Chap 21 powerpoint
advertisement

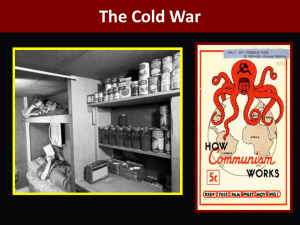
Chapter 21 The cold War Begins I. The Cold War begins (appx 1946-1991) A. What was the Cold War? 1. an era of rivalry & competition btwn US & USSR a. a clash of ideologies: Capitalism and Democracy vs Communism b. leads to space race, nuclear arms race c. a COLD war b/c no real battles btwn US and USSR 2. The Ideologies - very different a. US: Democracy and Capitalism 1) Democracy: form of gov’t where a constitution guarantees basic personal and political rights, fair and free elections, and independent courts of law 2) Capitalism: an economic system in which trade, industries, and the means of production are largely privately owned and operated for profit b. USSR: Communist Dictatorship 1) Economic and political system that calls for gov’t ownership and control of property and the means of production 2) individuals expected to contribute to society according to ability and receive from it according to need. II. The Impact of WWII A. New Superpowers Emerge 1. USA a. economically strong - Besides Pearl Harbor attack, no battles on US soil - US industry boomed in WWII b. militarily powerful but declining in size 2. USSR a. economically weak - war on Soviet soil - industries, cities devastated b. militarily strong and growing - Red Army controlled most of Eastern Europe and remained the world’s largest B. New Political Boundaries after WWII 1. Poland a. only allied country to lose territory (20%) b. Lost territory to east (to USSR), gained some to the west (at Germany’s expense) 2. Imperialism weakened – Colonies Independent a. Colonizers economically devastated by WWII 1) difficult/expensive to maintain colonies abroad, most independent within next few decades 2) Borders redrawn (ex. India/Pakistan) b. negative views of imperialism grew 1) abuses of imperialism highlighted by violent acquisition of territory by Japan and Germany 2) independence movements across the globe gained support and momentum 3. nearly all Eastern Europe became communist under USSR control 4. Japan under US military occupation Emperor Hirohito and General MacArthur, at their first meeting, at the U.S. Embassy, Tokyo, Sept. 27, 1945 C. International Organizations and Treaties 1. United Nations (UN) UN = an int’l org. founded to promote world peace and progress a. General Assembly = World forum, hears disputes, refers serious matters to Security Council b. Security Council = headed by big 5 plus rotating 10. Big 5 have VETO power 1) can block any UN action it opposes. 2) Investigates, recommends and takes action 3) Big 5: US; USSR; UK; France; China c. Eleanor Roosevelt (former 1st lady) appointed by Truman to represent the US in the UN. As chairman of the Commission on Human Rights, she guided the drafting of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1) condemns slavery and torture 2) encourages free speech and religion 3) affirms that all have a right to a “standard of living” adequate for health and wellbeing Standard of Living: A level of material comfort as measured by the goods, services, and luxuries available to an individual, group, or nation Sovereignty: freedom from outside control d. criticism of US membership in UN: giving decision-making authority to a global organization undermines US sovereignty 2. Trade Organizations – to foster global economic and financial stability a. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) 1) goal to expand world trade 2) reduces tariffs and other trade barriers b. World Bank 1) goal to reduce poverty and finance world economic development 2) offers loans and technical advice to developing nations developing nation: a nation whose economy is primarily agricultural 2. Trade Organizations – to foster global economic and financial stability a. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) 1) goal to expand world trade 2) reduces tariffs and other trade barriers b. World Bank 1) goal to reduce poverty and finance world economic development 2) offers loans and technical advice to developing nations developing nation: a nation whose economy is primarily agricultural c. International Monetary Fund (IMF) 1) goal to stabilize finances of nation and encourage economic growth 2) stabilizes exchange rates btwn countries 3) lends money to countries in financial crisis D. Dealing with the USSR 1. The Yalta Conference (FDR + Stalin + Churchill) Feb. 1945. 