field of view
advertisement

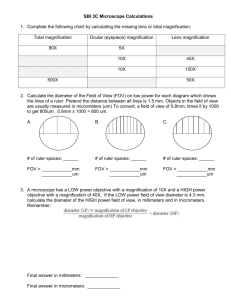
Entry Task Answer the following question on scratch paper & hand in (5pts.): If you look at the following slide under a microscope (40x magnification), sketch the image that you will see (does not have to be to scale) e Field of View (Update TOC) Learning Objective: I will determine the field of view width for each magnification of the microscope and use it to estimate the size of different cell samples so that I can label my sketches with a scale. Field of View (Update TOC) Which is bigger? Can you tell? What is missing??? Field of View (Update TOC) Which is bigger? You need a scale to tell! Field of View The field of view is the circular area that is visible when you look through the microscope. It is difficult to know the size of the objects that we view under the microscope because we can’t measure them with a ruler. 40x What I am actually looking at 100x What I see through the microscope 400x Field of View Size has to be measured indirectly, by comparing the object to something we know the diameter of the field of view! Because the size of objects is different at each magnification, you have to calculate the diameters of the fields of view at each magnification this is also called “calibrating your microscope” 40x What I am actually looking at 100x What I see through the microscope 400x Field of View As you change from the low power objective to the high power objective, the field of view changes. As the magnification increases, the area that you are viewing decreases. Magnification is inversely proportional to field of view In order to determine the size of the object that you are viewing, you need to understand the scale that corresponds to the magnification you are using. This is similar to zooming in on a map http://maps.live.com Day 4: Determining Field of View Copy the table in your science notebook. (from page 257) Eyepiece Magnification (a) Objective Magnification (b) 4x 10x 40x 10x 10x 100x 40x 10x 400x Total Mag. (𝒂 × 𝒃) FOV width diameter (mm) FOV FOV radius FOV radius width (mm) (μm) diameter (μm) You will need this table to estimate the size of the cells that you will be viewing in the next activities. Measuring Field of View width for the scanning objective (4X) We need to find the field-of-view width: using the scanning objective (4x), focus on a clear millimeter ruler. Place the center of a whole number mark on the left side of the field of view, making sure that your ruler edge is exactly across the center of the field. Measuring Field of View width for the scanning objective (4X) Count the number of lines that you see in the field of view. (The distance from the center of one line to the center of the next line is 1mm.) This is the diameter of the field of view for the scanning objective. Write this number in your table. Repeat for the Low Power Objective (10x) Calculating Field of View Width for the high power (40x) objective Total Magnification of high power objective = 400x Total Magnification of scanning objective = 40x 400𝑥 40𝑥 = 10 The magnification increases by a factor of 10 decreases Therefore, the field-of-view width _____________ by a factor of 10. Calculate the field of view width of the high power objective. Since the width is less than 1mm, we need to convert it to µmeters. (1mm = 1000 µ-meters) Calculating the Field of View Width for the low power (10x) objective • Total Magnification of low power objective = 100x • Total Magnification of scanning objective = 40x • 100𝑥 40𝑥 = 2.5 The magnification increases by a factor of 2.5 decreases • Therefore, the field-of-view width _____________ by a factor of 2.5. • Calculate the field of view width of the low power objective. • Convert it to µ-meters (1mm = 1000 µ-meters) Field of View Finally, calculate the field-of-view radius for each of the objectives. How can you use this table to estimate the size of cells that you view? How can we estimate the size of our samples using the microscope… Field of View Finally, calculate the field-of-view radius for each of the objectives. Now, we need to figure out how we can estimate the size of our samples using this information… Estimating the size of samples Work through the penny activity worksheet with your partner. Make sure you show all your work, and sketch your set-up. When you are finished, answer this question in your science notebook: How can you use the FOV table to estimate the size of something you view under the microscope? Be specific in your answer. Homework: Measuring worksheet Homework Tomorrow we will start looking at different types of cells under the microscope.