Minimal invasive dentistry
advertisement

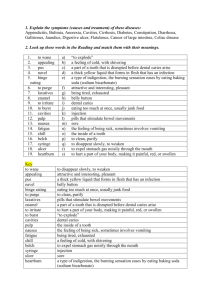
Good morning MINIMAL INVASIVE DENTISTRY Submitted by :Shyni kunhikrishnan Guided by :Mahmood moothedath Aseela ahmed INDEX • • • • • • • Introduction History Definition Principles Concepts Techniques MID in cosmetic dentistry • • Benefits of MID Conclusion INTRODUCTION • MID is focusing mostly on cariology and restorative dentistry • The goal is to conserve healthy tooth structure • Focused on remineralisation and minimal dentist intervention using scientific advances • Uses long lasting dental materials that conserve maximum tooth structure so need for future repair is reduced • One of the major tenets of MID is caries management by risk assessment(CAMBRA) HISTORY • • • • • • Historical development in dentistry Extraction Surgical approach(drilling and filling):after G. V black Highly formalized cavity design ‘Extension for prevention’ Based on limited knowledge about pathology and with limited available material MID medical approach “The day is surely coming, and perhaps within the lifetime of you young men before me, when we will be engaged in practicing preventive, rather than reparative, dentistry. ” - GV Black in 1896 MINIMAL INTERVENTION DENTISTRY • Defined as a philosophy of professional caries concerned with first occurrence, earliest detection and earliest possible cure of disease on micro levels followed by minimal invasive and patient friendly treatment inorder to repair irreversible damage caused by such disease • Includes many non surgical modalities • Key concept is that caries is treated as infectious disease PRINCIPLES Principles of MID are: • Accurate caries diagnosis • Classification of severity of caries • Assessment of individual caries risk • Reduces cariogenicity of bacteria • Uses preventive mineralisation • Early lesion remineralisation • Minimal surgeries on cavities Accurate caries diagnosis Implies whether a lesion is active, progressing rapidly or slowly or whether is already arrested - CONVENTIONAL METHOD OF CARIES DETECTION • • • • • Visual-tactile method Radiography Caries detecting dyes Fibre optic transillumination Electronic caries monitor Visual method • Detection of white spot,discolouration/frank cavitation • Magnification loupes-head worn prism loupes or surgical microscopes can be used • Use of temporary elective separation Tactile method • Explorers • Dental floss Radiography • Carious lesion are detectable radiographically when there has enough demineralization to allow it to differentiate from normal • Valuable in detecting proximal caries • Radiographic examination include: - bitewing radiograph - IOPA - dental panoramic radiograph Xeroradiography • Similar to photocopy machine • Consist of aluminium plate coated with selenium which provides an uniform electrostatic charge • Very good edge enhancement Digital imaging • Image formed and represented by a spatially distributed set of descrete sensors • Image is formed in computer Subtraction radiography • Structured noise is reduced in order to increase the detectability of changes on radiograph • Structured noise refers to the information on the radiograph which have not diagnostic value • Contrast can be enhanced with colour aid Computer image analysis • Software have been developed for automated procedures which are able to overcome the short coming of human eye Dyes for caries detection They selectively complex with carious tooth structure which is later disclosed with help of fluorescence • Dyes for enamel caries protion,calcein,zyglo ZL-22,brilliant blue • Dyes for dentin caries 1%acid red 52 in propylene glycol complexes specifically with denatured collagen, hence used to differentiate infected and affected dentin • Iodine penetration method (pot iodine) for evaluating permeability Fibre optic transillumination • Different index of light transmission for decayed and sound tooth • Decayed tooth has decreased index and appears dark • The tooth is illuminated by fibre optics • FOTI can detect caries on all types of teeth and also detect incipient caries and recurrent caries before their visibility on radiograph Electric measurement for caries • Tooth demineralization due to caries process causes increased porosity of tooth structure, this porosity contain fluid, containing ions.This leads increased electrical conductivity and decreased electrical resistance or impedance • ECM device uses fixed frequency (23Hz)alternatively current which measure ‘bulk resistance’ of tooth Electric measurement for caries Recent advances in caries detection • Research in last two decades lead to the development of new technologies that assess changes in fluorescence of enamel and dentin due to loss of mineral • Optical methods