Anticipation Guide: “The Spirit of Independence” pages 109-135
advertisement

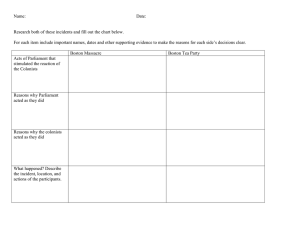
Anticipation Guide: “The Spirit of Independence” pages 109-135 1) Look at Page 110. When does this Chapter take place? 2) What year did the Boston Massacre occur? 1763-1776 1770 3) What World Event occurred in the same year of the Boston Massacre? James Cook explored the coast of Australia 4) What was taking place in Europe at about the same time the First Continental Congress met in America? Louis XVl (16th) becomes king of France 5) 6) Look at the Map on 110 and 111. Which colonial region appears to have the largest area of Loyalist (favored the British) support? Southern Colonies 7) Look at Lesson 2 starting on Page 117. Who was the first colonist killed by the British in the Boston Massacre? SKIM Lesson 2 and find one fact about him. Crispus Attucks he was a dockworker. Part African, Part Native American 8) Look at the picture on 119. Describe King George. Do you think he looks very frightening? 9) Look at the picture on Page 131. List three men who were on the Committee to write the Declaration? Franklin, Jefferson, Livingston, Sherman, Adams 10) Skim Lesson one and find out what the British officials placed on certain paper items to show that a tax had been paid. Draw a sketch below. A seal or Stamp Causes of the Revolution Vocabulary Part One 5.1 and 5.2 ● Banned town meetings in the colonies Boston Massacre-March 5, 1770. Incident where 5 colonists were killed by British soldiers. Used by colonial leaders as propaganda. Boston Tea Party (1773)-Violent demonstration by colonists over the Tea Act. ● Closed Boston Harbor until the colonists paid for the ruined tea. Coercive/Intolerable Acts-laws passed by Parliament to punish the colonists for resisting British authority. Committee of Correspondence-organization that spread political ideas and information through the colonies. Declaratory Act (1766)-Stated that Parliament’s authority was the same in the colonies as in Britain. ● Forced colonists to house British soldiers George Grenville-Britain’s prime Minister King George III-King of England. Quoted as saying, “ We must either master them or totally leave them to themselves”. Believed that the Coercive Acts would destroy the colonies, when in fact, it made them stronger. Loyalists-those who remained loyal to Great Britain Patriots-colonists who chose to fight for independence Petition-Formal Request. The delegates offered Britain a last chance to avoid war by sending a petition. Preamble-The Introduction to a formal document that often tells why the document was written Propaganda –Ideas or information spread to harm or help a cause. Sons of Liberty/Daughters of Liberty-Groups formed to protest British actions and goods. Stamp Act ( 1765) Passed by Parliament. This law taxed almost all of printed materials. All printed materials needed a stamp to show the tax had been paid. Sugar Act-( 1764) Passed by Parliament to lower the tax on molasses, imported by the colonists. Also allowed officers to seize goods from accused smugglers without going to court. Tea Act- Passed by Parliament to protect the British economy and made tea less expensive for colonists. Townshend Acts (1767)-Passed by Parliament to tax imported goods such as glass, tea, and paper.