EM2potE - The Evergreen State College
advertisement

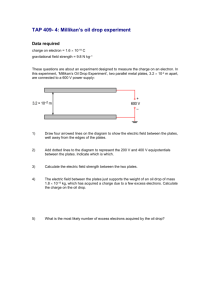
Methods of Math. Physics Dr. E.J. Zita, The Evergreen State College Lab II Rm 2272, zita@evergreen.edu Winter wk 4, Thursday 27 Jan. 2011 • Griffiths Ch.2: Fields & Potentials • Use Gauss’ Law in symmetric geometries • Boundary conditions • Energy stored in charge distributions • Conductors and capacitors E field due to infinite sheet of charge +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ uniform surface charge density s = q/area s E field due to (infinite) Parallel Plates ++++++++++++++++++ ------------------- s = dq/dA -s Parallel plates Conservative fields admit potentials E dl = 0 V = - E dl E = 0 b Therefore depends only on endpoints. a • Easy to find E from V • V is independent of choice of reference point V=0 • V is uniquely determined by boundary conditions • Every central force (curl F = 0) is conservative (prob 2.25) • Ex.2.5 p.74: parallel plates Potential between Parallel plates ++++++++++++++++++ ------------------- s = dq/dA -s Draw the direction of the Electric field Describe the potential (difference) E = -V V = - E dl Units of potential E = -V V = - E dl Capacitance is geometric • Capacitance = Q/V = the amount of charge that can be stored by a given potential DIFFERENCE • C depends on the geometry of the system (and on the dielectric between the plates) Parallel plate capacitor Prob. 2.40 p.106: Energy between parallel plates Ex. 2.10 p.104: Find the capacitance between two metal plates of surface area A held a distance d apart. Electrostatic boundary conditions: • E is discontinuous across a charge layer: DE = s/e0 • E|| and V are continuous • Prob 2.30 (a) p.90: check BC for parallel plates Electrostatic potential energy Shall we do a cylindrically symmetric problem? (Coax cable: 2.16 p.75, 2.24 p.82) charges ↔ electric fields ↔ potentials Properties of conductors: (in electrostatics) • • • • • E=0 inside a conductor r=0 inside a conductor Any net charge will be found on the surface A conductor is an equipotential E is perpendicular to the surface, just outside the conductor Coming up next – Modern physics H atom in wave mechanics