Access - Disability Requirements
advertisement

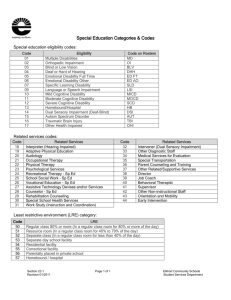
Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements What is the purpose of this Operational Guideline? 1. This Operational Guideline provides guidance to delegates in assessing whether a person meets the disability requirements, which are part of the access criteria that must be met for a person to become a participant. Legislation 2. Read s.24 of the National Disability Insurance Scheme Act 2013 (NDIS Act) and Parts 5 and 7 of the National Disability Insurance Scheme (Becoming a Participant) Rules 2013 (Becoming a Participant Rules). Becoming a participant 3. To become a participant a person must meet the age and residence requirements and either the disability or early intervention requirements. See s.21 of the NDIS Act. 4. For further guidance, refer to the following Operational Guidelines: a. Operational Guideline – Access – Age Requirements b. Operational Guideline – Access – Residence Requirements c. Operational Guideline – Access – Early Intervention Requirements See sections 21, 22, 23 and 25 of the NDIS Act and Parts 3, 4 and 6 of the Becoming a Participant Rules. The disability requirements 5. There are five separate factual matters that must be established when a delegate is determining whether a person meets the disability requirements set out in s.24 of the NDIS Act. 6. A person meets the disability requirements if: a. The person has a disability that is attributable to one or more intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory or physical impairments or to one or more impairments attributable to a psychiatric condition, and b. The impairment or impairments are, or are likely to be, permanent, and c. The impairment or impairments result in substantially reduced functional capacity to undertake, or psychosocial functioning in undertaking, one or more of the following activities: i. Communication Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014 Page 1 of 19 ii. Social interaction iii. Learning iv. Mobility v. Self-care vi. Self-management, and d. The impairment or impairments affect the person’s capacity for social and economic participation, and e. The person is likely to require support under the National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) for the person’s lifetime. See s.24 of the NDIS Act. 7. If a person is found not to meet one or more of the above criteria, the delegate should consider whether the person could meet the early intervention requirements as an alternative. 8. For children under 7 years of age (except where diagnosed with a condition on ‘List A at Appendix A’ of this Operational Guideline) a delegate should first consider whether the child meets the early intervention requirements, before considering the disability requirements. Streamlined process where a delegate may be satisfied that a person meets one or more parts of the disability requirements 9. This section gives guidance on the circumstances in which a delegate may generally be satisfied that a person meets one or more parts of the disability requirements by reference to one of the lists appended to this Operational Guideline. 10. For the avoidance of doubt, a person does not need to have a condition on List A or List B to become a participant in the NDIS. These lists have been developed to streamline the access process for people with a condition on one of these lists. The lists are not exhaustive and in no way suggest that a person with a condition not on a list is excluded from the NDIS. 11. Where a person has a diagnosed condition that appears on ‘List A at Appendix A – Permanent impairment/functional capacity – no further assessment required’, a delegate may generally be satisfied that the person meets all elements of the disability requirements in s.24 of the NDIS Act without requiring additional evidence. This is because the nature of the conditions on List A at Appendix A is such that these conditions are considered to result in a disability that is attributable to a permanent impairment that results in substantially reduced functional capacity. List A at Appendix A is not exhaustive and in no way suggests that a person with a condition different to those listed would not have a permanent impairment that results in substantially reduced functional capacity. 12. Where a person has a diagnosed condition that appears on ‘List B at Appendix B – Permanent impairment/functional capacity variable – further assessment of functional capacity required’, a delegate may generally be satisfied that the person’s disability is attributable to a permanent impairment without requiring additional evidence. This is because the nature of the conditions on List B at Appendix B is such that they are generally considered to result in a disability that is attributable to a permanent impairment. However, the severity of the resulting disability is variable and people with these conditions will not necessarily have substantially reduced functional capacity. Accordingly, a delegate would require further evidence to be satisfied that the person, as a result of that impairment: Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 2 of 19 has substantially reduced functional capacity or psychosocial functioning; their capacity for social or economic participation is affected; and is likely to require support under the NDIS for the person’s lifetime. 