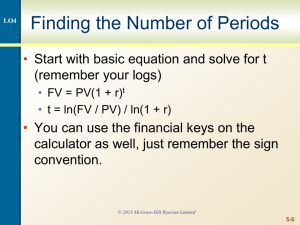
8s-1
The Transportation Model
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8s-2
The Transportation Model
Chapter 8 Supplement
The
Transportation Model
Available on Student CD-ROM and
Online Learning Centre
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8s-3
The Transportation Model
Requirements for Transportation Model
• List of origins and each one’s capacity
• List of destinations and each one’s
demand
• Unit cost of shipping
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8s-4
The Transportation Model
Transportation Model Assumptions
• Items to be shipped are homogeneous
• Shipping cost per unit is the same
• Only one route between origin and
destination
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8s-5
The Transportation Model
The Transportation Problem
Figure 8S-1
D
(demand)
S
(supply)
S
(supply)
D
(demand)
D
(demand)
S
(supply)
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
D
(demand)
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8s-6
The Transportation Model
A Transportation Table
Table 8S-1
A
Factory
Warehouse
C
B
4
D
7
7
1
100
1
3
12
8
8
200
2
10
8
16
5
150
3
Demand
80
90
120
Warehouse B can use 90
units per period
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Factory 1
can
supply
100
units per
period
160
Total
supply
450 capacity
per
450
period
Total demand
per period
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8s-7
The Transportation Model
Special Problems
• Unequal supply and demand
• Dummy: Imaginary number added equal
to the difference between supply and
demand when these are unequal
• Degeneracy: The condition of too few
completed cells to allow all necessary
paths to be constructed
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8s-8
The Transportation Model
Summary of Procedure
• Make certain that supply and demand
are equal
• Develop an initial solution using
intuitive, low-cost approach
• Check that completed cells = R+C-1
• Evaluate each empty cell
• Repeat until all cells are zero or
positive
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8s-9
The Transportation Model
Excel Template
Figure 8S-2
McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Operations Management, 2nd Canadian Edition, by Stevenson & Hojati
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.