3 decisions a. Soviet backed communist Gov’t recognized in Poland – but included pledge from Stalin that free elections would be held in Poland ASAP!! b. Declaration of Liberated Europe - the right of all people to choose the form of gov’t under which they live c. Germany & Berlin ÷ into 4 zones Division of Germany/Berlin 2. Potsdam Conference (US, GB, USSR) July 1945 The Big Issues a. Reparations: a difference of opinion 1) US: let German economy revive (less likely to turn to communism) 2) USSR: pay heavy reparations (keeps Germany weak!) 3) The decision? Soviets to take reparations from the German sector they controlled b. Truman continues to press for free elections in Poland c. Stalin pledged to enter war against Japan Stalin, Truman, Churchill (Churchill leaves office and is replaced by Atlee in later meetings) 3. Broken Soviet Promises a. Romania pressured by USSR to appoint Communist gov’t b. Allow only 3 non-Communists in Polish gov’t c. No indication that free elections in Poland will be allowed 4. A clash of the Allies – different ideas What the Americans Believed What the Soviets Believed Economic growth was the key to world peace Communism was a superior system Economic growth should be promoted by increasing world trade Communism would eventually replace capitalism Democratic gov’ts that protect people’s rights made countries more stable Communism should be encouraged in other nations The free enterprise system was Germany should be kept weak the best route to prosperity economically and militarily The German economy should be allowed to recover To increase their security, countries between USSR and Germany should be under Soviet Control E. Iron Curtain Descends a. USSR Red Army in Eastern Europe: clear that pro-Soviet gov’ts will be established in Poland, Bulgaria, Hungary & Czechoslovakia b. These nations = satellite nations satellite nation: formally independent, but dominated by another power (USSR) - had to remain Communist, friendly to USSR & follow policies approved by USSR c. Churchill: “an iron curtain has descended across Europe.” - this iron curtain separated Communist nations of Eastern Europe from the West IRON CURTAIN http://users .erols.com/ mwhite28/ communis. htm The Iron Curtain II. The Early Cold War Years A. Containing Communism 1. The Long Telegram a. US State Dept in Moscow asked to explain Soviet behavior in Eastern Europe – reply came from diplomat George Kennan Kennan in 1947 b. The Long Telegram – Soviet behavior due to: 1) mistrust of the West 2) WWII losses WOW! 3) insecurity and the need to control Eastern Europe 4) historical struggle against capitalism c. Kennan’s Conclusion? Communists still interested in world dominion. So… no way to reach permanent settlement with them d. Recommended Solution? In Foreign Affairs using pseudonym X proposed: Containment – the post WWII foreign policy that sought to prevent the expansion of the USSR through diplomatic, economic and military means Containment 2. The Truman Doctrine – a military approach to containment a. Gov’ts of Greece (guerilla war w/ Communists) and Turkey (USSR wanted control of Dardanelles straits) Greece and Turkey b. Truman Doctrine = “it will be the policy of the US to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures.” c. Came to mean that the US would oppose the overthrow of any democratic gov’t – a pledge to fight communism Worldwide 3. Marshall Plan (1947) – an economic approach to containment a. Problem: Europe a “rubble heap” b. Sec. of State George Marshall proposes that US begin a program of massive economic aid to Europe c. Marshall Plan: a massive US aid program to help European nations recover economically from WWII Truman Doctrine & Marshall Plan Marshall Plan B. Berlin Crisis 1. West Germany is founded a. USSR had set up Communist gov’t in their zone, removed wealth from Germany to strengthen USSR b. US, GB, France united their sections of Germany 1948 c. USSR blocked all land routes into Berlin – Berlin Blockade d. West responded with Berlin Airlift (best option for avoiding war) e. For almost 1 yr, Brits and US flew tons of goods into West Berlin f. May 1949, Soviets lift blockade Two Germanys: West Germany & East Germany 2. NATO: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) a. US convinced that USSR was bent on conquest b. NATO formed to defend member nations from Communist threats c. It is a mutual defense alliance where members agree to come to the aid of any member who is attacked d. USSR response? Warsaw Pact NATO 12 members originally. Today 28 + US & Canada Berlin & NATO C. Cold War Spreads to East Asia 1. Civil War & Revolution in China a. Civil War in China resumed after WWII – Communists under Mao Zedong vs. Nationalists under Chiang Kai-shek b. China falls to Communism Oct 1949 – establish the People’s Republic of China (PRC) c. Chinese Nationalists flee to Taiwan and establish gov’t of “China” Republic of China (ROC) 2. After the Fall a. US did not recognize PRC, blocked their entrance into UN b. US decided to aid friends in Asia like Indochina & Japan. US recovery efforts focus on Japan! 