used are: -Quantitative light induced fluorescence - QLF -Infrared laser fluorescence - DIAGNODENT QLF DIAGNODENT Newer classification of caries Based on site and size of lesion LOCATION PIT/ FISSURE 1 CONTACT AREA 2 CERVICAL 3 NO.CAVITY MINIMAL 1 MODERATE ENLARGED 2 3 EXTENSIVE 4 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Assessment of individual caries risk Risk factors • Microflora • Diet • Tooth Risk indicators • Past disease experience • Salivary flow rate,PH,buffer capacity,antimicrobial effect • Sociodemographic factors • Fluoride exposure • Genetic make up Microflora prevalence and proportions of streptococcus mutans in plaque are positively correlated with caries activity Diet Poor oral hygiene and poor dietary habits-good predictors of caries risk in preschool children Tooth • Tooth size • Tooth morphology and cusp and fissure pattern Reduces cariogenicity of bacteria • Antimicrobial agent Fluoride,chlorhexidine,xylitol • Green tea extract Rich in catechin,a class of oxidant, inhibits mutans growth,kills oral bacteria • Macelignan from nutmeg • Barley tea • Lollipop Effective sugar free herbal lollipops are developed to kill cavity forming bacteria Early lesion remineralisation • Factors promoting remineralisation -PH>5.5 -Phosphate ion -Calcium ion -Fluoride CONCEPTS IN MID • Restoration of tooth become last treatment decision rather than first consideration at present • The 3main concepts in MID are: 1. Identification 2. Prevention 3. control Concept of identification Aimed at risk assessment and creating awareness It includes: • Evaluation of saliva • Evaluation of caries activity(caries activity test) • Assessing the occlusion and tooth factor • Understanding the patient environment such as socioeconomic status education status etc. • Health education • Diet analysis and counseling Concept of prevention 1. Combating caries inducing microorganism 2. Modifying caries promoting ingredient of diet and use of sugar substitutes 3. Increasing the resistance of teeth to decay Combating caries inducing microorganism can be done by: • Bisguanide antiseptic,chlorhexidine: At high conc. act as detergent damaging cell membrane, Low conc. Inhibit sugar transport and glycolitic rate • Triclosan:non ionic agent against gram+ve bacteria.hence used in dentifrice • Delmophinol hydrochloride:highly surface active substance,shown to reduce plaque formation • Caries vaccine:Active or passive immunisation,but it is less significant due to involvement of bacteria and factors in etiology of caries • Replacement therapy:Cariogenic bacteria are replaced by non cariogenic bacteria,practically difficult to achieve • Blocking plaque build up:Studies are going on to produce substance that inhibit glucosyl transferase, interfere with adhesion and coaggregation of bacteria and an effective antibacterial agent Modifying caries promoting ingredients in diet • Addition of preservatives with enhanced antibacterial activity • Addition of natural demineralization inhibitors • Increased consumption of protective food components such as polyphenols in chocolates,oat hulls,cheese and milk .calcium phosphate complexes of casien phoshate in milk have anticaries activity • Calcium phoshate can also be incorporated into dentifrices and other fluoride containing dental products Increasing resistance to tooth decay • Use of fluorides and pit and fissure sealants • Remineralising agents like amorphous calcium phosphate combination of tetracalcium phosphate and dicalcium phosphate anhydrous • Polymeric coating consisting of coating the tooth surface with monomer and polymer • Laser :alter the surface of enamel and increase its resistance to acid challenge .CO2 laser is absorbed by the tooth mineral and transformed into heat and forms ceramic like surface highly resistant to caries • Augmenting host resistance:protective system in saliva can be produced by recombinant DNA technology Concept of control Aims at treatment of caries and maintanence of restored tooth.treatment of caries is aimed at removing only active caries and restored with an adhesive restorative material. Continued professional prophylaxis is important to maintain good condition to reduce secondary caries Special means of caries control include: • Ozone application:Interfere with the metabolism of bacterial cell • Preventive resin restoration • Atraumatic restorative technique TECHNIQUES IN MINIMAL INVASIVE DENTISTRY • Fluoride application • Casien phosphopeptide and amorphous calcium phosphate • Sealants • Antimicrobials • Preventive restorative material -GIC -composite • Repair of defective restoration • • • • • • ART(Atraumatic restorative treatment) Carisolv Bite splints Inlays and onlays Tunnel restoration slot and minibox preparation