influent
advertisement

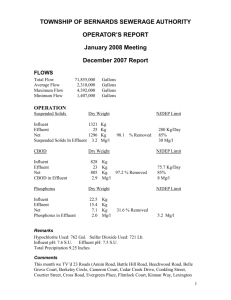
Use of Ultrafiltration for Mercury Removal CMS Land Company Little Traverse Bay Environmental Project (LTBEP) (Bay Harbor Development, Petoskey, MI) 2011 MWEA Annual Conference Shanty Creek Resort, Bellaire MI June 28, 2011 Prepared by: Environmental Consulting & Technology, Inc. Peter F. Hill, P.E. Jeremy S. Lewandowski Mark D. Mikesell, Ph.D. William E. Stone Environmental Consulting & Technology, Inc. 2200 Commonwealth Blvd., Ste. 300 Ann Arbor, MI 48105 Traverse City, MI 49684 Ph: (734) 769-3004 Ph: (231) 946-8200 Fax (734) 769-3164 Fax: (231) 946-8208 SUMMARY OF LITTLE TRAVERSE BAY ENVIRONMENTAL PROJECT (LTBEP) GOALS & RESULTS • Characterize Cement Kiln Dust (CKD) Leachate for Hg, TSS & other parameters. • Determine effectiveness of Ultrafiltration (UF) Technology to Treat CKD Leachate. • Characterize Effluent from UF to Determine Compatibility with WQS. • Demonstrate CKD Leachate can be Treated & Discharged to Little Traverse Bay (LTB). • Assist CMS Land Co. (CMSL) in obtaining Permits/Authorizations to discharge Leachate. • UF achieved 97% Hg Removal (1.8 ng/L achieved). • MDEQ considers UF as Best Available Technology (BAT) for this site. 2 BAY HARBOR – SITE LOCATION Little Traverse Bay (Lake Michigan) • CMSL Bay Harbor Site located 5 miles west of Petoskey • Located on south shore of Little Traverse Bay, Lake Michigan. Photo Source: Google Earth. 3 Emmet County HISTORICAL USE OF SITE CEMENT-MANUFACTURING TIMELINE: • 1917 - Petoskey Portland Cement Co. formed. • 1954 – Penn-Dixie Cement Co. purchased land. • 1980 – Cement-Making Operations end Penn-Dixie files for bankruptcy. Photo Source: http://www.flickriver.com/photos/odalaigh/ 1532444089/ Source: Tip of the Mitt Watershed Council, www.watershedcouncil.org. 4 CEMENT MAKING PROCESS & CKD • Leftover material from grinding /heating limestone + other raw materials is CKD. • Leachate formed when water contacts CKD…caustic & contains heavy metals (mercury, arsenic, & lead). • Estimated 2.5 Million CY of CKD waste left behind. Source: Tip of the Mitt Watershed Council, www.watershedcouncil.org. Photo Source: Friends of the Jordan, Concerning the Bay Harbor Cercla Site, Presentation by Edward E. Timm, Ph.D., P.E. 5 BAY HARBOR – RE-DEVELOPMENT OF SITE • 1993 – Bay Harbor Resort Properties Ltd. & CMSL team to develop site. 6 Photo Source: Friends of the Jordan, Concerning the Bay Harbor Cercla Site, Presentation by Edward E. Timm, Ph.D., P.E. ISSUES WITH SITE • Oct. 1988 – Caustic groundwater found leaching into LTB. • 1989 – East & West CKD areas show detectable concentrations of arsenic, chromium, copper, lead, nickel, selenium and zinc. Source: Tip of the Mitt Watershed Council, www.watershedcouncil.org. Photo Source: Friends of the Jordan, Concerning the Bay Harbor Cercla Site, Presentation by Edward E. Timm, Ph.D., P.E. 7 ISSUES WITH SITE (CONT’D) • 1994 – CKD piles contoured, covered with topsoil & turned into golf course. • 1997 – Leachate still reaching LTB @ Seep 2… Seepage collection line installed. • Collected Leachate transported to Petoskey’s WWTP. • 2003 – CMSL constructed Pre-Treatment Facility to ↓ pH of Leachate & built discharge