1) sent MacArthur to rebuild Japan – strengthen economy 2) new constitution(no war!) c. US sees W. Germany as key to defending all of Europe against communism, and now saw Japan as the key to defending Asia E. Korean War – 1st armed conflict of Cold War 1. Background a. US & USSR in Korea after WWII to disarm Jap. troops there b. Korea ÷ at 38ºN 1) North = USSR = communist 2) South = USA 2. June 25, 1950: NK invades SK in an effort to unite the peninsula under Communism PBS Summary of Korean War 3. The UN intervenes a. Truman calls for meeting of UN Security Council (USSR boycotting over China policy so wasn’t there to veto) b. UN agrees to a “police action” – 17 nations, but 90% from US or SK c. Douglas MacArthur in command d. US troops pushed back to Pusan perimeter; US then push NK back across 38ºN - then all the way to the Yalu River – the border of China 4. China enters the War a. PRC enters war & pushes back UN army b. MacArthur wants to expand war – 1) block Chinese ports 2) utilize Chiang’s Nationalist forces from Taiwan 3) bomb Chinese cities with atomic weapons 5. Truman fires MacArthur a. Truman committed to a limited war - a war fought to achieve a limited objective 1) in this case, the objective was to contain communism 2) did not want to expand war with China or use atomic weapons Pres. Truman b. To maintain control of policy + show he was Commander in Chief, Truman fires MacArthur - in the US, we have civilian control of the military! “In war there is no substitute for victory.” Douglas MacArthur MacArthur’s Farewell Speech to Congress 6. Changes in US Policy a. Peace talks begin Nov. 1951 – armistice (cease-fire) signed July 1953 b. Korea remains divided d. Turning pt in Cold War – prior to Korea, US relied on political pressure & economic aid to contain communism. Now, US begins major military build up d. Defense agreements signed in Asia ( you guessed it! US in more mutual defense alliances!) 1) ANZUS 2) SEATO 3) Indochina – aid to French forces fighting Ho Chi Minh’s Communist guerillas in Vietnam (US was subsidizing France’s colonial war in Indochina – 80% by 1954) III. The Cold War and American Society A. A New Red Scare 1. Origins of the New Red Scare a. Sept 1945: Soviet defector revealed that USSR was infiltrating orgs. & gov’t agencies (in US & Canada) to obtain info on the atomic bomb. b. Americans began to fear that Communists were secretly working to subvert US gov’t Subversion = effort to weaken a society and overthrow its gov’t 2. Loyalty Review Program a. Early 1947: Truman launched Loyalty Review Program to screen all federal employees for loyalty b. Led to increased fear that Communists had infiltrated US gov’t c. Over 6m Federal employees screened 1) intense scrutiny by FBI 2) some quit from the pressure, others fired for “questionable” loyalty 3. HUAC a. 1938: House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) formed 1) a committee in H of R created to expose communist & Fascist activities in US 2) expanded by FBI director J. Edgar Hoover in 1947 b. FBI infiltrated groups suspected of subversion $ wiretapped 1000s of phones - even went after Hollywood HUAC 4. Alger Hiss a. 1948: Time Magazine editor and former Communist Party member, Whittaker Chambers, testified to HUAC that several gov’t officials were former Communists or spies b. Alger Hiss accused/denied c. Chambers produced “pumpkin papers” Hiss convicted of perjury; (lying under oath). d. Case left many Americans believing there were indeed spies in US gov’t Alger Hiss Trial 5. The Rosenbergs a. 1949: USSR gets THE bomb! b. Most believe USSR could not have produced atomic bomb w/o help – US hunts for spies c. 1951: Julius & Ethel Rosenberg, NY Communist members, arrested & charged & convicted of heading Soviet spy ring – executed in 1953 - 1st civilians in US history put to death for espionage Alger Hiss & Rosenbergs Julius & Ethel Rosenberg 6. Project Venona a. launched to crack the Soviet spy code b. 1946: code cracked. Confirmed the existence of Soviet Spy ring c. Project Venona not revealed to US public until 1995 – confirmed guilt of Rosenbergs B. McCarthyism 1. By 1949, Americans were convinced the US was losing the Cold War & that Communists had infiltrated the US gov’t 2. Enter Joseph McCarthy…”McCarthyism” a. Senator McCarthy conducted “witch hunts” for suspected Communists in the US gov’t in early 1950s b. Claimed he had a list of Communists in the US State Dept. c. made numerous accusations and charges of disloyalty d. his tactic was to damage people’s reputations with vague and some times unfounded charges. 3. The McCarren Act a. Established the following: 1) illegal to support totalitarianism 2) required all Communist Party orgs to register with the US Atty General 3) no passport or foreign travel for Communists 4) Allowed for the arrest and detention of Communists and Communist sympathizers in the case of a nat’l emergency 4. McCarthy’s downfall a. McCarthy alleged that there were Soviet spies in the US Army b. Army conducted investigation, but found no evidence of spies c. Televised hearings were held - McCarthy seen as a mean bully and lost his influence to arouse public fear d. Censured by the Senate censure: formal disappoval 5. Distinguishing the US from USSR a. 1954: US adds “Under God” to the Pledge of Allegiance b. 1956: US adopts “In God We Trust” as a national motto c. These were not added to endorse a particular religion, rather to distinguish the US from the USSR where atheism was promoted C. Americans Live in Fear of Nuclear War 1. The Nukes a. USSR tested atomic bomb in 1949 b. USSR tested more powerful Hydrogen bomb in 1953 2. “Duck and Cover” drills held in preparation for a surprise Soviet attack Duck and cover drills 3. Fallout Shelters a. Fear of nuclear fallout fallout: radioactive particles dispersed by a nuclear explosion b. For protection, some built backyard fallout shelters & stocked them with food etc. fallout shelter: a shelter built with the intent to house and protect people from nuclear fallout Fallout Shelters IV. President Dwight D Eisenhower A. Eisenhower’s New Look in Defense 1. 