Properties & Changes of Matter
advertisement

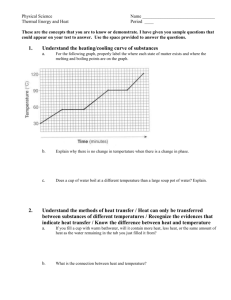
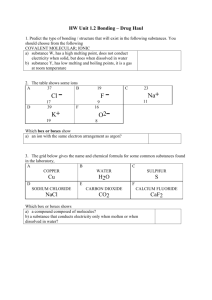
Physical Property- a property that can be observed and measured without changing the identity of the substance. Examples- Viscosity, density, meltingpoint Chemical Property-relates to a substance’s ability to undergo changes that transform it into different substances. Example-Alkali metals are highly reactive to water and halogens to form ionic compounds Chemists use properties to identify and separate matter. More than one property must be used for identification. Intensive Properties – do not depend on the amount of matter present Ex. Melting pt., boiling pt, density, conduct electricity Extensive Properties – depend on the amount of matter present Ex. Volume, mass A physical change does not change the composition or identity of the substance. Examples? Boiled water is still water. All phase changes are physical changes Condens e Freeze Evaporat e Mel t Solid Liquid Gas Sublimation is a process in which a solid changes directly to a gas without going through the solid phase. Examples: dry ice CO2 A chemical change occurs when one or more substances are changed into new substances. Reactants- substances that react Products- substances that form Products have NEW PROPERTIES Indications of chemical change 1.) Production of heat, light, sound, or electricity 2.) Production of a gas 3.) Formation of a precipitate 4.) A change in color 5.) A change in odor Energy Changes • Some changes in matter release energy. • For example, the explosion that occurs when hydrogen and oxygen react to form water is a release of energy. • Heat energy and light energy are released as the reaction takes place. Energy Changes • A change in matter in which energy is absorbed from the surroundings is an endothermic process (heat enters). • EXAMPLES: melting ice & boiling water • When barium hydroxide reacts ammonium nitrate are mixed the test-tube feels cold to touch because energy has been absorbed Energy Changes • A change in matter in which energy is released is an exothermic process (heat exits). • Examples: freezing water & condensation • Burning of paper gives off heat to the surroundings.