13. List B at Appendix B is not exhaustive and in no way suggests that a person with a condition different to those listed would not have a permanent impairment. 14. Where a person has already been considered eligible for certain state or territory schemes (listed in Appendix C), the delegate would generally be satisfied that the person meets the Disability Requirement. This is because some state and territory schemes have been assessed as having eligibility requirements equivalent to the NDIS disability requirements and therefore the relevant state or territory has already assessed that the person has a disability that is attributable to a permanent impairment that results in substantially reduced functional capacity. The list at Appendix C is not exhaustive and in no way suggests that a person who has not been found eligible for a listed program or who is receiving supports from a program that is not listed would not meet the disability requirement. What is a disability attributable to impairment? 15. Under s.24(1)(a) of the NDIS Act a delegate is required to determine whether a person has a disability and whether that disability is attributable to one or more intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory or physical impairments, or to one or more impairments attributable to a psychiatric condition. This is essentially a question of fact and a delegate should consider all of the available evidence, including diagnostic evidence. 16. The Administrative Appeals Tribunal (AAT) considered the meaning of “disability” and “impairment” in Mulligan and National Disability Insurance Agency [2014] AATA 374 (Mulligan). The AAT stated that “disability” takes its meaning from the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Article 1 which refers to a: “long term physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairments which in interactions with various barriers may hinder their full and effective participation in society on an equal basis with others,” 17. The AAT also referred to the Explanatory Statement to the Becoming a Participant Rules which explains that the focus of “disability” is on the reduction or loss of an ability to perform an activity resulting from an impairment. The Explanatory Statement notes the NDIS “will be open to people with a permanent disability which results in substantially reduced functional capacity” and explains: “Although the definition of “disability” under these Rules does not precisely correspond with that of the CRPD, the eligibility and assessment of need has been based on the World Health Organisation’s International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF). The narrower definition of “disability” employed by the [NDIS] is aimed at achieving a legitimate purpose by targeting those people with disability who have a significant impairment to their functional capacity. This functional definition of disability focuses on outcomes for the segment of the disability population that has the most unmet need.” 18. The AAT also noted that a person may have a disability without necessarily meeting all, or even any, of the disability requirements in s.24(1)(b), (c), (d) and (e). For example, a person might have a temporary disability, or a permanent disability that has only minimal effect on functioning, or no effect on his or her social or economic participation. 19. An “impairment” is a recognised intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory, physical or psychiatric condition identified by a qualified professional as affecting a person. The AAT noted that “impairment” commonly refers to a loss of, or damage to, a physical, sensory or mental function. Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 3 of 19 20. The Access Request Form requires a prospective participant to provide information in relation to all of the access criteria to support their request. Diagnostic information will generally be required to determine whether a person has a disability attributable to an impairment. In relation to the impairments listed in s.24(1)(a) of the NDIS Act, information about the person’s diagnosis may be supplemented with other information about the person’s reduced functioning. It is expected that this information will generally be provided in the form set out in the ‘Evidence of Disability’ form. The NDIA can assist people to gather the necessary information if needed. 21. A delegate may refer people for a specialist assessment. If a person has made an access request a delegate can request, within the limitations of s.26 of the NDIS Act, information that is reasonably necessary, such as information on previously completed assessments or examinations. A referral for an assessment or examination would only be expected to occur in limited circumstances, such as where other sources of information have been exhausted or there is inconsistent information, the information is outdated or a matter needs to be resolved to enable a decision to be made. What is a permanent impairment? 22. The test in the NDIS Act is whether the impairment or impairments ‘are, or are likely to be permanent’. 