Lenses Worksheet - EMS Secondary Department
advertisement

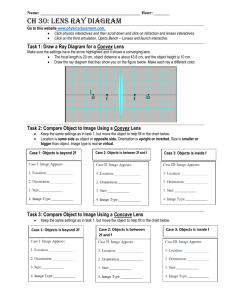
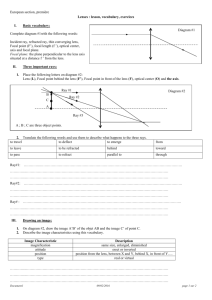
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT IGCSE YEAR 10 PHYSICS LENSES NAME……………………………. ………DATE…………. 1. 2. TASK 1: KEY WORDS Name the two types of lenses. The diagrams below show some pieces of glass. (a) Which of A, B, C and D is (i) a converging lens, ..................................................................................... A B C D (ii) a diverging lens? ............................................................................................... (b) Complete the diagrams below to show what happens to the rays of light when they pass through B. 3. (a) Identify the type of lens below (b) Explain the reason for your answer. 1 4. You are provided with a list of words shown below. Convex Optic centre Converges Concave Focal length Virtual Focal point Refraction Real Principal axis Diverges (a) Complete the following paragraph using the words given above. i. There are two types of spherical lens which are………………………lens and ………………………lens. ii. When a parallel beam of light strikes a lens…………………………...occurs. iii. For a convex lens, the light…………………………………..after refraction and for a concave lens the light………………………..after refraction. iv. A horizontal line passing through the centre of a lens is known as the……………………………. v. The centre of lens is called …………………………….. vi. For a convex lens, …………………………………….is the point where all refracted rays converge and it is …………… vii. For a concave lens, focal point is the point where refracted rays appear to come from. This shows that its focal point is imaginary and ------------------------------. 5. The THREE rules: Principal ray, Central ray and focal ray. Principal ray: A from top of the object and parallel to the principle axis is refracted to the focal point on opposite side. Central ray: A ray from top of object to centre of lens continues straight through. Focal ray: A ray from top of object through focal point on the same side is refracted parallel to the principle axis. On the diagram below, label the principal ray, central ray and focal ray on the diagram. 2 6. On the diagram below, draw the central ray and principal ray, hence determine where the mage will be formed. 7. An object was placed at a point between the lens and the focal point. The image was formed as shown below. Write down 4 properties of this image. (i) ……………………………. (ii) ……………………………….. (iii) …………………………………… (iv) …………………………………. 8. 3 4 9. DESCRIBING THE IMAGE (i) Real: When the rays actually do intersect. (ii) Virtual: Rays of light do not meet. Image formed by imaginary rays. (iii)Diminished: Image is smaller than object. (iv) Magnified: Image is larger than object. (v) Erect: Image is standing upright as the object. (vi) Inverted: Image is upside down. The figure below shows 5 ray diagrams. On diagram (a) to (e), describe the image formed. Write your answers besides each diagram. 5 10. The ray diagrams show rays from the object to the lens as used in different optical instruments. (a) Complete both ray diagrams. On each diagram label the nature of the image formed. A F F Inverted object B F object (b) F Complete the table below to describe the images formed.[2] larger or smaller than object real or virtual A B 11. (a) The diagram shows a lens used as a magnifying glass. The position of the eye is shown and the size and position of an object standing at point O. (i) What type of lens is shown in the diagram? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) (iii) Two points are marked as F. What are these points? What is the name of the straight line which goes through the point F, through the point L at the centre of the lens, and through the point F on the other side? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iv) On the diagram, use a ruler to construct accurately the position of the image. You should show how you construct your ray diagram and how light appears to come from this image to enter the eye. 6 F O L F Eye (v) The image is virtual. What is a virtual image? ........................................................................................................................... 12. (a) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. (i) Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. [2] (ii) Name the point where the rays come together. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) What word can be used to describe this type of lens? ........................................................................................................................... (1) 13. 14. 7 15. 16. 17. 8 18. 9 19. 10 20. 11 12 22. 13 23. 24. 14