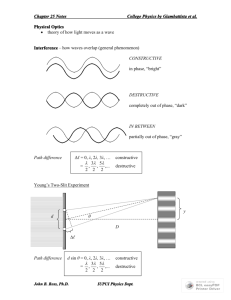
Diffraction
advertisement

http://www.launc.tased.edu.au/online/sciences/physics/diffrac.html What is the difference between interference & diffraction? Interference involves the superposition of waves of (the same / two different) wave fronts, in diffraction there is a superposition of waves from (the same part / different part )of the same wave front. Diffraction of Light http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/lightandcolor/diffractionintro.html Aperture: Slit, circular and square http://www.falstad.com/diffraction/index.html Aperture: Slit, circular and square http://www.falstad.com/diffractio n/index.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/diffraction/particlesize/index.html Diffraction of Light http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/diffraction/basicdiffraction/index.html http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/phyopt/diffracon.html Central Maximum Normal incidence The secondary sources on the wavefront between the edges of the barrier sending waves arriving at the central point are in phase. First Maximum First maximum The slit is divided into 3 equal parts and the wavelets from the strips in two adjacent parts cancel, leaving only wavelets from one part to give a much less bright band. First Minimum 2CD=/2 or BE= At a particular direction , CD=/2 or BE=. A and C and C and B are out of phase. The points just below A and points just below C are also out of phase. Consecutively, pairs of points are out of phase also. It gives destructive interference. Hence By similar pairing process, other minima occur when , where n = 1, 2, 3….. The maxima occur roughly half-way between the minima at angles such that sin = 3/2a, 5/2a …… a sin CD sin 2 2 a n sin n a Diffraction Grating http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/phyopt/grating.html#c1 http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/phyopt/gratcal.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/diffraction/diffractionorders/index.html Line Spacing Calculations from Diffraction Gratings http://www.ppo.ca/gratings.htm Transmission grating Reflection grating For the 1st order Max What is the path difference between the 1st slit and 2nd slit? What is the path difference between the 1st slit and 3rd slit? 2 Max at: a sin 2a sin 2 Angular width of the first maximum Intensity Angular position ’ Angular width = 2(’ - ) Angular width of the first maximum Consider 8 slits, for example Max at: (1) (2) (3) a sin 4a sin 4 (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) Min at: 1 4a sin ' (4 ) 2 angular width ' Pairwise cancellation : 1-5, 2-6, 3-7, 4-8 Angular width of the first maximum Intensity Angular position ’ Angular width = 2(’ - ) Explanation of the grating equation d=a+b grating The path difference between the wavelets is d sin , as it is for all pairs of wavelets from other corresponding points in these 2 slits and in all pairs of slits in the grating. d sin m m 0, 1, 2, 3......... http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/imageformation/gratingdiffraction/index.html http://lectureonline.cl.msu.edu/~mmp/kap27/Gary-Diffraction/app.htm http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~teb/optics/java/slitdiffr/ http://www.schulphysik.de/suren/Applets.html Example 1 Example 2 Diffraction of electrons …… http://phys.educ.ksu.edu/vqm/html/doubleslit/ http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/imageformation/airydiskbasics/index.html END http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/search/index.asp