Minimal cavity preparation technique -Fissurotomy bur -Air abrasion -Laser abrasion -Sono abrasion -Chemomechanical method -Smart prep Fluoride delivery methods • Topical fluoride Placed directly on teeth • Some preparation provide high concentration of fluoride over a short period of time. Other preparation, such as dentifrice provide continous low concentration of fluoride to teeth -Sodium fluoride -Stannous fluoride -Acidulated phosphate fluoride -fluoride varnish -Fluoride dentifrice -Fluoride mouth rinse Systemic fluoride • Provides low concentration of fluoride to the teeth over a long period of time Water fluoridation Milk fluoridation Fluoride tablets/drops/lozenges Salt fluoridation Casien phosphopeptide –Amorphous calcium phosphate ‘RECALDENT’ with technical name casien phosphopeptide – Amorphous calcium phosphate or CPP-ACP is a milk derived product that strengthens and remineralised teeth and helps to prevent dental caries • Deliver super charged calcium and phosphate ion to enamel • Work with fluoride tooth paste to strengthen enamel Clinical application Recaldent chewing gum Tooth mousse/MI paste CPP-ACP plus F(tooth mousse plus) SEALANTS • Sealant is thin plastic coat painted usually the back tooth(premolar & molar) to prevent caries • Plastic material binds to depression and groove • Protect enamel from plaque and acid • Types 1. Polyurethanes 2. Cyanoacrylates 3. Bisphenol A- glycidyl methacrylates (BIS-GMA) PREVENTIVE RESIN RESTORATION • Adhesive dental materials make it possible to conserve tooth structure using minimally invasive cavity preparations • Several materials can be used: - Glass ionomer cements, or GICs; -Resin-based composite/dentin bonding agents - Layered combination of resin-based composites and GICs applied with a technique called lamination. REPAIR OF DEFECTIVE RESTORATION • Removal of restoration result in an inevitable increase in cavity size • Depending on clinical judgement of dentist ,repair could be considered as an alternative to replacement in some circumstances • Cavity preparations Should ensure independent retention and resistance form for the repair. • Repair with a GIC may be preferable in cervical areas, because of the potential for fluoride release and GICs’ excellent adhesion. ATRAUMATIC RESTORATIVE TREARMENT(ART) • Indicates both prevention and treatment of dental caries • Two main principles of ART are: 1. Removing carious tooth tissue using hand instruments only 2. Restoring the cavity with a restorative material that sticks o the tooth Indication • Small cavities (involving dentin) • Caries that are accessible to hand instruments • Public health programmes CONTRAINDICATION • Swelling (abscess or fistula)near the carious tooth • Tooth with exposed pulp • Teeth have been painful for a long time &chronic inflammation of pulp • Carious cavity but opening is inaccessible to hand instruments INSTRUMENTS AND MATERIALS ESSENTIAL FOR ART • Hand instruments used: I. Mouth mirror II. Explorers III. Pair of tweezers IV. Spoon excavators -Hatchets -Hoe & carvers • Materials used: -Cotton wool rolls&pellets -Petroleum jelly -Plastic strip :to shape restoration -Wedges:to hold plastic strip ADVANTAGES • Biological approach that require minimal cavity preparation that conserves sound tooth structure and produce less trauma • As ART is painful the need local anesthesia is reduced • Simplifies infection control as hand instrument can easily be cleaned • No electrically driven and expensive dental equipment needed which enables ART to practice in remote areas • This technique is simple enough to train nondental personnel or primary health care workers • Coast effective • Friendly procedure;great potential for its use among children,fearful adults,physically &mentally handicapped and the elderly INLAYS & ONLAYS • Inlay and onlay do not require to remove as much as tooth structure • Inlays are similar to filling except that they are custom made to fit the cavity in your tooth and are typically the same colour as the tooth or gold coloured • Onlay are used for more substantial reconstruction • When decay or fracture incorporate areas of a tooth that make amalgam or composite restorations inadequate, such as cuspal fracture an onlay might be indicated BITE SPLINTS • Grinding or bruxism may cause serious damage to teeth and may require need of crown • Grinding often begins in teenage or early 20’s ,can be detected and corrected before damage has been done • Dentist can create bite splints to wear at night or during stressful times when most teeth grinding occurs TUNNEL RESTORATION • Designed with idea of preserving the marginal ridge during posterior proximal restoration Advantages • Marginal ridge is maintained thereby maintaining the strength