Radioactive Decay Overview Read this document and try the
advertisement

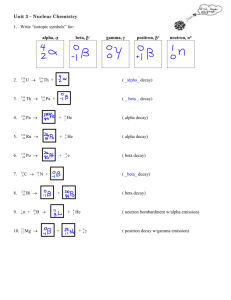
Radioactive Decay Overview Read this document and try the practice problems. 1. What is RADIOACTIVITY? o Radioactivity is when an unstable nucleus emits particles or electromagnetic rays in order to gain stability o This emission actually changes the element o The emission is called RADIATION 2. What is RADIATION? o Radiation is ENERGY in the form of PARTICLES or ELECTROMAGNETIC RAYS released from radioactive atoms o The Particles released are Alpha, Beta, and Neutrons. o The Energy released are Gamma Rays. 3. Alpha Particles ( α ): o The largest of the particles o Helium nucleus (2 protons and 2 neutrons) o Symbol: α or 42𝐻𝑒 o Shielding: can be stopped by a piece of paper, a layer of skin, a few centimeters of air 234 4 o 238 92𝑈 90𝑇ℎ + 2𝐻𝑒 4. Beta Particle (β ) o An extra neutron from the nucleus that converts from a neutron into a proton and electron (over charge is still neutral) o The converted proton stays in the nucleus but the electron is ejected from the nucleus as a β particle o Usually accompanied by the emission of a gamma ray as well if the emission of the β doesn’t rid the nucleus of enough of the extra energy o Symbol: β or −10𝑒 − or −10𝛽 − o Shielding: few millimeters of aluminum or plastic, or a block of wood 90 0 o 38 𝑆𝑟 90 39𝑌 + −1𝑒 − 5. Gamma Ray ( γ ) o High-energy WAVES which can travel long distances and have a great ability to penetrate other materials o Often used in medical applications for treatment of cancer or equipment sterilization o They do NOT have the ability to make other materials radioactive o Occur after alpha or beta emissions as a way for the element to release energy (not to change the nucleus) o Symbol: γ o Shielding: several feet of concrete or a few inches of dense material (such as lead) 137 o 137 56𝐵𝑎 56𝐵𝑎 + γ 1 6. Neutrons ( 0𝑛) o Elements with atomic masses over 90 can undergo SPONTANEOUS FISSION in which the unstable nucleus will spontaneously break apart into smaller nuclei releasing with it one or more NEUTRONS o These neutrons are high-speed nuclear particles with exceptional penetration ability o The only form of radiation that can actually make another substance RADIOACTIVE 1 o Symbol: 0𝑛 o Shielding: VERY thick hydrogen-containing materials (such as concrete and water) 140 108 1 o 252 98𝐶𝑓 54𝑋𝑒 + 44𝑅𝑢 + 4 0𝑛 Practice Questions: 1. Complete the blanks with the correct type of particle or ray. Remember that matter and energy are conserved this means that the total mass on the left side and the right side of the equation should be equal. o 232 92𝑈 → 228 90𝑇ℎ + ______ o 144 58𝐶𝑒 o ______ → o 222 86𝑅𝑛 → ______ + −10𝑒 99 43𝑇𝑐 +𝛾 → ______ + o 129 53𝐼 → 129 54𝑋𝑒 + ______ o 239 94𝑃𝑢 o 237 92𝑈 → 237 93𝑁𝑜 + ______ o 236 92𝑈 92 → 36 𝐾𝑟 + → ______ + 42𝐻𝑒 4 2𝐻𝑒 2. Write the balanced decay reaction for the following: o 45 20𝐶𝑎 (beta decay) o 210 84𝑃𝑜 (alpha decay) o 234 94𝑃𝑢 (alpha decay) o 24 11𝑁𝑎 (beta decay) o 235 92𝑈 (neutron decay making cesium-140, rubidium-92, and 3 neutrons) 141 56𝐵𝑎 + ________