Section 1.1.2 * *Introduction to Forces (Unbalanced & Balanced)
advertisement

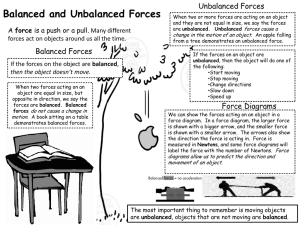
Section 1.1.2 – “Introduction to Forces (Unbalanced & Balanced)” 7.P.1.2 Explain the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces acting on an object (including friction & gravity). KAHOOT MINI QUIZ – “INTRODUCTION TO FORCES!” Lesson Objectives By the end of this lesson, students will be able to: I. Explain that motion is a result of forces acting on an object - Describe how objects at rest resist a change in their position or direction of motion. - Describe how objects in motion resist a change in their position. - Use knowledge of forces and inertia to analyze how an object moves. - Classify that forces are at work in a given situation such as balanced or unbalanced. II. Explain that changes in motion are due to unbalanced forces acting on an object III. Describe Newton’s First Law of Motion IV. Create examples of real life situations where forces are at work. V. Briefly describe how changes in velocity, acceleration, and speed affect motion. Lesson Questions By the end of this lesson, students will be able to answer: I. What kinds of forces can act on an object? II. What happens when two unbalanced forces act on an object? III. Why does an object change its position when there is unbalanced force acting on it? What Kinds of Forces Act on an Object? There are many different kinds of forces. I. Contact forces: are forces that occur when two masses are directly touching, such as the force of friction. II. Frictional forces: oppose motion, and are dependent on the nature of the materials in contact, the mass of the materials in contact, and other forces acting on the materials in contact. III. Forces that can act from a distance are the electrical force, magnetic force, and gravitational force. Forces that can act from a distance tend to be stronger as the distance between interacting objects decreases. What Kinds of Forces Act on an Object? • On Earth’s surface, the forces of gravity and friction act on all moving objects, so moving objects do not stay in motion for very long. • Gravity pulls objects downward. • Friction acts against the direction of movement. • For example, when you throw a ball on Earth’s surface the ball falls back to Earth and stops rolling on the ground due to the unbalanced forces of gravity and friction. However, if you threw a ball in space it would continue to move in a straight line until an unbalanced force acted on the object to change its motion. I think Bernie wants to play “fetch”. What types of forces allow bernie to play fetch on Earth? How is Bernie able to run after the ball? What Kinds of Forces Act on an Object? Frictional Force Gravitational Force What happens when two unbalanced forces act on an object? • A force is a push or a pull. How do you suppose a vector diagram should look according to the car? • When a force is applied to one object by a Include Friction, Gravity, and the second object, the first object will exert an “Motor” of the car. equal and opposite force on the second object. If there is only one force acting on an object, that object will move in the direction of the applied force. • If there are multiple forces acting on an object from different directions, the net movement of the object will be in the direction indicated by the sum of the vectors corresponding to each force. • Note that this net movement will not be in the direction of the strongest force. Why does an object change its position when there is unbalanced force acting on it? • A force is a push or a pull • Objects move due to forces that act on an object. • When all the forces acting on an object are balanced, the object’s motion does not change. • This phenomenon is described by Newton’s First Law of Motion, which states that an object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will continue moving in a straight line unless an unbalanced force acts on the object. • This tendency to resist a change in motion is called inertia. It takes an unbalanced force to overcome inertia and change an object’s motion. Does the coin have inertia? Explain your reasoning? Common Misconceptions • Students may believe that force is a property that an object has, and when it stops moving, it has run out of force. In fact, a force is an interaction between two objects. • Students may believe that a force must be constantly applied to an object for that object to stay in motion. In fact, according to the law of inertia an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. This means that, barring other outside forces, an object that is moving does not require the constant application of a force in the direction of motion. Check for Understanding: StudyJams – Forces & Motion • Complete the studyjams activity – Forces & Motion • View the video, and take notes on a pages document (you may keep the pages document for future reference) • Download the pages document labeled “StudyJams – Forces & Motion Mini-Quiz” on the class weebly website! Small Group Instructional Activities I. Exploration: “Monster Truck Pull” II. Reading Exploration: “Look Out Below” Make sure you download the pages document on the class website link! Section 1.1.2 Review I. What kinds of forces can act on an object? II. What happens when two unbalanced forces act on an object? III. Why does an object change its position when there is unbalanced force acting on it? That was a lot for one day! Let’s take a break!!!