of the tooth • Contact area is usually not disturbed • Risk of overhanging is minimal Disadvantage • Complete excavation of caries is not feasible • Marginal adaptability of the restoration is poor • Difficulty in insertion and finishing of the restorative material FISSUROTOMY BURS Smaller burs for cavity preparation using MI techniques. The burs are spherical, tapered or elliptical. Examples include fissurotomy burs and narrow diamond burs Used with the aid of magnification, these allow very precise preparation of teeth. AIR ABRASION • Used instead of traditional drill and may not require anesthesis.Resembles microscopic sand blasting and uses steam of air combined with superfine abrasive powder • It is a parallel stream of focused narrow beam of 27 micron size of aluminium oxide. • When directed towards toothsurface it abrade with out heat, vibration,and noise. • Air abrasion conserve the tooth structure and maintains the structural integrity of the tooth. • Contraindicated in asthma ,dust allergy,and periodontal disease SONO ABRASION • A recent development from the original ultrasonics ,is the use of high-frequency, sonic, air-scalers with modified abrasive tips – a technique known as ‘sonoabrasion’ • This technique is based on the removal of tooth material by an air-driven hand piece equipped with a diamond-coated working tip that removes tooth material by ultrasonic kinetic energy. DIAMOND COATED HEMISPHERICAL CUTTING TIP ++ LASER CAVITY PREPARATION • Erbium: yttrium aluminum garnet lasers and erbium,chromium:yttrium-scandiumgallium-garnet lasers are being used to cut dental hard tissues. • These lasers can remove soft caries, as well as hard tissue • Remove caries selectively while maintaining healthy dentin and enamel. • Used without anesthetic most of the time. CHEMOMECHANICAL METHOD • Involves the application of a chemical solution to the infected carious dentine,selectively softening the carious dentine by proteolysis, facilitating its removal with mechanical hand instruments, and without affecting sound non-carious dentine. • The most efficient system available is Carisolv™ CARISOLV • Method of gentle treatment of cavities • Gel softens the caries & saves sound tooth • Reduce or eliminates the need for drill & local anesthetics Procedure : • Cover cavity with carisolv gel • Wait for 30 seconds for carious dentin to soften • Carefully scrape away softened caries • Carisolv gel may be applied again and gentle scrapping is repeated until the cavity is caries free • Inspect and fill it like any cavity Recommended in: -cavities on root surface -Deep cavities -Children -Patient with anxiety -Whenever local anesthesia is not an option SMARTPREP(SMARTBUR) INSTRUMENT • The SMARTPREP Instrument is a medical grade polymer that safely and effectively remove decayed dentin, leaving healthy dentin intact. • The hardness of instrument is less than that of healthy dentin and enamel but harder than carious dentin • SELFLIMITING The polymer instrument is self-limiting and will not cut sound dentin unless applied with great force, and then it will only wear away, rather than cut, the healthy dentin • They are single-patient-use rotary instruments • Used for deep caries removal in anticipation of an indirect pulp capping procedure MID IN COSMETIC DENTISTRY • Cosmetic procedure require extensive tooth preparation can leave a patient with severly compromised dentition with little room to manoeuver if the desired outcome is not achieved • MI direct replacement technique require only minimal tooth preparation BENEFITS OF MID • Better oral health through disease healing and not merely symptom relief • Further more minimal intervention may assist in reducing widespread patient dental anxieties CONCLUSION • Allows dentist to perform least amount of dentistry needed while never remove more of tooth structure than is required to restore the teeth to normal condition • It use long lasting dental materials that conserve maximum tooth structure • MID gives better oral health through disease healing not merely symptom relief • It assist in reducing dental anxieties • Cost effective compared to other treatment mode • Cause less trauma to patient • Although further research is needed it can so far concluded that minimal invasive dentistry has the potential for dentist to apply a more conservative approach to caries treatment and simultaneously offer patient more friendly health oriented treatment option REFERENCE • STURDEVANT’S ARTS AND SCIENCE OF OPERATIVE DENTISTRY • TEXT BOOK OF OPERATIVE DENTISTRY -VIMAL SIKRI • PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE OF PEDODONTICS –ARATHI RAO • ESSENTIALS OF PREVENTIVE AND COMMUNITY DENTISTRY-SOBEN PETER • KENNEDY’S PAEDIATRIC OPERATIVE DENTISTRY