1952 Election a. Dwight D Eisenhower(R) vs Adlai Stevenson(D) b. Ike wins! (WWII hero) 2. The scenario when Ike takes office a. USSR had THE bomb b. China fell to Communism c. US Troops in Korean War 3. Key to Cold War Victory = military might + strong economy 4. “New Look” defense policy a. More Nukes; Less conventional weapons/forces = money saved b. More “bang for the buck” with Nukes! The New Look 5. Massive Retaliation Policy a. a policy of threatening a massive response, including the use of nuclear weapons, against a Communist state trying to seize a peaceful state by force b. Result? Military spending down, nuclear arsenal up 6. New Technology a. Nukes required new technology to deliver them 1) B-52 bombers 2) ICBMs 3) submarines capable of nuclear launch 7. The Sputnik Crisis a. Oct 1957: USSR launched Sputnik, the 1st artificial satellite to orbit the earth b. US Response? Alarm!! A sign the US was falling behind the USSR in technology and scientific research c. Led to: 1) creation of Nat’l Aeronautics & Space Administration (NASA): to coordinate research in rocket science and space exploration 2) Nat’l Defense Education Act (NDEA): to provide $$ for education/training in science, math & foreign language B. Brinkmanship in Action 1. Brinkmanship (the willingness to go to the brink of war to force an opponent to back down) John Foster Dulles was Ike’s Sec of State and was responsible for the aggressive brinkmanship policy. Dulles is speaking to Uncle Sam in the Cartoon 2. The Korean War Ends a. Korean War a campaign issue for Ike – said it was too costly, too many US casualties b. Ike hints to the Chinese of a possible US nuclear attack c. Brinkmanship seemed to work – armistice signed July 1953 d. Korea divided near the pre-war boundary of 38ºN parallel - Divided by a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) e. No victory for either side, but the spread of communism in Korea was stopped. Thus, the goal of Containment was achieved in Korea! 3. The Taiwan Crisis Flag of China Flag of Taiwan a. China threatens Taiwan 1) Ike considers Taiwan as barrier against spread of Communism in Asia 2) Ike hints at the use of nukes if China doesn’t back down b. China backs down – brinkmanship works C. Fighting Communism Covertly 1. To prevent Communist uprisings in other countries, Ike decides to use covert, or hidden operations conducted by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) 2. Containment in Developing Nations (3rd World) 1st - The bloc of democratic-industrial countries within the American influence sphere 2nd - The Eastern bloc of the communist-socialist states 3rd - The remaining three-quarters of the world's population, states not aligned with either bloc – mostly poor, underdeveloped a. Many covert operations in developing (aka 3rd world) nations (developing nation = a nation whose economy is primarily ag) b. To stop Soviet/Communist influence, the US: 1) sent financial aid 2) CIA staged covert ops to overthrow anti-American leaders and replace them with pro-American leaders c. Covert operations conducted in Iran, Guatemala 3. Uprising in Hungary a. 1953: Stalin Dies, Nikita Khrushchev new leader of USSR b. Khrushchev attacks Stalin’s policies leading many to believe that he will be different – that he’ll allow more freedom in Eastern Europe c. 1956: uprising begins in Eastern Europe d. Oct 1956: full-scale uprising in Hungary Hungarian Uprising Stalin decapitated e. Khrushchev willing to tolerate more freedom, but would not tolerate an end to communism in Eastern Europe f. Soviets send tanks into Budapest to crush the uprising D. Continued Tensions 1. B/C of Hungarian Uprising, Khrushchev forced to reassert Soviet power & superiority of communism a. accuses capitalists of starting an arms race b. 1958: K demands US, GB and Fr withdraw from W. Berlin - US response? Says NATO will respond! (brinkmanship in action) - Soviets back down 2. Attempt to improve relations: US/USSR plan a Summit (formal face to face meeting) in 1960 a. But before Summit occurs, the USSR shoots down a US U-2 spy plane - US claims it was a weather plane that strayed off course - USSR produces pilot, Francis Powers - US refuses to apologize b. USSR calls off summit 3. Ike’s Farewell Address 1961 a. Highlighted new relationship btwn the military and defense industry b. Warned against influence of military-industrial complex (an Farewell speech informal relationship that some people believe exists btwn the military and the defense industry to promote greater military spending - a potential threat to democracy & influence gov’t policy)