Chapter 11
Cardiovascular System
Copyright © 2008, 2005 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Introduction – page 398
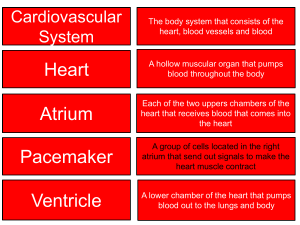
• Cardiovascular System: delivers oxygen
and nutrients to cells of body tissue
–Heart (muscular pump)
–Blood vessels (fuel line and
transportation network)
1
2
BLOOD VESSELS
• Arteries are the vessels that lead away from the
heart.
• Veins are thinner walled vessels compared to
arteries. They move deoxygenated blood toward
the heart from the tissues.
• Capillaries are the smallest vessels. They form
the point of exchange for oxygen and nutrients
into body cells and waste products coming from
body cells.
3
BLOOD VESSELS
4
Blood circulation / systemic
circulation page 400
5
Major vessels – page 401
6
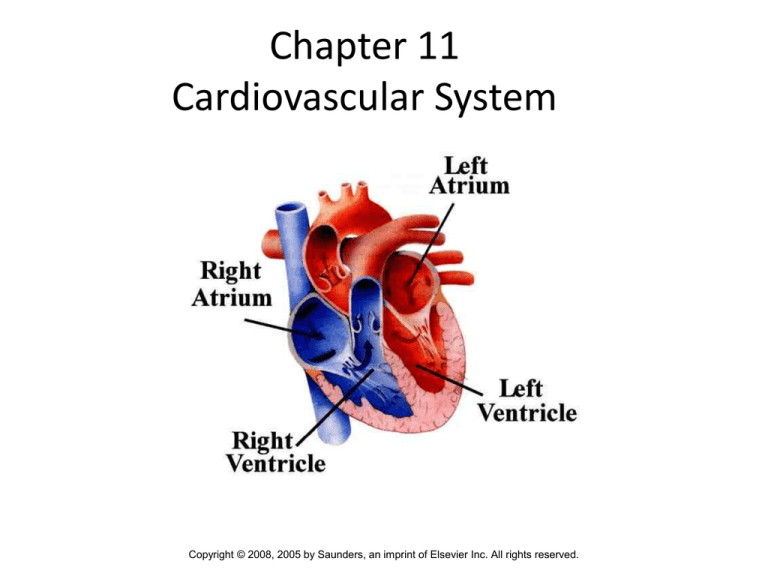
Anatomy of the heart – page 403
7
Major valves of the heart
• tricuspid valve (cusps are flaps of the
valves): between right atrium and right
ventricle
• pulmonary valve: between right ventricle
and pulmonary artery
8
Major Valves of the Heart
• mitral valve: between left atrium and the
left ventricle
• aortic valve: between left atrium and
aorta
9
10
Pathway of blood through the heart
– page 404
11
HEARTBEAT
• Two phases of the heartbeat:
• diastole: relaxation
• systole: contraction
– The diastole-systole cardiac cycle occurs between 7080 times per minute (100,000 times per day).
– The heart pumps 3 ounces of blood with each
contraction. This means that about 5 quarts are
pumped per minute (75 gallons an hour and about
2000 gallons a day).
12
Heart sounds
Closure of valves associated with sounds “lubbdubb, lubb-dubb”
• lubb: closure of the tricuspid and mitral valves
at the beginning of systole
• dubb: closure of the aortic and pulmonary
valves at the end of systole
• murmur: abnormal heart sound caused by
improper valve closure
13
PHASES OF THE HEARTBEAT
14
15
CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART
– page 405-406
sinoatrial node (SA node): pacemaker
of the heart.
pacemaker: origin of electrical impulse
causing walls of the atria to contract and
force blood into the ventricles (ending
diastole)
16
CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART
• atrioventricular node (AV node): This
sends the excitation wave to a bundle of
specialized fibers called atrioventricular
bundle or Bundle of His.
• Bundle of His (pronounced “hiss”): Helps
form conduction myofibers that extend to
ventricle walls and stimulate them to
contract, beginning systole. A short rest
period follows.
17
CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART
• The pacemaker begins wave of excitation
again.
• ECG or EKG (electrocardiogram): The
record used to detect electrical changes
in heart muscle as the heart beats.
18
CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART
19
Electrocardiogram – page 407
20
Electrocardiogram – page 407
• P wave = spread of excitation wave over the
atria just before contraction;
• QRS wave = spread of excitation wave over the
ventricles as the ventricles contract;
• T wave = electrical recovery and relaxation of
ventricles.
• A heart attack (myocardial infarction or MI)
can be recognized by an elevation in the S-T
segment of the ECG.
21
Electrocardiogram
22
Electrocardiogram
23
BLOOD PRESSURE
• Blood pressure: The
force that blood
exerts on arterial
walls.
• Measured using
sphygmomanometer
24
BLOOD PRESSURE
• Expressed as a fraction:
systolic pressure / diastolic pressure
–example: 120/80 mm Hg
25
Vocabulary pages 408-409
• Aorta – largest artery in the body
• Atrium – One of two upper chambers of the
heart.