to Petoskey’s sanitary sewer. Source: Tip of the Mitt Watershed Council, www.watershedcouncil.org. Photo Source: Friends of the Jordan, Concerning the Bay Harbor Cercla Site, Presentation by Edward E. Timm, Ph.D., P.E. 8 ISSUES WITH SITE (CONT’D) • Petoskey WWTP complications… Leachate drained directly to LTB for several months. • Sept. 2004 – HIGH pH readings in LTB lead to Public Health Advisory from NW Michigan Health Dept. & restricted access for > 1 mile of BH shoreline. • CMSL accepts environmental liability due to prior agreements. • Feb. 2005 – Admin. Order of Consent issued by EPA… CMSL to take immediate remedial action & ultimately “remove, isolate or contain” the CKD. Source: Tip of the Mitt Watershed Council, www.watershedcouncil.org. 9 REMEDIATION EFFORTS: COLLECT & TREAT BAY HARBOR DEVELOPMENT PRE-TREATMENT FACILITY Photo Source: Google Earth. Short-Term Response: Collect & Pre-Treat 1. System of collection drains/trenches: 2. Pump to Pre-Treatment • Seep 1 Facility (↓ pH) • Seep 2W (Seep 2 + West CKD) • Edge Drain • Total Leachate Collection System (TLC) Ongoing Efforts: • Plan for extensive testing of hydrology/geology. • Up-gradient groundwater interceptor wells. 10 COLLECTION DRAIN LOCATIONS – Lake Michigan – (Little Traverse Bay) Map Source: Barr Environmental 11 LEACHATE INTERCEPT SYSTEM Photo Source: Friends of the Jordan, Concerning the Bay Harbor Cercla Site, Presentation by Edward E. Timm, Ph.D., P.E. 12 BAY HARBOR DEVELOPMENT PRE-TREATMENT FACILITY 13 BAY HARBOR DEVELOPMENT PRE-TREATMENT FACILITY (CONT’D) • Automated Acid Injection System • Loading/ Transport System • Frac Tanks to Store Pre-Treated Leachate) 14 BAY HARBOR DEVELOPMENT PRE-TREATMENT FACILITY (CONT’D) • pH-neutralize ~ 150,000 gpd w/ concentrated H2SO4. • Storage in Frac Tanks. • Treated leachate transported to deep well injection facility near Gaylord, MI. • Leachate previously transported to GT Co. Septage Treatment System (discharges to TC WWTP). • Period when leachate transported to Petoskey’s WWTP. 15 BAY HARBOR – LEACHATE • Dark brown in color • Brown color, TOC & COD due to dissolved organic acids…fulvic, humic, tannic, etc. • CKD originally placed in cedar swamp. • Caustic (pH >12) • TDS = 2,700 to 21,000 mg/L • TSS = Non-Detect to 17 mg/L • Mercury = 15 to 544 ng/L • Copper = 19 to 84 µg/L • Vanadium = 42 to 130 µg/L • High COD & TOC • Low BOD 16 • pH, TDS & metals due to groundwater flow through CKD piles. BAY HARBOR – LEACHATE (CONT’D) • COSTLY $$ !! • Trucks run 24/7/365 disposal to deep well injection. • Public opposition to both deep well injection & constant trucking. • CMSL begins to explore other options!! 17 PREVIOUS/ON-GOING STUDIES • CMSL has done extensive research on Hg treatment & disposal tech., including: • On-site deep well injection; • Discharge into municipal sanitary sewer (City of Petoskey); • Creation of interceptor trenches, collection and hauling of waste to off-site deep well (Current Operation); • On-site collection and treatment with point source discharge to Little Traverse Bay; • Adsorption Technology • Ultrafiltration Technology • Ultrafiltration is seen as the most promising Best Available Technology (BAT). 