Chapter 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics
advertisement

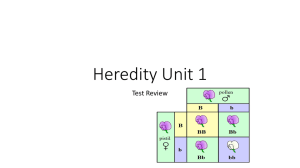
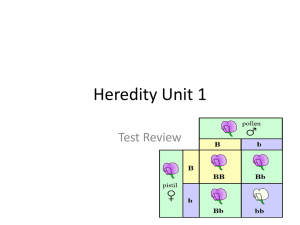
Chapter 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics Autosomal Recessive Genetic Disorders A recessive trait is expressed when the individual is homozygous recessive for the trait. Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance Affects the mucus-producing glands, digestive enzymes, and sweat glands Chloride ions are not absorbed into the cells of a person with cystic fibrosis but are excreted in the sweat. Without sufficient chloride ions in the cells, a thick mucus is secreted. Video Cystic Fibrosis Caused by altered genes, resulting in the absence of the skin pigment melanin in hair and eyes Albinism Caused by the absence of the enzymes responsible for breaking down fatty acids called gangliosides Gangliosides accumulate in the brain, inflating brain nerve cells and causing mental deterioration. Tay-Sachs Disease Cystic Fibrosis Punnett Square Autosomal Dominant Genetic Disorders Huntington’s disease affects the nervous system. Achondroplasia is a genetic condition that causes small body size and limbs that are comparatively short. Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance Huntington’s Disease Punnett Square A diagram that traces the inheritance of a particular trait through several generations Pedigrees Inferring Genotypes Knowing physical traits can determine what genes an individual is most likely to have. Predicting Disorders Record keeping helps scientists use pedigree analysis to study inheritance patterns, determine phenotypes, and ascertain genotypes. Sex chromosomes determine an individual’s gender Sex Determination Genes located on the X chromosome Red-green color blindness Hemophilia Punnett Square Sex-Linked Traits Dosage Compensation The X chromosome carries a variety of genes that are necessary for the development of both females and males. The Y chromosome mainly has genes that relate to the development of male characteristics. In females, one X chromosome is inactivated in each cell. The inactivated X chromosome is visible in stained cells as a Barr body. Tutorial X Chromosome Inactivation Variety is the result of one allele hiding the effects of another allele. An epistatic gene can interfere with the expression of other genes. Albinism in mammals is caused by an epistatic gene that blocks the production of pigments. Epistasis Phenotype can depend on interactions of alleles. Complex Patterns of Inheritance The heterozygous phenotype is an intermediate phenotype between the two homozygous phenotypes. Incomplete Dominance Both alleles are expressed in the heterozygous condition. Sickle-cell disease is one example. People who are heterozygous for the trait have both normal and sickle-shaped cells. Codominance Blood groups in humans ABO blood groups have three forms of alleles. Sometimes said to be codominant. Multiple alleles can demonstrate a hierarchy of dominance. Multiple Alleles Polygenic traits arise from the interaction of multiple pairs of genes. Read pg. 206 in textbook. Polygenic Traits Environmental factors influence an organism’s phenotype Diet and exercise Sunlight and water Temperature Environmental Influences Read pgs.209-211 Gene Linkage Karyotype—micrograph in which the pairs of homologous chromosomes are arranged in decreasing size Images of chromosomes stained during metaphase Chromosomes are arranged in decreasing size to produce a micrograph. Karyotype Studies Is this a normal karyotype? Male or female? Is this a normal karyotype? Male or Female? Is this a normal karyotype? Male or Female? Cell division during which sister chromatids fail to separate properly Down syndrome, also called trisomy 21 Nondisjunction