Curved Lenses
advertisement

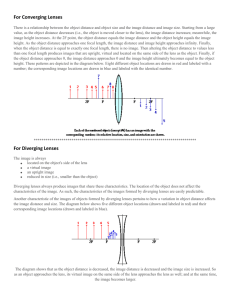
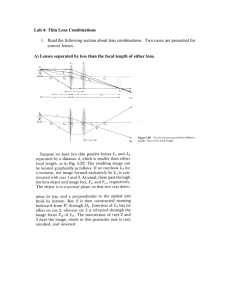
Curved Lenses SNC2P – Optics Lenses • Lenses are thin pieces of glass or plastic that have at least one curved side. There are two basic types of lenses: • convex (converging – cause light rays to be refracted toward the principal axis) Lenses • Lenses are thin pieces of glass or plastic that have at least one curved side. • concave (diverging – cause light rays to be refracted away from the principal axis). From our lesson and demos on refraction we know that light bends when it enters and exits a material. For our purposes, we will understand that lenses are very thin and assume that light refracts only once in the material, at the axis of symmetry. Important Terms • Principal axis - a straight line that passes through the optical centre, O. • Focal point (lenses have 2 because light can pass through in either direction) • The point where light rays converge after refraction is designated the principal focal point - F • The focal point on the other side of the lens is designated the secondary focal point - F’ (“F prime”). • If light were coming from the other direction, F and F’ would be reversed. • Optical centre (O) – centre of lens (vertically and horizontally) • Axis of symmetry – vertical line through optical centre Diagrams Finding Images in Lenses – The Rules Lens Rules: Convex (Converging) Lenses Rules for drawing ray diagrams: 1. A light ray travelling parallel to the principal axis is refracted through the principal focus, F. 2. A light ray travelling toward the secondary focus, F’, refracts parallel to the principal axis. 3. A light ray that passes through the optical centre goes straight through, without refracting. Examples Examples Examples Examples Examples Examples Finding Images in Lenses – The Rules Lens Rules: Concave (Diverging) Lenses Rules for drawing ray diagrams: 1. A ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted as if it had come through the principal focus (F). 2. A ray that appears to pass through the secondary principal focus (F’) is refracted parallel to the principal axis. 3. A ray through the optical centre (O) continues straight through on its path. • All images using diverging lenses have the same characteristics Homework • Complete the lenses drawing practice sheet