palate; raise back of tongue Hixon, T.J., et al. (2008). Preclinical Speech Science: Anatomy, Physiology, Acoustics, and Perception. • • • • Lips Teeth Tongue Palate • Hard • Soft • Mandible Zemlin, pg 227. • Roof of the mouth/floor of the nasal cavity • Formed by palatine processes of maxilla (upper jaw bone) • Rugae: ridges behind the alveolar ridge • Midline raphe: midline/sulcus in the roof of the mouth Zemlin, pg 264. • Connects to the posterior portion of the palatine processes • 1/3 of the soft palate is connective tissue • 2 major muscles Zemlin, pg 227. • Tensor Veli Palatini (Tensor Palati) • Connects the pterygoid plates at one end, and forms the palatal aponeurosis (connects soft and hard palates; “skeleton” of the soft palate) • Contraction: lowers soft palate; opens Eustachian tube http://www.drjimboyd.com/Masticatory_Musculature04.html Levator Veli Palatini (Lavator Palati) • Bulk of the soft palate • Connects soft palate with petrous bone and Eustachian tube • Contraction: raises soft palate, contacts soft palate and pharyngeal wall (to divide oral and nasal cavities) Zemlin, pg 264. http://imaging.consult.com/image/chapter/Pediatric?title=Temporal%20Bone%20and%20Ear%20%28Pediatric%29&image=fig2&locator=gr2&pii=S1933-0332%2808%2973386-X • Musculus Uvulae (Azygos Uvulae) • Connects soft palate and uvula • Contraction: raise soft palate • Palatoglossus • Contraction: lower soft palate; raise back of tongue • Palatopharyngeous • Posterior faucial pillars • Main function in swallowing Zemlin, pg 264. • • • • Lips Teeth Tongue Palate • Hard • Soft • Mandible Zemlin, pg 227.