23. In some cases the available information will need to be assessed very carefully to determine whether the impairments are, or are likely to be, permanent. The Becoming a Participant Rules set out in legislation some circumstances in which an impairment is not permanent and also some guidance on when an impairment may be permanent. A delegate must apply the criteria below in assessing whether the impairments are, or are likely to be, permanent for the purpsoes of s.24(1)(b) of the NDIS Act. 24. An impairment is, or is likely to be, permanent only if there are no known, available and appropriate evidence-based clinical, medical or other treatments that would be likely to remedy the impairment. See r.5.4 of the Becoming a Participant Rules. 25. An impairment that varies in intensity (for example, because the impairment is of a chronic episodic nature) may be permanent despite the variation. See r.5.2 of the Becoming a Participant Rules. 26. An impairment may be permanent notwithstanding that the severity of its impact on the functional capacity of the person, may fluctuate or there are prospects that the severity of the impact of the impairment on the person's functional capacity, including their psychosocial functioning, may improve. See r.5.5 of the Becoming a Participant Rules. 27. Under the Becoming a Participant Rules an impairment is, or is likely to be, permanent only if the impairment does not require further medical treatment or review in order for its permanency or likely permanency to be demonstrated (even though the impairment may continue to be treated and reviewed after this has been demonstrated). In relation to this requirement: a. What is required is information that is sufficient to demonstrate to a delegate that the impairment is permanent or likely to be permanent. This is matter of judgment but what the Becoming a Participant Rules are trying to do is rule out cases where the permanency or likely permanency has not been established because the person requires further medical treatment or review before the permanency or likely permanency can be demonstrated. b. This does not mean that an impairment will not be permanent or likely to be permanent if it requires further medical treatment or review. In addition to that described in paragraph 15a above, in some cases an impairment may continue to be treated and reviewed after it has been demonstrated that is permanent or likely to be permanent. Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 4 of 19 See r.5.6 of the Becoming a Participant Rules. 28. If an impairment is of a degenerative nature, the impairment is, or is likely to be, permanent if medical or other treatment would not, or would be unlikely to, improve it. See r.5.7 of the Becoming a Participant Rules. What is an impairment that results in substantially reduced functional capacity or psychosocial functioning? 29. The test in the NDIS Act is that the impairment or impairments result in substantially reduced functional capacity to undertake, or psychosocial functioning in undertaking, one or more of the activities listed in s.24(1)(c) of the NDIS Act. 30. An impairment results in substantially reduced functional capacity of a person to undertake one or more of the relevant activities – communication, social interaction, learning, mobility, self-care, selfmanagement (see paragraph 4c above) – if its result is that: a. The person is unable to participate effectively in the activity, or perform tasks or actions required to undertake or participate effectively in the relevant activity due to their impairment, without assistive technology, equipment (other than commonly used items such as glasses) or home modifications. See r. 5.8(a) of the Becoming a Participant Rules. For the purpose of paragraph 18a, commonly used items could include glasses, walking sticks, non-slip bath mats, simple adapted kitchen utensils and dressing aids. Commonly used items also include items such as bathroom grab rails, hand rails installed at stairs and age-appropriate child safety locks. In considering the role played by assistive technology, home modifications and equipment, the delegate should usually only consider needs specific to the impact from the person’s impairment and that are specifically designed to assist in increasing the functional capacity and participation of people with disability. Such items would usually be assessed and prescribed by a qualified practitioner such as an occupational therapist, physiotherapist, speech therapist or continence nurse and may traditionally be supplied through a specialist disability aids and equipment service or multidisciplinary team. A person is usually considered to be unable to undertake an activity effectively due to their impairment if they cannot safely complete a task within an acceptable time period. The person may complete the task more slowly or in a different manner to others and still be considered to be effective in the task. Or: b. the person usually requires assistance (including physical assistance, guidance, supervision or prompting), from other people to participate in the activity or to perform tasks or actions required to undertake or participate effectively in the activity. Delegates may also take into account the person’s age and whether they are able to perform tasks that they would normally be expected to perform independently at their age. See r. 5.8(b) of the Becoming a Participant Rules. For example, the need for assistance from other people on most days is inconsistent with expectations of tasks or activities that would