Politics of the Gilded Age
advertisement

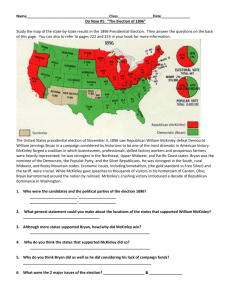
Politics of the Gilded Age Mr. Owens Essential Questions • How did big business influence government economic policies including tariffs, currency, corporate expansion, and promotion of laissez-faire, and how did this eventually lead to calls for reform? • What inspired the creation of the People’s (Populist) Party and what was their agenda? Political Stalemate Causes of “Politics of Equilibrium” 1. Conservative government: “Laissez-Faire” Social Darwinism for both parties, weak presidents 2. Divided government Democrats controlled 8 of 10 elections for House, 5 out of 6 presidents Republican 3. Party loyalty w/ well-defined voting blocs 4. Party patronage: controlled by Party Bosses like Roscoe Conkling (Stalwarts) & James Blaine (Halfbreeds) 5. Popular campaigns: beer halls, parades & brass bands near 80% voter turnout Republicans: North, “waving the bloody shirt” support from business, middle class, WASPs, Blacks, tariffs, temperance/prohibition Democrats: Southern whites, in North urban political machines (Tammany Hall), immigrants, nonProtestants, working class Presidential Politics 1877-1885 • Rutherford B. Hayes (1876-1881) – ended Reconstruction attempted to end corruption – fired Chester Arthur • James Garfield (1881) “Halfbreed” frustrated w/patronage, assassinated by Charles Guiteau in 1881 • Chester A. Arthur (1881-1885) Stalwart, surprise: signed Pendleton Act of 1881 =civil service reform through merit examinations • Weak leadership in Congress – most prominent John Sherman (brother of William), Thomas “Czar” Reed bully & Speaker from Maine, James Blaine Sen. of Maine party boss pushed Republicans away from civil rights and toward business Presidential Politics 1885-1893 • 1884 Election: Republican choice of Boss Blaine caused reform-minded “Mugwumps” to support NY reform Gov. Grover Cleveland, dirty election “Ma where’s my Pa?” & “Rum, Romanism, & Rebellion” • Grover Cleveland’s 1st Term 1885-1889: used veto 414 times!, signed Interstate Commerce Act, Dawes Act, & reclaimed 81 million acres from railroads & ranchers • Tariff Issue: Cleveland wanted to lower tariff caused business leaders to support Harrison in 1888 • Benjamin Harrison 1889-1893 (grandson of Tippecanoe) supported high tariffs • Billion Dollar Congress: Republicans controlled presidency & both Houses 1889-1891: McKinley Tariff of 1890 (highest ever), Civil War pensions, Sherman Antitrust Act, Sherman Silver Purchase Act • Cleveland again? Defeats Harrison in rematch in 1892 due to high prices & debt fears due to McKinley Tariff Rise of the Populists • The Grange 1870s Oliver Hudson Kelley Granger Laws regulated railroad rates & grain storage – weakened by Supreme Court in “The Wabash Case” in 1886 • Farmer’s Alliance 1880s ran candidates & controlled Western states by 1890s, speakers like Mary Elizabeth Lease “Raise less corn & more hell!” • People’s Party “Populists” in 1892 Omaha Platform: – Political: Direct election of Senators, secret ballot – Economic: “Bimetalism” - free silver, graduated income tax, Gov. ownership of RRs, telephone & telegraph companies, 8-hour work day for government employees, “sub-treasuries” • 1892 Election Populist James Weaver of Iowa won more than 1 million votes for president & 22 electoral votes but scared away white in South & industrial workers in NE Panic of 1893 & “Money Question” • • Panic of 1893: Stock market crashed & many railroad co.’s went bankrupt &16,000 businesses collapsed unemployment 20%, 500 banks closed panic! Money Question: battle over money supply – Debtors, Farmers, & small-businesses wanted “easy” of “soft” money campaigned for paper currency “greenbacks” and “free” silver – Bankers, creditors, investors, large businesses wanted “sound” or “hard” currency – Gold Standard • • • • • Greenback Party: opposed to Specie Resumption Act of 1875 elected 14 members of Congress in 1878 Silver: “Crime of 1873” Congress stopped minting silver, Bland-Alison Act of 1878 resumed silver but limited to $24 million per month – Sherman Silver Purchase Act of 1890 Due to Panic of 1893, Cleveland led repeal of Sherman Act gold reserves depleted (borrow $65 million from J.P. Morgan) call for “Free Silver!” Cleveland lost support: laissez-faire, gold standard & crush Pullman Strike “Coxey’s Army” 1894 Populist Jacob Coxey led thousands on march to Washington – arrested for trespassing Election of 1896 • • • • • • • • • • • Populists victories in 1894 midterms Democrats divided between “gold” Democrats loyal to Cleveland and pro-silver Dems – William Jennings Bryan of Nebraska “Cross of Gold” Speech at convention dark horse Democratic candidate at 36 Populists’ dilemma? Endorse Bryan Bryan campaigned on “free silver” at ratio of 16:1 “bimetalism” Republicans: William McKinley business interests & Gold Standard tried to blame Democrats for Depression Mark Hanna political operative raised millions to support McKinley Bryan gave 600 speeches and traveled 18,000 miles by train McKinley victory due to 1. $$$ 2. “Gold Bug” Democrats defection 3. Fears of industrial workers Klondike Gold Rush Gold Standard Act of 1900 Significance of 1896 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. End of the stalemate and stagnation of Gilded Age Era of Republican dominance (7 of next 9 presidential elections and both Houses for 17 of next 20 sessions) as the party of business, industry and strong national government Demise of Populists - but many goals lived on were adopted by Progressives & FDR Urban dominance of America Beginning of modern politics media & $$$$