• Mitral Valve – Valve between left atrium and
left ventricle
26
COMBINING FORMS
AND TERMINOLOGY – page 409 - 410
Combining Form
Meaning
• angi/o
vessel
– angiogram, angioplasty,
• aort/o
aorta – largest artery
in the body
– Aortic stenosis
• arter/o
artery
- Arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
27
Cardiac angiogram
28
• ather/o
yellowish plaque
–Atherosclerosis – yellow plaque containing
cholesterol and lipids are found within the
lining of the artery
• atri/o
atrium
–Atrial – referring to the upper heart
chambers
29
Combining forms and terminology
Combining Form
Meaning
• brachi/o
brachial artery
arm
• cardi/o
cardiomegaly
heart
• cholesterol/o
cholesterol
30
Normal heart size and cardiomegaly
31
Combining forms and terminology
• Combining Form
Meaning
• coron/o
coronary arteries
heart
• cyan/o
cyanosis
blue
• myx/o
mucus
32
Combining Forms and Terminology
Combining Form
• ox/o
•
hypoxia
Meaning
oxygen
• pericardi/o
pericardium
pericardiocentesis
• phleb/o
phlebotomy
vein
33
34
Combining Forms and Terminology
Combining Form
Meaning
• sphygm/o
•
sphygmomanometer
pulse
• steth/o
•
stethoscope
chest
• thromb/o
thrombolysis
clot
35
Combining Forms &Terminology – p. 412
Combining Form
Meaning
• valvul/o
mitral valvulitis
valve
• valv/o
tricuspid valve
valve
• vas/o
vasoconstriction
vessel
36
• Combining Form
Meaning
• vascul/o
vascular
vessel
• ven/o, ven/i
venous
vein
• ventricul/o
interventricular
ventricle
37
QUICK QUIZ:
1. The double-layered
membrane surrounding the
heart is the ___________
A. pericardium
B. arteriole
C. endocardium
D. endothelium
38
QUICK QUIZ:
2. The contraction phase of the
heartbeat is called
_________
A. diastole
B. vena cava
C. systole
D. septum
39
PATHOLOGY: THE HEART AND BLOOD
VESSELS – page 412
HEART
arrhythmias
• heart block (atrioventricular block)
• Flutter
• fibrillation
40
Atrial and Ventricular Fibrillation
41
PATHOLOGY:THE HEART – page 415
congenital heart disease
• coarctation of the aorta (CoA)
• patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
• septal defects (ASD and VSD)
• tetralogy of Fallot
42
Coarctation of the aorta
43
44
VSD
45
Tetraology of Fallot
46
PATHOLOGY: HEART page 417
congestive heart failure (CHF): The heart is
unable to pump the required amount of
blood.
• In U.S., primarily the result of high
blood pressure and coronary artery
disease (see next slide)
• Results in pulmonary edema
• Fatal if untreated
47
CHF
48
PATHOLOGY: Heart – page 417
coronary artery disease (CAD)
–Atherosclerosis
• thrombotic occlusion
(occlusive/mural)
• ischemia
• necrosis
• infarction
49
CAD - Plaque
50
51
Pathology Heart – page 419
–Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) –
caused by myocardial ischemia
• unstable angina – chest pain
• myocardial infarction (MI)
52
PATHOLOGY: Heart – page 419
Drug therapies for CAD
• nitrates (nitroglycerin)
• aspirin
• beta-blockers
• ACE inhibitors
• calcium channel blockers
• statins
53
54
PATHOLOGY:
THE HEART AND BLOOD VESSELS
Coronary artery disease
Surgical therapies for CAD
• coronary artery bypass grafting
(CABG)
• percutaneous coronary intervention
(PCI)
55
56
Acute MI
57
PATHOLOGY:Heart – page 420
endocarditis – inflammation of inner lining of heart
caused by bacteria
hypertensive heart disease
mitral valve prolapse (MVP) – improper closure
Murmur – extra heart sound between beats
Pericarditis
Rheumatic heart disease
58
PATHOLOGY: Blood Vessels p 421 - 422
–aneurysm
–deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
–hypertension (HTN)
–peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
–Raynaud disease
–varicose veins
59
60
61
62
QUICK QUIZ:
3. Which arrhythmia refers to rapid,
random, inefficient and irregular
contractions of the atria and
ventricles (350 beats or more per
minute?
