Chapter 1
Why Study
Money, Banking,
and Financial
Markets?
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
Why Study Money, Banking, and
Financial Markets
• To examine how financial markets such as bond and
stock markets work
• To examine how banks, other financial institutions and
financial regulation work
• To examine the role of monetary policy in the economy
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1-2
Financial Markets
• Markets in which funds are transferred from people
who have an excess of available funds to people who
have a shortage of funds
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1-3
The Bond Market and Interest
Rates
• A security (financial instrument) is a claim on the
issuer’s future income or assets
• A bond is a debt security that promises to make
payments periodically for a specified period of time
(that is, IOU)
• An interest rate is the cost of borrowing or the price
paid for the rental of funds
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1-4
FIGURE 1 Interest Rates on
Selected Bonds, 1950–2008
Sources: Federal Reserve Bulletin; www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H15/data.htm.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1-5
The Stock Market
• Common stock represents a share of ownership in a
corporation (IOBU)
• A share of stock is a claim on the earnings and assets of
the corporation
• Common stock holders are residual claimants.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1-6
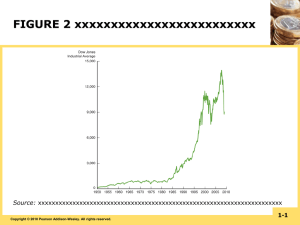
FIGURE 2 Stock Prices as Measured by the
Dow Jones Industrial Average, 1950–2008
Source: Dow Jones Indexes: http://finance.yahoo.com/?u.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1-7
Financial Institutions and
Banking
• Financial Intermediaries: institutions that borrow funds
from people who have saved and make loans to other
people:
– Banks: accept deposits and make loans
– Other Financial Institutions: insurance companies, finance
companies, pension funds, mutual funds and investment
banks
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1-8
Financial Crises
• Financial crises are major disruptions in financial
markets that are characterized by sharp declines in asset
prices and the failures of many financial and
nonfinancial firms.
• Severe financial crises typically spill over into the real
economy.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1-9