injury terms - New Paltz Central School District
advertisement

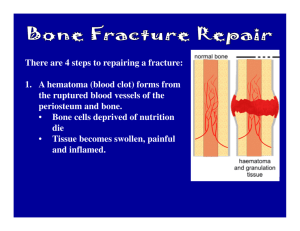
DEFINITION OF SPORTS INJURY • 1. Occurs as a result of participation in an organized practice or game. • 2. Requires medical attention by a team athletic trainer or physician. • 3. Results in restriction of athlete’s participation for one or more days beyond day of injury DEFINITION OF ACUTE INJURY • “Characterized by a rapid onset, resulting from a traumatic event.” • Critical Force or impact force • Example: Broken bone from a one time traumatic force. • Ex: Sam Bradford (Oklahoma QB out 2-4 weeks with shoulder injury sustained on a hit by BYU linebacker) DEFINITION OF CHRONIC INJURY • “Characterized by a slow, insidious (spreading harmfully and quietly) onset, implying a gradual development of structural damage.” • Not associated with one traumatic episode • Develops progressively over time • Overuse injuries that cause a progressive breakdown over tissue, leading eventually to failure • Popular sites for these are Achilles tendon (running), patellar tendon (jumping, landing, kicking), and rotator cuff(overhead movements)in shoulder. • Example: Deceleration phase of a swing or throw. “Slamming the brakes!” • EX: Daisuke Matsuzaka (Red Sox P shoulder fatigue) SOFT TISSUE VS. SKELETAL TISSUE • There is a difference between an injury that involves soft tissue and skeletal tissue. SOFT TISSUE • • • • • • • MUSCLES FASCIA TENDONS JOINT CAPSULES LIGAMENTS BLOOD VESSELS NERVES MUSCLES (SOFT TISSUE) • MUSCLES – Contractile tissue of the body responsible for movement FASCIA (SOFT TISSUE) • FASCIA – Fibrous membrane that covers, supports, and separates muscles TENDONS (SOFT TISSUE) • TENDONS – A tendon is a tough yet flexible band of fibrous tissue that connects muscle to bone JOINT CAPSULES (SOFT TISSUE) • JOINT CAPSULES – Sac-like structure that encloses the ends of bones in a diarthrodial (movable) joint LIGAMENTS (SOFT TISSUE) • LIGAMENTS – Ligaments are the fibrous, slightly stretchy connective tissues that hold one bone to another in the body, forming a joint. Ligaments control the range of motion of a joint, preventing your elbow from bending backwards, for example, and stabilizing the joint so that the bones move in the proper alignment. BLOOD VESSELS (SOFT TISSUE) • BLOOD VESSELS - Blood vessels are hollow utensils for carrying blood. NERVES (SOFT TISSUE) • NERVES - Any of the cordlike bundles of fibers made up of neurons through which sensory stimuli and motor impulses pass between the brain or other parts of the central nervous system and the eyes, glands, muscles, and other parts of the body. Nerves form a network of pathways for conducting information throughout the body. SKELETAL TISSUE • SKELETAL TISSUE INCLUDES ANY BONY STRUCTURE IN THE BODY WHAT IS CARTILAGE? • CARTLAGE - Cartilage is a type of connective tissue in the body. It is made of cells called chondrocytes embedded in a matrix, strengthened with fibers of collagen and sometimes elastin, depending on the type of cartilage. There are three different types: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage. Cartilage serves to provide structure and support to the body's other tissues without being as hard or rigid as bone. It can also provide a cushioning effect in joints. • Cartilage is avascular, meaning that it is not supplied by blood vessels; instead, nutrients diffuse through the matrix. Cartilage is usually flexible, again depending on the type. Some of the bodily structures that include cartilage are the ears, nose, ribcage, and intervertebral discs. SOFT TISSUE INJURIES VS. SKELETAL TISSUE INJURIES • SOFT TISSUE INJURIES: CONTUSIONS, SPRAINS, STRAINS SKELETAL TISSUE INJURIES: FRACTURES WHAT IS A CONTUSION? • CONTUSION – A contusion is a fancy word for a BRUISE. Broken Blood Vessel. Ecchymosis (dicoloration) and Hematoma (pooling of blood) WHAT IS A SPRAIN? • SPRAIN – Sprains are injuries to