Processes and Guidelines in Technical Writing Part (2)

Types of Audiences
Experts
Technicians
Executives
Nonspecialists
Audience Analysis
Audiences, regardless of category, must also be analyzed in terms of characteristics such as the following:
Background-knowledge, experience, training
Needs and interests
Other demographic characteristics
Audience analysis can get complicated by at least two other factors:
More than
Wide variability in an audience one audience
Add information readers need to understand your document.
Omit information your readers do not need.
Change the level of the information you currently have.
Add examples to help readers understand.
Change the level of your examples.
Change the organization of your information.
Strengthen transitions.
Write stronger introductions—both for the whole document and for major sections.
Create topic sentences for paragraphs and paragraph groups.
Change sentence style and length.
Work on sentence clarity and economy.
Use more or different graphics.
Break text up or consolidate text into meaningful, usable chunks.
Add cross-references to important information.
Use headings and lists.
Use special typography, and work with margins, line length, line spacing, type size, and type style.
This section shows you a step-by-step method for: "translating" technical discussions, that is, specific techniques you can use to make difficult technical discussions easier for nonspecialist readers to understand.
The audience of the report and its background
The needs or uses the audience has for the report
The event, circumstance, or situation that requires the report to be written
Help to decide:
What information to include in the report
What information to exclude from the report
How to discuss the information you do include in the report
Definitions of unfamiliar terms
Comparisons to familiar things
Elaborating the process
Providing descriptive detail
Providing illustrations
Providing examples and applications
Shorter sentences
a) b) c)
Stronger transitions and overviews
Repetition of key words
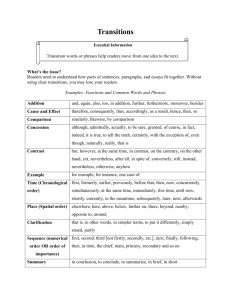
Transition words and phrases.
Reviews of topics covered and topics to be covered
The "in-other-words" technique
Posing rhetorical questions
Explaining the importance
Providing historical background
Reviewing theoretical background
Providing the human perspective
Combining the translating techniques
SEE the attatched Word file and
REFER to the book when writing the report.