Week of 11/4 Teacher S. Petrill Course: Science Day Anchor
advertisement

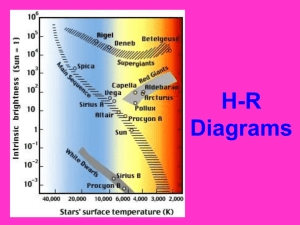
Week of 11/4 Day Teacher S. Petrill Course: Anchor Descriptor Eligible Content or Academic Standard R6.A.2 Understand nonfiction appropriate to grade level. S8.D.3.1 Explain the relationships between and among the objects of our solar system Science Objective Strategies for this lesson Assessment Chapter 13 Lesson 2 Direct Instruction, Formative and Pages DD88-D96 Guided Practice, SummativeUnderstand that the Independent Work, apparent magnitude of a Cooperative In class discussion, white board response, star depends on its size Learning, Note thumbs-up/thumbs-down, choral response, and distance. Recognize Taking, quiz, test, main idea/detail, vocabulary cards, the direct relationship Differentiated various graphic organizers, cooperative between the magnitude of Instruction learning. a star and its temperature. Describe how stars can be Brightness of stars is described by their classified. Describe the life absolute and apparent magnitudes. cycle of a star. Identify the 3 types of galaxies. Stars are classified according to their Text, Workbook, Power magnitude, surface temperature, and Point, LCD Projector, size. Document Camera, Vocabulary Picture Cards, Graphic Organizers, Individual Dry Erase Boards Connection to Anchor: Reading Comprehension, Identify/define new vocabulary, main idea/detail, analyzing the past to understand today. R6.A.2 Chapter 13 Lesson 2 Direct Instruction, S8.D.3.1 Formative and Tues. Understand Pages DD88-D96 Guided Practice, Explain the relationships Summativenonfiction Understand that the Independent Work, between and among the appropriate to grade apparent magnitude of a Cooperative In class discussion, white board response, objects of our solar system level. star depends on its size Learning, Note thumbs-up/thumbs-down, choral response, and distance. Recognize Taking, quiz, test, main idea/detail, vocabulary cards, the direct relationship Differentiated various graphic organizers, cooperative between the magnitude of Instruction learning. a star and its temperature. Describe how stars can be Brightness of stars is described by their classified. Describe the life absolute and apparent magnitudes. cycle of a star. Identify the 3 types of galaxies. Stars are classified according to their Text, Workbook, Power magnitude, surface temperature, and Point, LCD Projector, size. Document Camera, Vocabulary Picture Cards, Graphic Organizers, Individual Dry Erase Boards Connection to Anchor: Reading Comprehension, Identify/define new vocabulary, main idea/detail, analyzing the past to understand today. Mon. Wed R6.A.2 Understand nonfiction appropriate to grade level. Connection to Anchor: Thur R6.A.2 Understand nonfiction appropriate to grade level. Connection to Anchor: Fri Chapter 13 Lesson 2 Direct Instruction, Formative and Pages DD88-D96 Guided Practice, SummativeUnderstand that the Independent Work, apparent magnitude of a Cooperative In class discussion, white board response, star depends on its size Learning, Note thumbs-up/thumbs-down, choral response, and distance. Recognize Taking, quiz, test, main idea/detail, vocabulary cards, the direct relationship Differentiated various graphic organizers, cooperative between the magnitude of Instruction learning. a star and its temperature. Describe how stars can be The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram shows classified. Describe the life the relationship between a star’s cycle of a star. Identify the 3 types of galaxies. temperature and its absolute Text, Workbook, Power magnitude. For example the chart Point, LCD Projector, shows that blue and white stars are Document Camera, hotter and brighter than orange and red Vocabulary Picture Cards, Graphic stars. Yellow stars are in the middle. Organizers, Individual Dry Erase Boards Reading Comprehension, Identify/define new vocabulary, main idea/detail, analyzing the past to understand today. S8.D.3.1 Explain the relationships between and among the objects of our solar system Chapter 13 Lesson 2 In class discussion, white board response, Pages DD88-D96 thumbs-up/thumbs-down, choral response, Understand that the quiz, test, main idea/detail, vocabulary cards, apparent magnitude of a various graphic organizers, cooperative star depends on its size learning. and distance. Recognize the direct relationship The Life Cycle of a Star. Stars begin in a between the magnitude of cloud of dust and gases called a nebula. a star and its temperature. They go through one of several versions Describe how stars can be of the life cycle. Stars similar in size to classified. Describe the life cycle of a star. Identify the our sun eventually become white 3 types of galaxies. dwarfs. Massive stars eventually Text, Workbook, Power explode in a supernova. Point, LCD Projector, Document Camera, Vocabulary Picture Cards, Graphic Organizers, Individual Dry Erase Boards Reading Comprehension, Identify/define new vocabulary, main idea/detail, analyzing the past to understand today. R6.A.2 Understand nonfiction appropriate to grade level. S8.D.3.1 Explain the relationships between and among the objects of our solar system S8.D.3.1 Explain the relationships between and among the objects of our solar system Chapter 13 Lesson 2 Pages DD88-D96 Understand that the apparent magnitude of a star depends on its size and distance. Recognize In class discussion, white board response, thumbs-up/thumbs-down, choral response, quiz, test, main idea/detail, vocabulary cards, various graphic organizers, cooperative learning. Connection to Anchor: the direct relationship The sun is part of the Milky Way Galaxy. The between the magnitude of Milky Way is made up of 3 main parts; a a star and its temperature. bulge, a halo, and a disk. There are three Describe how stars can be types of galaxies and they are classified by classified. Describe the life their shape. Spiral Galaxy, Elliptical Galaxy, cycle of a star. Identify the and an Irregular Galaxy. 3 types of galaxies. Text, Workbook, Power Point, LCD Projector, Document Camera, Vocabulary Picture Cards, Graphic Organizers, Individual Dry Erase Boards Reading Comprehension, Identify/define new vocabulary, main idea/detail, analyzing the past to understand today.