LIGAMENTS/CAPSULES, which surround all synovial joints (the most common and most movable type of joints in the human body) • First Degree Sprain – Mildest form of sprain (little or no swelling with minor ligament damage) • Second Degree Sprain – More damage, swelling is more pronounced. • Third Degree Sprain – Most severe, Complete tear of ligament. Extensive damage, pain, swelling and hemorrhage along with considerable loss of joint stability WHAT IS A STRAIN? • STRAIN –Injury involving MUSCLES and TENDONS or the junction between the two. • FIRST DEGREE STRAIN – Mildest form of strain. Pain is noticable during use. There may be mild swelling and muscle spasm present • SECOND DEGREE STRAIN – More extensive. Pain and swelling are more pronounced. Functional loss is moderate. These types of injuries are associated with excessive forced stretching. • THIRD DEGREE STRAIN – Most severe form and imply a complete rupture of the soft-tissue structures involved. WHAT IS A FRACTURE? FRACTURE – A break or crack in a bone • • Swelling, • Deformity – compare injured part with noninjured part • Pain and tenderness – usually can point to pain at site – feel gently along bone to find pain • Loss of Use • Grating Sensation – broken bone ends rub together . DO NOT MOVE INJURED LIMB • History of Injury – suspect a fracture when severe forces are involved. Athlete may have heard or felt the bone snap. WHAT IS A STRESS FRACTURE? • STRESS FRACTURE – A break or crack in the bone that develops over a long period of time as opposed to a break that occurs from one traumatic event. (Can also be caused by low calcium levels in diet) • Things to look for: • Pain/Tenderness - A constant ache is NOT relieved with rest • Absence of Trauma - Suspect a fracture when there is no history of traumatic event, yet symptoms persist • Repetitive Activity – Athlete is involve in repeated stressful episodes • Duration – Symptoms have slowly developed over a longer period of time. WHAT IS AN AVULSION FRACTURE? AVULSION FRACTURE –An avulsion fracture is an injury to the bone in a place where a tendon or ligament attaches to the bone. When an avulsion fracture occurs, the tendon or ligament pulls off a piece of the bone. WHAT IS A GREENSTICK FRACTURE? GREENSTICK FRACTURE –A fracture in which one side of a bone is broken while the other is bent (like a green stick). Usually associated with infants or young children. WHAT IS A SPIRAL FRACTURE? SPIRAL FRACTURE – A fracture, sometimes called a torsion fracture, in which a bone has been twisted apart. Usually associated in abuse cases. WHAT IS A COMMINUTED FRACTURE? COMMINUTED FRACTURE – A fracture in which bone is broken, splintered or crushed into a number of pieces. WHAT IS A TRANSVERSE FRACTURE? TRANSVERSE FRACTURE – A fracture in which the break is across the bone, at a right angle to the long axis of the bone. WHAT IS A COMPOUND FRACTURE? COMPOUND FRACTURE – A fracture in which the bone is sticking through the skin. Also called an open fracture. WHAT IS A COMPRESSION FRACTURE? COMPRESSION FRACTURE – A compression fracture is usually understood to mean a compression fracture of the spine, or vertebral compression fracture. A compression fracture occurs when a number of vertebrae in the spine are broken. WHAT IS A DISCLOCATION? DISLOCATION – The displacement of contiguous surfaces of bones comprising a joint. Examples: Shoulder joint and Hip Joint TYPES OF DISLOCATIONS TWO TYPES OF DISLOCATIONS CAN OCCUR DEPENDING ON THE SEVERITY OF THE INJURY. SUBLUXATION – Partial or Incomplete dislocation of an articulation LUXATION – Complete dislocation of a joint WHAT IS SUBLUXATION? SUBLUXATION– A partial or incomplete dislocation of an articulation WHAT IS LUXATION? LUXATION– A complete dislocation of a joint DEFINITION OF CATASTROPHIC INJURY • Sport injury that results in a brain or spinal cord injury or skull or spinal fracture. • Majority of fatalities occur with brain injuries.