17.2 Kidneys - YISS-Anatomy2010-11
advertisement

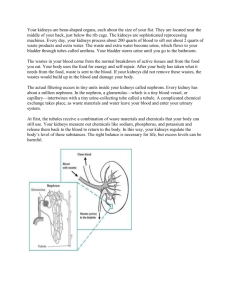
By Yoon Kim and Allen Shin Introduction Urinary System removes certain slats and nitrogenous wastes Helps maintain the normal concentrations of water and electrolyses within body fluids, regulates pH and volume of body fluids, and help control red blood cell production and blood pressure Pair of kidneys – remove substance from blood Pair of tubular ureters- transport urine from kidney Tubular urethra- conveys urine to the outside of the body Kidneys Kidney is a reddish-brown, bean-shaped organ Kidneys are located on either side of the vertebral column and are positioned retroperitoneally (behind parietal peritoneum) Connective tissues and adipose tissues surround the kidneys to hold them in position Structure of the kidneys Medial depression caused by the lateral and medial surface of the kidneys creates a depression into hollow chamber called renal sinus Inside the renal pelvis, a funnel-shaped sac expands from the end of the ureter. Functions of the Kidneys Secretes hormone erythropoietin to help control the rate of red blood cell production Activates vitamin D Helps maintain blood volume and blood pressure by secreting the enzyme renin Renal Blood Vessels Renal arteries : Supply blood to the kidneys Afferent arterioles : the final branches of the interlobular arteries; lead to the nephrons Renal Vein: joins the inferior vena cava as it courses through the abdominal cavity Nephrons Kidney contains 1 million nephrons Nephrons consists of renal corpuscle and renal tubule Fluid flows through renal tubules out of the body Nephrons Renal corpuscle is composed of glomerulus blood capillaries. Glomerulus capillaries filter fluids Thin walled, saclike structure called glomerular capsule surrounds the glomerulus Nephron Blood Supply After passing through the glomerular capillaries, blood enters efferent arteriole Efferent arteriole resists blood flow which then backs up blood into the glomerulus Peritubular capillary system surrounds the renal tubule Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Juxtaglomerular cells: smooth muscle cells attached to the walls of arterioles near glomerulus Juxtaglomerular apparatus: fuction in the control of renin secretion Review Questions Review Questions 1. Kidneys activates vitamin ____ 2. __________: Supply blood to the kidneys 3. _______________: the final branches of the interlobular arteries; lead to the nephrons 4. ________: joins the inferior vena cava as it courses through the abdominal cavity 5. ________ capillaries filter fluids