fungi
advertisement
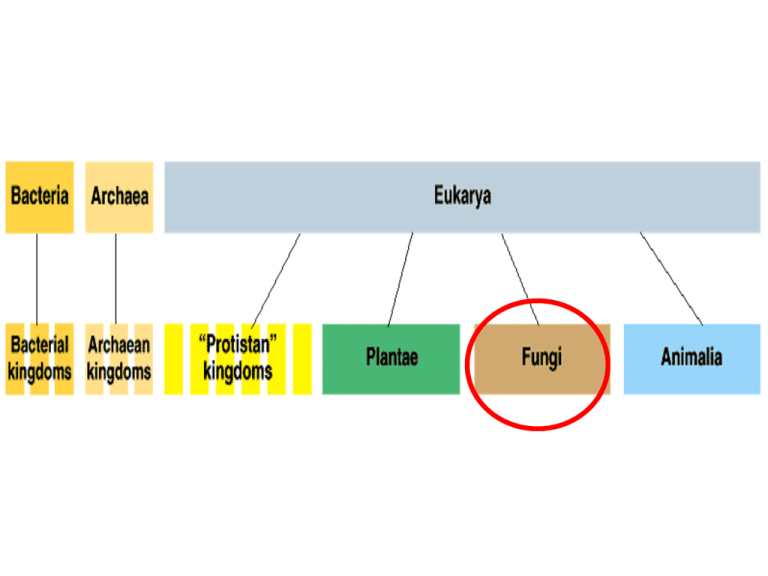
FUNGI Eukaryotic cells Most are multi-celled Some are uni-cellular Heterotrophs Live in moist, warm areas Have Cell Walls FUNGI • Fungi used to be classified in the plant kingdom because, like plants, many fungi grow anchored in soil and have cell walls. • The basic structural units of multicellular fungi are their threadlike filaments called hyphae, which develop from fungal spores. Some hyphae anchor the fungus, some invade the food source, and others form fungal reproductive structures. Spores Bread Mold Hyphae Mycelium Fungal Structure • Fungal body – mycelium • thread-like cells • Network of hyphae • Cell wall – Made of chitin • polysaccharide • just like insect exoskeletons Internal structure • Eukaryotic cells – long, thread-like cells • filamentous – incomplete divisions between cells • septum – multiple nuclei Modes of Nutrition • Heterotrophic fungal hypha – secrete digestive enzymes – feed by absorption • parasites – feeding on living creatures • predators – paralyzing prey plant cell membrane • saprobes (decomposers) – breakdown dead remains plant cell wall plant cell Reproduction • Asexual – budding in yeast – fragmentation – zygospores • spread by wind, water, animals • Sexual – joining of haploid hyphae – ascospores Zygomycota (Bread & Fruit Mold) Decomposers Hyphae without septa Reproduction: Asexual- zygospores Sexual- hyphae fuse Zygomycota (Bread & Fruit Mold) • • • • Ascomycota sac fungi Largest phylum of fungi Saprobes, parasites, pathogens. Yeast are microscopic, while most other Ascomycota are macroscopic • Produce sexual ascospores in sac-like structures called asci Basidiomycota • • • • Include mushrooms, puffballs, shelf fungi, stinkhorns macroscopic forms -saprobes. microscopic forms - pathogens & parasites. Form sexual spores called basidiospores found in the gills Deuteromycota. These fungi are often termed “fungi imperfecti” because sexual reproduction has never been observed in them. They lack the structures for sexual reproduction, and produce their spores asexually. Imperfect Fungi Around 25,000 additional fungus species are grouped in this phylum. Daniel Members include Trichophyton (Athlete's foot), Penicillium notatum (Penicillin), Candida albicans ("Yeast“ infections) Ecological Roles • Decomposers – recycle nutrients • Symbiotic Relationships – lichen • fungi + algae (Mutualism) – cyanobacteria or green algae • pioneer species in ecosystems • makes soil from bare rock – mycorrhizae • fungi + plants • live in & amongst plant roots • enables plants to absorb more water & nutrients Mycorrhizae • Critical role in plant growth – extends water & nutrient absorption of roots without mycorrhizae with mycorrhizae