Introduction to Fungi: Evolution, Characteristics and Life Cycle
advertisement
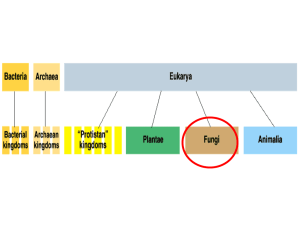
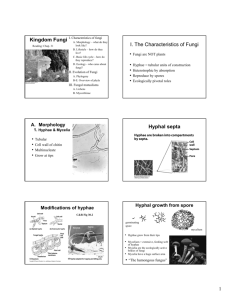
Introduction to Fungi: Evolution, Characteristics and Life Cycle BIOL 1407 Fungi • http://www.poetv. com/video.php?v id=16788 • Photo Credit: Field Biology Student, Enchanted Rock Field Trip 2005 Characteristics of Fungi • Absorptive heterotrophs • Cell walls made of chitin • No flagella (most) • Photo Credit: M. Hirsch, BIOL 1407 Bastrop Field Trip 2004 Fungal Hyphae • Hyphae – Thread of cells – One cell thick – High surface area to volume ratio Fungal Hyphae • Hyphae – Absorb water, ions, nutrients – Gas exchange – Waste disposal Hyphal Types • Septate • Coenocytic Fungal Body • Mycelium • Loosely woven mat of hyphae • Feeding structure Reproductive Structures • Made of hyphae • Different shapes for different fungal groups Reproductive Structures • Make spores, either by mitosis or meiosis • Some are called “fruiting bodies” Heterokaryon • Formed after plasmogamy • n+n • Unfused nuclei from both parents Dikaryon • Special type of heterokaryon • Long-lasting • As cells divide, cells retain n + n Fungal Lifestyles Saprobes = Decomposers Fungal Lifestyles Parasites Fungal Lifestyles Predators Fungal Lifestyles Mutualists: Mycorrhizae Fungal Lifestyles Mutualists: Lichens Photo Credit: Field Biology Student, 360 Overlook 2005 Types of Lichens Crustose Types of Lichens Foliose Photo Credit: Field Biology Student, 360 Overlook 2005 Types of Lichens Fruticose Photo Credit: M. Hirsch, BIOL 1407 Bastrop Field Trip 2004 Evolution of Fungi • Earliest fossil fungi – Fungal spores – 460 million years old Opisthokonts • Sister taxon to Fungi: Nucleariids The End Unless otherwise specified, all images in this presentation came from: Campbell, et al. 2008. Biology, 8th ed. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.