A. fibrillation
B. flutter
C. bradycardia
63
LABORATORY TESTS – 425
• BNP test – brain natriuretic protein
– Secreted when heart is overloaded. Diureitc
• lipid test profile
– measures cholesterol and triglycerides in blood
• lipoprotein electrophoresis
– separation of LDL and HDL in blood sample
• serum enzyme tests
– Chemical measured in blood as evidence of heart
attack. (CK and troponin)
64
CLINICAL PROCEDURES: DIAGNOSTIC
X-Ray
– angiography and arteriography
– computerized tomography
angiography
– digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
– Electron beam computed tomography
(EBCT or EBT)
65
CLINICAL PROCEDURES:
DIAGNOSTIC
Ultrasound Tests:
• Doppler ultrasound
• echocardiography (ECHO)
66
Echo Cardiogram
67
CLINICAL PROCEDURES: DIAGNOSTIC
Nuclear Cardiology
– positron emission tomography (PET) scan
– technetium (Tc) 99m Sestamibi scan
(Cardiolite)
– Thallium-201 scan
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
– cardiac MRI
68
Cardiolite stress test
69
CLINICAL PROCEDURES: DIAGNOSTIC
Other diagnostic procedures:
– cardiac catheterization
– electrocardiography (ECG,
EKG)
– Holter monitoring
– stress test
70
71
72
CLINICAL PROCEDURES:
DIAGNOSTIC
• Identify the normal sinus rhythm and
arrhythmias
73
CLINICAL PROCEDURES: DIAGNOSTIC
A Normal sinus
rhythm. Notice the
regularity of the P,
QRS, and T waves.
B Atrial flutter. Notice the
rapid atrial rate (P
wave) compared to the
slower ventricular rate
(ARS).
74
• C Atrial fibrillation.
P waves are replaced
by irregular and rapid
fluctuations.
• D Ventricular
tachycardia.
• The rhythm is regular,
but the atria are not
contributing to
ventricular filling and
blood output is poor.
75
CLINICAL PROCEDURES
• cardioversion (defibrillation)
• Endarterectomy – surgical removal of plaque
from the inner layer of an artery
• extracorporeal circulation
• heart transplantation
• thrombolytic therapy (tPA, streptokinase)
76
77
78
79
Defibrillation
80
81
CLINICAL PROCEDURES:
DIAGNOSTIC
• Coronary artery bypass
graft (CABG) surgery. A section of a vein is
removed from the leg
and anastomosed to a
coronary artery to
bypass an area of
arteriosclerotic
blockage.
82
Treatment procedures (cont’d.)
• percutaneous coronary intervention
(PCI)
• percutaneous transluminal coronary
angioplasty (PTCA)
• stent placement
• laser angioplasty
• atherectomy
83
Laser Angioplasty
84
Atherectomy
A special catheter can scrape out deposits
blocking an artery to open it.
85
86
Abbreviations
• AED – automatic external defbrillator
• DVT – Deep Vein Thrombosis
• EF – Ejection Fraction
• PCI
• CHF
87
Abbreviations – page 432
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Cath
MR
PCI
PVC
HTN
ECG
LDL
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
BBB
CAD
CVP
Vfib
PDA
BP
SOB
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
LMWH
ICD
LVAD
ASD
CABG
ECHO
MVP
88
QUICK QUIZ:
4. Which procedure involves insertion of a
balloon-tipped catheter into a coronary
artery?
A. thrombolytic therapy
B. coronary artery bypass grafting
C. percutaneous coronary intervention
D. endarterectomy
89
Stay Healthy
90
REVIEW SHEET
COMBINING FORMS
Combining Form
Meaning
•
•
•
•
•
vessel
aorta
artery
artery
yellowish
angi/o
aort/o
arter/o
arteri/o
ather/o
plaque
• atri/o
atrium
91
REVIEW SHEET
COMBINING FORMS
Combining Form
Meaning
•
•
•
•
•
•
arm
heart
cholesterol
heart
blue
mucus
brachi/o
cardi/o
cholesterol/o
coron/o
cyan/o
myx/o
92
REVIEW SHEET
COMBINING FORMS
Combining Form
•
•
•
•
•
•
ox/o
pericardi/o
phleb/o
sphygm/o
steth/o
thromb/o
Meaning
oxygen
pericardium
vein
pulse
chest
clot
93
REVIEW SHEET
COMBINING FORMS
Combining Form
Meaning
•
•
•
•
•
•
valve
valve
vessel
vessel
vein
ventricle
valvul/o
valv/o
vas/o
vascul/o
ven/o, ven/i
ventricul/o
94
REVIEW SHEET
SUFFIXES
Suffix
•
•
•
•
•
-constriction
-dilation
-emia
-graphy
-lysis
• -megaly
Meaning
narrowing
widening; stretching;
blood condition
process of recording
breakdown; separation;
destruction; loosening
enlargement
95
REVIEW SHEET
Suffix
Meaning
• -meter
measure
•
•
•
•
•
•
-oma
tumor; mass; fluid collection
-osis
condition; usually abnormal
-plasty
surgical repair
-sclerosis
hardening
-stonosistightening; structure
-tomy
process of cutting
96
REVIEW SHEET
Prefix
Meaning
• a-, an
no; not; without
• brady-
slow
• de-
lack of; down; less; removal
• dys-
bad; painful; difficult;
• endo-
in; within
• hyper-
above; excessive
97
Prefix
REVIEW
SHEET
Meaning
• hypo- deficient; below; under; less than
normal
• inter-
between
• peri-
surrounding
• tachy-
fast
• tetra-
four
• tri-
three
98