Second law of motion
advertisement

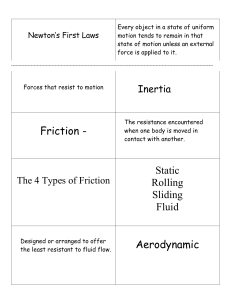
Newton’s Laws of Motion NOTE TAKING WORKSHEET Section 1: Motion • • A. Motion is a change in POSITION __________________. 1. ______________ - the entire path an object travels. DISTANCE 2. The distance and direction between starting and stopping positions is _________________________. DISPLACEMENT • • 3. _____________ motion - an object’s position change is described in terms of a RELATIVE reference point. • B. SPEED ______________ - distance traveled divided by the time needed to travel the distance, or speed = distance/time • 1. ___________________________ - speed is the same at any given moment in CONSTANT SPEED time. INSTANTANEOUS • 2. Speed at a particular instant in time is ________________________ speed. Section 1: Motion • C.VELOCITY __________________ - displacement divided by time, or v = displacement/time. • AVERAGE 1. Formula calculates ___________________ velocity. • 2. Includes concept ofDIRECTION ___________________ as well as speed. • • • D. Change in velocity divided by the time required for the change to occur is ACCELERATION _____________________________. SLOWS DOWN 1. Acceleration occurs when an object _____________________ as well as speeds up. SPEED • 2. For an object traveling in a straight line, a change in _____________ can be used to calculate acceleration. TIME • • a. Acceleration is final speed minus initial speed divided by __________, or acceleration = (final speed - initial speed) • TURNING ZERO time Section 2: Newton’s First Law • • A. Laws of MOTION __________________ are sets of rules first stated by Isaac Newton. 1.FORCE ____________ - a push or pull with a size and direction. CONTACT LONG-RANGE • 2. ____________ force involves objects touching each other. • 3. ________________ forces include gravity, magnetism, and electricity. • 4. When scientists measure force, they use the _______________, abbreviated N. • B. _____________ law of motion - an object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant speed unless a force acts on it. NEWTON FIRST INERTIA MASS • • 1. _______________ measures an object’s tendency to remain at rest or keep moving. 2. Inertia is related to ____________; objects with more mass have more inertia. Section 2: Newton’s First Law MORE THAN one force acts on an object. C. Adding forces - sometimes __________________ BALANCED 1. __________________ forces - forces that are equal but in opposite directions, canceling each other. 2. If one force is greater than another, a change in motion will result from the UNBALANCED __________________________ forces. VELOCITY 3. An object acted on by an unbalanced force changes __________________. Section 3: Newton’s Second Law A. Second law of motion - an object acted on by an unbalanced force will ACCELERATE ____________________ in the direction of the force. 1. Acceleration equals force divided by mass or a = force/mass NET force that acts on 2. Force is equal to the combination of all forces, or the __________ an object. B. Second law can also be used to find ______________ if mass and acceleration are FORCE known. 1. Near Earth’s surface, the force of gravity causes all objects to fall with the same __________________________ 9.8 m/s2 ACCELERATION EQUALS mass times a. For any object that is falling, the force of gravity ____________ acceleration due to gravity, or F = m x (9.8 m/s2 ) b. Because weight is the force of gravity on an object, an object’s weight EQUALS ________ mass times acceleration due to gravity, or weight = m x (9.8 m/s2 ) 2. Weight and mass are not the same thing. a. Weight changes when the acceleration due to ______________ GRAVITY changes. b. Mass remains the ____________ SAME no matter what weight is. Section 3: Newton’s Second Law FRICTION C. _________________ - a force that resists motion and is always present between two moving surfaces. STATIC 1. _____________ friction - keeps a stationary object from moving on a surface when a force is applied to the object. 2. _____________ SLIDING friction - occurs when two surfaces slide past each other; slows down the moving object. 3. _____________ ROLLING friction - friction between a surface and a wheel when the wheel rolls over the surface. 4. Air ___________________ RESISTANCE - typical action of air molecules on a forward-moving object, slowing its motion. Section 4: Newton’s Third Law FORCES A. Third law of motion - _______________ always act in equal but opposite pairs. SAME amount of 1. When a force is exerted on an object, the object exerts the _________ force. LONG-RANGE 2. Third law of motion applies whether forces are contact or _________________. ALL B. Things move because action and reaction forces work on _________________ objects. 1. Friction is a factor in the third law. 2. Using the second law equation, the object with the larger mass has the smaller _________________________ if the same force is applied. ACCELERATION MASS 3. All objects in the universe exert a force on all others; however, differences in _______ may make these forces unnoticeable. FORCES act on it. C. The three laws of motion describe how any object moves when ____________ Overview Newton’s Laws of Motion 1. If you walk from your house to your friend’s house, the distance and direction between your house and your friend’s house is your _________________________ DISPLACEMENT 2. The distance traveled divided by the time needed to travel the distance is ______________________________ SPEED 3. Displacement divided by time is ____________________________ VELOCITY BALANCED 4. Forces that cancel each other out are _____________________________ According to NEWTON’S FIRST ___________ 5. law of motion an object in motion will stay in motion until a FORCE 6. ____________ acts upon it NEWTON’S NEWTON’S 7. ____________ SECOND law of motion THIRD 9. ____________ law of motion an object forces always act in 8. acted upon by a FORCE ____________ 10. EQUAL ______________ but opposite pairs will accelerate in the direction of that force