Honors Chemistry Syllabus
advertisement
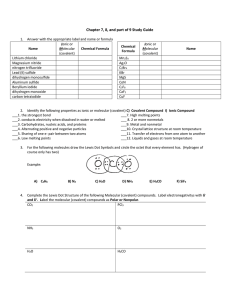
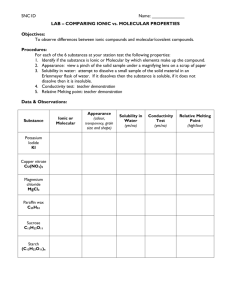
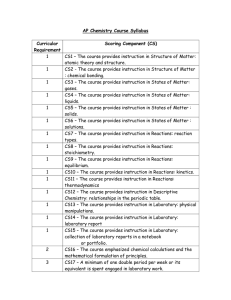
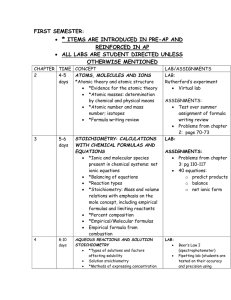
Honors Chemistry Syllabus Modern Chemistry, Holt, et al. (2006) Mr. Lawson Period 1 First 9 weeks August 23, 2010-October 29, 2010 Chapter 1: pages 2-23, and XVII-XXI Areas of chemistry, Lab safety, Lab Equipment Chapter 1: pages 28-31 Scientific Method, Types of Research, Scientific Knowledge Chapter 2: pages 33-57 Measurement, Calculations, Data Representations Chapter 3: pages 6-20 Properties and changes of matter, Types of Matter, Separation of mixtures, and Introduction into the periodic table Chapter 10: pages 329-348 Energy, States of Matter, Phase changes Chapter 3: pages 66-76 Early Ideas/Theories and models of the atom, Subatomic Particles, Ions, Atomic number, Mass number, and Isotopes Second 9 weeks November 3, 2010-January 20, 2011 Chapter 21: pages 680-709 Nuclear radiation, Decay/Half-life, Fusion/Fission Chapter 4: pages 96-110 Light and quantized energy, electromagnetic spectrum, visible spectrum, radiant energy, electron configuration Chapter 5: pages 132-173 Periodic law, Classification of elements, Periodic Trends Chapter 6: pages 174-217 Bonding (ionic, covalent, metallic), structures (ionic and molecular), properties of ionic and covalent molecular and metallic substances, Forces (Van der Waals force, Hydrogen Bonding) Chapter 7: pages 218-236 Writing formulas for ionic compounds, nomenclature for ionic and covalent compounds, and acids 1 Third 9 weeks January 24, 2011-April 1, 2011 Chapter 8: pages 260-297 Describing chemical reactions, types of chemical reactions, balancing chemical reactions Chapter 17: pages 560-587 Collision theory, factors effecting reaction rates, energy diagrams Chapter 3: pages 82-87, Chapter 7: pages 237-249 Introduction to the Mole, Conversions with the Mole, Percent Composition, Empirical and Molecular Formulas, Hydrates Chapter 9: pages 298-237 Introduction into Stoichiometry, Stoichiometric Calculations, Limiting Reactants and Percent Yield Chapter 10: pages 328-341, Chapter 6: pages 203-207 Kinetic Molecular Theory, Forces of Attraction, Properties of Liquids, Properties of Solids Fourth 9 weeks April 5, 2011-June 9, 2011 Chapter 11: pages 360-399 Kinetic Molecular Theory and Gases, Gas Laws, Gas Stoichiometry Chapter 12: pages 400-434, Chapter 13: pages 446-456 Types of Solutions, Factors that affect Solubility, Solution Concentrations, Colligative Properties Chapter 10: pages 342-348, Chapter 16: pages 530-550 Energy, Thermochemistry, Entropy Chapter 14: pages 466-497, Chapter 15: pages 498-529 Properties of Acids and Bases, Acid-Base Theories, Strengths of Acids and Bases, Neutralization Grading scale Exams/Projects: 40% •A grade of 0% is assigned to any student who does not complete an Exam/Project on the date due and/or as the result of an UNEXCUSED ABSENCES. •A scientific calculator is RECOMMENDED and will be a useful tool for exams. Labs: 20% •Labs are performed in class and a grade of 0% is assigned for any lab missed by a student as a result of an UNEXCUSED ABSENCE. •A one-time lab fee of $10.00 is due the week of September 13, 2010. Quizzes: 15% •Quizzes are taken in class and a grade of 0% is assigned for any quiz not turned in or missed by a student as a result of an UNEXCUSED ABSENCE. 2 Class work: 15% •Class work is completed in class and a grade of 0% is assigned for any assignment that is not turned in on the date due or missed as a result of an UNEXCUSED ABSENCE. Homework: 10% •Homework will be assigned on a regular basis and will be graded as follows: Check+ is equivalent to 100%: all homework problems were given a REASONABLE effort to complete. Check is equivalent to 85%: all homework problems partially complete. Check – is equivalent to 70%: minimal effort to complete homework problems. •For each SCHOOL DAY that a homework assignment is late a 10% grade deduction will be applied. No homework will be accepted that is more than three (3) SCHOOL DAYS late. This deduction will not be applied to homework that is turned in late as the result of an EXCUSED ABSENCE. **TOPICS COVERED DURING THE THIRD AND FOURTH 9 WEEKS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE BASED ON THE LENGTH OF FCAT SCIENCE CRUNCH TIME ACTIVITIES AND OTHER FACTORS. 3