Transport in Plants
advertisement
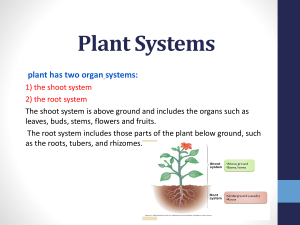
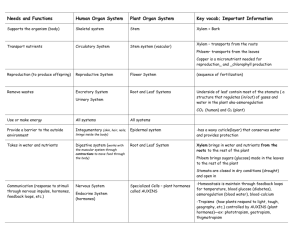
Transport in Plants Objectives: *Describe the passage of water through root, stem and leaf. **Describe the structure of xylem and phloem ***Explain how the structures are suited to their functions H/W Revise for a short test tomorrow the 25th Jan Complete worksheet pg 12 only for 27th Jan 1. Where is the entry point of water and minerals in plants? 2. What is the process by which water enters the plant ? 3. What process is involved in absorption of food from small intestine to blood? 4. Name the tissues transporting water and minerals and sugar in plants. How do plants get what they need? What do plants need for healthy growth? minerals water sunlight oxygen for respiration carbon dioxide for photosynthesis Where do plants get these nutrients? Like all organisms, plants have to get materials for growth from their environment. Plants must then get these nutrients to the part of the plant that needs them. Which cells transport nutrients? Plants contain two types of cell adapted for transportation. Xylem cells transport water and minerals up the stem from the roots to the shoots and leaves. This transport occurs in one direction only. Soil – root – stem – leaves - ? Phloem cells transport sugars produced in the leaves up and down the stem to growing and storage tissues. The cells are arranged in plants as vascular bundles. Both phloem and xylem form continuous systems connecting roots, stems and leaves. How is xylem adapted for transportation? Water and minerals travel in xylem vessels. Xylem vessels are have thick cellulose cell walls, strengthened by lignin stacked end to end . The inside of the cell is hollow. Xylem vessels are dead cells. The thick walls of xylem cells also help support plants. . How is phloem adapted to transportation? Phloem is made of columns of living cells. They transport food, in the form of sugars. Sugars are carried from the leaves to the growing and storage parts of the plants. This movement takes place in both directions. Phloem cells are also called sieve tubes. Cells are joined by small holes in the cell wall at the end of each cell, forming a continuous system. The end cell walls are called sieve plates.