HW: Intro to Density Worksheet
advertisement
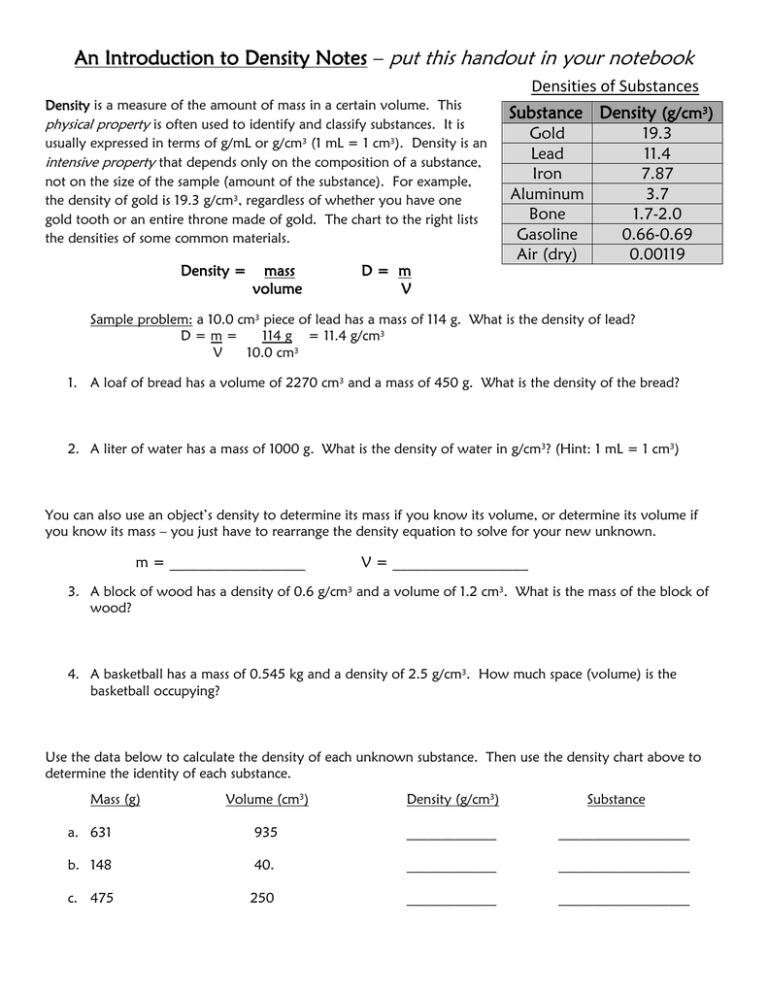
An Introduction to Density Notes – put this handout in your notebook Density is a measure of the amount of mass in a certain volume. This physical property is often used to identify and classify substances. It is usually expressed in terms of g/mL or g/cm3 (1 mL = 1 cm3). Density is an intensive property that depends only on the composition of a substance, not on the size of the sample (amount of the substance). For example, the density of gold is 19.3 g/cm3, regardless of whether you have one gold tooth or an entire throne made of gold. The chart to the right lists the densities of some common materials. Density = mass volume D= m V Densities of Substances Substance Density (g/cm3) Gold Lead Iron Aluminum Bone Gasoline Air (dry) 19.3 11.4 7.87 3.7 1.7-2.0 0.66-0.69 0.00119 Sample problem: a 10.0 cm3 piece of lead has a mass of 114 g. What is the density of lead? D=m= 114 g = 11.4 g/cm3 V 10.0 cm3 1. A loaf of bread has a volume of 2270 cm3 and a mass of 450 g. What is the density of the bread? 2. A liter of water has a mass of 1000 g. What is the density of water in g/cm3? (Hint: 1 mL = 1 cm3) You can also use an object’s density to determine its mass if you know its volume, or determine its volume if you know its mass – you just have to rearrange the density equation to solve for your new unknown. m = __________________ V = __________________ 3. A block of wood has a density of 0.6 g/cm3 and a volume of 1.2 cm3. What is the mass of the block of wood? 4. A basketball has a mass of 0.545 kg and a density of 2.5 g/cm3. How much space (volume) is the basketball occupying? Use the data below to calculate the density of each unknown substance. Then use the density chart above to determine the identity of each substance. Mass (g) Volume (cm3) Density (g/cm3) Substance a. 631 935 _____________ ___________________ b. 148 40. _____________ ___________________ c. 475 250 _____________ ___________________