18 PREVIOUS STUDIES U.S. EPA • Aug. 2007 - Treatment Technologies for Hg in Soil, Waste and Water, U.S. EPA Office of Superfund Remediation and Technology Innovation, Washington D.C. PARSONS GROUP • 2005 - Pilot scale study conducted over a 6-week period (Nov. to Dec.). • Demonstrated that Pretreatment (pH adjustment ) + UF could reduce Hg from 700 ng/L to 200 ng/L. • Hg reduced further to 20-30 ng/L when Coag./Precip. added. 19 ON-GOING STUDIES CAPTUR TECHNOLOGY • On-going evaluation of proprietary system using coag./floc. and adsorption technology to remove Hg. • Promising effluent Hg concentrations < 1.3 ng/L (WQS). • If technology is effective & efficient @ full-scale, Captur technology will likely be used at Bay Harbor. 20 SUMMARY OF UF TECHNOLOGY • Low pressure (5 psig to 150 psig) process . • Uses semi-permeable tubular membrane. • Removes high MW components/suspended solids from aqueous solutions. • Low MW components pass through UF membranes. • Membranes are physical barrier that permits passage of materials up to a certain size/shape/character. 21 SUMMARY OF ECT PILOT STUDY • Nov. 2009 - ECT begins UF pilot treatment study. • Changes in volume/quality of Leachate since Parsons study. • New waste stream – TLC. • Used technology & operating conditions determined as optimal by Parsons study: • pH-adjustment using 98% H2SO4 • Coag.-Floc. w/ Aluminum sulfate (alum) • Cationic polymer floc. aid (metal precipitant) • UF • Provided additional data for National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) Permit Application. • Koch Membrane Systems (KMS) provided UF Pilot System & Operational/Technical assistance. 22 INFLUENT COLLECTION • 4 Influent Streams • Edge Drain • TLC • Seep 1 • Seep 2W (Seep 2 + WCKD) 23 “COMBINED” INFLUENT Influent Daily Avg. Flow Rate (GPM) Percent (%) of Total Daily Flow Flow1 (GPM) Flow1 (GPH) Flow1 (mL/MIN) Batch2 (gal) pH (Standard Units; S.U.) Hg (ng/L) Seep 1 38.29 39.0% 2.7 163.9 10,339.0 117.0 12.5 50 Seep 2W (Seep 2 + WCKD) 51.00 52.0% 3.6 218.3 13,771.7 156.0 12.0 20 Edge Drain 8.09 8.2% 0.6 34.6 2,184.7 24.6 12.5 80 TLC 0.75 0.8% 0.1 3.2 202.5 2.4 13.2 500 Total 98.13 100% 7.0 420.0 26,497.9 300 - - • Batches combined based on daily avg. flow of each stream. 24 INFLUENT METERING/MIXING • 55-GAL. head tanks 25 pH-ADJUSTMENT • ↓ From >12 to 7.5 - 8.5 • 98% H2SO4 • 300-GAL. tank 26 COAGULATION/FLOCCULATION MP Addition Alum Addition 27 ULTRAFILTRATION 28 ULTRAFILTRATION (CONT’D) Process Tank (50 GAL.) Feed/Supply Tank (280 GAL.) 29 STORAGE OF EFFLUENT/CONCENTRATE • 2 x 1,500-GAL. polytanks 30 PILOT TREATMENT – FLOOR PLAN 31 SUMMARY OF UF TECHNOLOGY • Koch Membrane Systems (KMS) provided UF Pilot System & Operational/Technical Assistance. Photo Source: Koch Membrane Systems 32 SUMMARY OF UF TECHNOLOGY (CONT’D) Photo Source: Koch Membrane Systems Photo Source: Koch Membrane Systems 33 Photo Source: Koch Membrane Systems 34 UF PERMEATE/CONCENTRATE LEACHATE/ FEED WATER (INFLUENT) PERMEATE (EFFLUENT) UF CONCENTRATE • ` • Combined Influent • Water, salts, ↓MW constituents • To Discharge 35 • Solutes ↑ than UF membrane pore size • Suspended solids • Circled back to feed tank • Needs disposal UF FLOW – SIMPLE BATCH PROCESS Figure Source: Koch Membrane Systems 36 UF FLOW – MODIFIED BATCH PROCESS Figure Source: Koch Membrane Systems 37 UF FLOW – ONE-STAGE CONTINUOUS PROCESS Figure Source: Koch Membrane Systems 38 SUMMARY OF PILOT RUNS Runs 1 -3: • Used Combined Influent (based on daily avg. flow of each seep). • Purpose: Demonstrated effectiveness to MDEQ, EPA & Stakeholders. 