Bias and Confounding Tutorial
advertisement

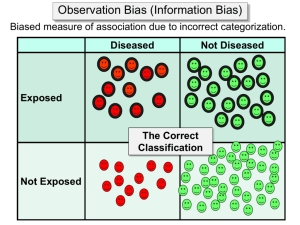
Dr. Rufaidah Dabbagh MBBS, MPH Dr. Armen Torchyan MD, MPH CMED 304 Family and Community Medicine Department To understand bias and how it can be minimized Recognize different types of bias Understand concept of confounding Learn how to think of possible confounding factors for associations between exposures and outcomes Types of Bias: ◦ Selection bias ◦ Information bias Information bias can lead to “misclassification” of your study participants. What could cause misclassification? Why misclassification of disease status? •Incorrect Diagnosis •Limited knowledge •Diagnostic process complex •Inadequate access to technology •Laboratory error •Disease subclinical •Detection bias (e.g. more thorough exam in exposed) •Subject Self report •Incorrect recall •Reluctant to be truthful •Records incorrectly coded in data-base Available at: http://www.sph.emory.edu/activepi/Instructors/Kevin_MSword/Lesson_9boh.htm. Accessed on Oct 18, 2011. Why misclassification of exposure status? •Imprecise measurement •Subject Self report •Interviewer bias •Incorrect coding of exposure data Available at: http://www.sph.emory.edu/activepi/Instructors/Kevin_MSword/Lesson_9boh.htm. Accessed on Oct 18, 2011. Two general surgeons wanted to measure the association between eating healthy vegetables and having gall stones. They recruited patients in their hospital and formed two groups of participants: gall stone group, non-gall stone group. They interviewed individuals from each group to inquire about the previous intake of fruits and vegetables over the past 5 years. Reducing non-response Reducing loss to follow up Increasing sample size You and your colleagues would like to conduct a study to see the prevalence of substance abuse among high school students living in Riyadh. You randomly chose your sample from a number of schools in Riyadh and distributed your questionnaires. What type of bias is this study be subject to? You were conducting a study on the association between duration of breastfeeding and malnutrition. You randomly select a group of mothers attending the MMR immunization clinic and ask them about the pattern and duration of breastfeeding they had for their children. What type of bias might this study be subject to? Differential misclassification: ◦ When the misclassification results in exposure is incorrectly more in cases than in controls. Or vice versa; like one group has a lot more incorrect information than the other group Non-differential misclassification: ◦ When the misclassification is not related to exposure status or disease status. And is occurring at the same proportion in both groups; e.g. if 20% of cases are classified incorrectly on exposure in cases and about 20% in controls too An obstetrician wanted to study the association between congenital malformations and history of infections during pregnancy. He interviewed women (a group who delivered children with malformations, and a group of women with normal children). He asked about history of all types of infections during pregnancy. After finishing the interviews, he also wanted to go through the women's’ medical records, in order to minimize recall bias. He discovered that women who had a baby with malformation tended to remember all infections during pregnancy more than the mothers with normal babies. What kind of misclassification is this? Available at: http://ebp.lib.uic.edu/applied_health/files/images/random_cry.gif. Accessed on Oct 18, 2011. A case-control study was conducted to investigate the association between artificial sweetener and bladder cancer. Controls were selected from a group of people diagnosed with obesity related conditions. It is well known that obesity related conditions are associated with an increased likelihood of using artificial sweetener. Could the association between artificial sweetener and bladder cancer be confounded by any external factors? Obesity related conditions Artificial sweetener --- Bladder Cancer Unhealthy lifestyle (consumption of other artificial preservatives & carcinogens) Can you think of any other factors? A study was done to explore the association between birth order and Down syndrome. It was found with increasing birth order, there was also an increase in the occurrence of Down syndrome. The prevalence of Down syndrome was 6/1000 live births at the first birth and 16/1000 live births, for birth of 5 or greater. Affected babies per 1000 live births 18 16 14 12 1st Child 10 2nd Child 8 3rd Child 6 4th Child 4 5th Child 2 0 Birth Order Kennith J. Rothman, Epidemiology and introduction, p 102 Mother’s age Birth order ------------ Down syndrome Because mother age and birth order are highly correlated, we expect that mothers who give birth to their fifth baby might be considerably older than mothers giving birth to first baby. We also know that the risk of Down syndrome increases with maternal age. A study was done to examine the association between Caffeine and Breast cancer. The following data was obtained: Caffeine Breast Cancer No breast cancer Yes 30 18 No 70 82 Total 100 100 What are the odds of caffiene intake in cases compared to controls?OR= 30x82 = 1.95 70x18 The investigators thought that the calculated OR was confounded by the effect of age. They stratified participants according to age: Age <40 Age ≥ 40 Caffeine Ca No Ca Caffeine Ca No Ca Yes 5 8 Yes 25 10 No 45 72 No 25 10 Total 50 80 Total 50 20 OR=? OR= 5x 72 = 1 OR=? What do you conclude? Age confounds the association between caffeine intake and breast cancer 45x8 OR= 25x10 = 1 25x10 Nurse’s Health study; a cohort study was done to determine the association between oral contraceptive use and ovarian cancer. The following data were obtained: Oral contraceptive Ovarian Ca No ovarian Ca Total Yes 350 200 550 No 125 200 325 Total 475 400 875 What is the crude RR? RR= 350÷550 = 1.65 125÷325 The investigators thought that the calculated Risk ratio might be confounded by the effect of smoking. Data were stratified according to smoking status and relationship was studied : Smokers Non-smokers OCP Ovarian Ca No ovarian Ca Total OCP Ovarian Ca No ovarian Ca Total Yes 95 5 100 Yes 298 152 450 No 150 25 175 No 100 50 150 RR=? RR= 95÷100 = 1.1 150÷175 RR=? RR= 298÷450 = 0.99 100÷150 http://stattrek.com/ap-statistics-2/surveysampling-bias.aspx Thank you