39 SUMMARY OF PILOT RUNS (CONT’D) Runs 4 - 14: • Determined optimum mix of seeps. • Collect WQ & System Operation Data to support full-scale commercial treatment system design. • Used individual seeps, various combinations, various additives, various concentration factors, longer run-times, etc. 40 SUMMARY OF PILOT RUNS (CONT’D) 41 SUMMARY ANALYTICAL DATA • Analysis included: • • • • • • • • COD TDS* TSS* TOC Alkalinity Hardness Anions (incl. Chloride* & Sulfate*) Various individual stream component concentrations… • Heavy metals: Cu* , Hg*, Pb, Ni, Mo*, Se* & V* • Sulfate • salts Note: Asterisk (*) indicates “Constituent of Concern” • Acute & Chronic Toxicity Data 42 ANALYTICAL RESULTS • 97% Hg Removed (Influent 42 to 78 ng/L) (Effluent 1.8 to 8.1 ng/L) • 97% TSS Removed (Influent 13 to 107 mg/L) (Effluent <3.3 to 8.5 mg/L) • 90% Cu Removed (Influent 13 to 49 µg/L) (Effluent <5.0 to 14 µg/L) 43 ANALYTICAL RESULTS • 32% Molybdenum Removed (Influent 76 to 100 µg/L) (Effluent 53 to 140 µg/L) • 30% Selenium Removed (Influent 16 to 23 µg/L) (Effluent 14 to 27 µg/L) • 28% TDS Removed (Influent 4,700 to 7,200 mg/L) (Effluent 4,000 to 8,300 mg/L) • 24% Sulfate Removed (Influent 1,700 to 2,900 mg/L) (Effluent 1,700 to 3,900 mg/L) • 23% Chloride Removed (Influent 330 to 1,100 mg/L) (Effluent 310 to 1,200 mg/L) • Use of both Alum & Metal Precipitant provided best metals removal 44 RESULTS – MERCURY REMOVAL • 97% Hg Removed 45 RESULTS – TSS REMOVAL • 97% TSS Removed 46 RESULTS – COPPER REMOVAL • 90% Copper Removed 47 TCLP RESULTS TOXICITY CHARACTERISTIC LEACHING PROCEDURE: • Effluent Does NOT exceed regulatory limits for hazardous waste. Constituent Abbreviation TCLP Metals Limit (mg/L) Run 1 UF Concentrate 10X TCLP Results (mg/L) Run 2 UF Concentrate 30X TCLP Results (mg/L) Run 3 UF Concentrate 20X TCLP Results (mg/L) Arsenic As 5.0 <0.10 <0.10 <0.10 Barium Ba 100.0 <0.35 0.38 <0.35 Cadmium Cd 1.0 <0.010 <0.020 <0.010 Chromium Cr 5.0 <0.050 <0.050 <0.050 Lead Pb 5.0 <0.050 <0.050 <0.050 Mercury Hg 0.2 0.00025 0.00043 0.00025 Selenium Se 1.0 <0.10 <0.10 <0.10 Silver Ag 5.0 <0.010 <0.010 <0.010 48 FULL-SCALE TREATMENT SYSTEM 49 CONCLUSION • UF System Effective in Removing Hg: • 97% Hg Removal • 1.8 ng/L [Hg] achieved • MDEQ Considers UF To Be Best-Available-Technology In This Case • NPDES Permit Issued for Discharge to LTB • With Hg Limits • With WET Limits • New Treatment Building currently under construction. 50 Little Traverse Bay Environmental Project (LTBEP) (Bay Harbor Development, Petoskey, MI) QUESTIONS/COMMENTS? Prepared by: Environmental Consulting & Technology, Inc. Peter F. Hill, P.E. Jeremy S. Lewandowski Mark D. Mikesell, Ph.D. William E. Stone Environmental Consulting & Technology, Inc. 2200 Commonwealth Blvd., Ste. 300 Ann Arbor, MI 48105 Traverse City, MI 49684 Ph: (734) 769-3004 Ph: (231) 946-8200 Fax (734) 769-3164 Fax: (231) 946-8208