normally be performed independently by a person of their age in one or more of these areas: Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 5 of 19 Communication (understanding and being understood by others) Social interaction (making and keeping friends and relationships, behaving within limits accepted by others, and/or coping with feelings and emotions) Learning (understanding and remembering information, learning new things, practicing and using new skills and ideas) Mobility (moving around their home and community and/or performing other tasks involving movement, e.g. using hands and arms) Self-care (e.g. daily showering, bathing, dressing, eating, toileting and grooming; and/or special health care needs attended to by self, family members or carers) Self-management (planning and organising daily life and managing household personal finances) In Mulligan the AAT considered the case of a person with chronic ischaemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, Conn’s Syndrome, and sciatica from two ruptured discs in their lower back. The AAT accepted that the person performs most activities with difficulty, often with a great deal of pain, and more slowly than they would without impairments. However, the AAT considered that in the areas of mobility and self-care, the person participates effectively, if not efficiently, and can complete tasks within a reasonable time, for the most part without aids of any sort, and that the aids that the person does use (being handrails, a grab rail, and an Easi-reacher), are commonly used by many people. On this basis, the AAT was not satisfied that the person’s capacity in those areas is substantially reduced. Or: c. The person is unable to participate in the activity or to perform tasks or actions required to undertake or participate in the activity, even with assistive technology, equipment, home modifications or assistance from another person. See r. 5.8(c) of the Becoming a Participant Rules. For example, a person may require complete assistance as they are not at all able to perform one or more essential daily activities or tasks appropriate to their age (e.g. a person over the age of 3 years cannot stand, use their hands or arms to perform tasks, communicate their needs in any way, and/or interact with others). In Mulligan the AAT held that a person’s inability to mow a lawn for the purpose of maintaining a tenancy did not amount to substantially reduced functional capacity. 31. For NDIS purposes, where the person’s impairment is fluctuating or episodic (e.g. due to a mental illness or a condition such as epilepsy), substantially reduced functional capacity is determined when the person’s impairment is fully treated and stabilised, (i.e. the person’s level of functional capacity due to residual and long term impairment is determined in the periods between acute episodes). See r. 5.8 of the Becoming a Participant Rules. Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 6 of 19 Substantially reduced functional capacity and children – matters to consider 32. The above criteria are to be applied in a way that is appropriate to the child. 33. In particular with children under 7 years of age, and noting that for this group the recent diagnosis and resulting impairment may not be fully resolved, a delegate may first consider the early intervention requirements in preference to the disability requirements in determining whether a child meets the access criteria. 34. When considering access in accordance with s.24(1)(c) of the NDIS Act and as described in r.5.8 of the Becoming a Participant Rules, a delegate is to consider the impact on functional impairment for the child relative to the result for other children of the same age. For example: a. The child requires more assistive technology, equipment (other than commonly used items such as glasses) or home modifications to participate in one or more of the activities listed in s.24(1)(c) of the NDIS Act than most other children of the same age, or b. The child usually requires more assistance than most other children of the same age to participate in one or more of the activities listed in s.24(1)(c) of the NDIS Act ,or c. The child is unable to participate in the activities listed in s.24(1)(c) of the NDIS Act that would usually be expected of most other children of the same age. 35. If a child’s impairment does not currently result in substantially reduced functional capacity but could in the future, the delegate should consider whether the child meets the early intervention requirements. What is an impairment that affects a person’s capacity for social and economic participation? 36. Under s.24(1)(d) of the NDIS Act, a delegate needs to be satisfied that the person’s impairment or impairments is affecting their capacity for social and economic participation to meet this disability requirement. For example, the impairment may be affecting the person’s capacity to look for and maintain employment. 37. A delegate does not need to be satisfied that a person’s capacity for social and economic participation is reduced or substantially reduced. It is enough for the person’s capacity for social and economic participation to be merely affected by their impairment, which is a relatively low threshold. See Mulligan and National Disability Insurance Agency [2014] AAT 374. When is a person likely to require support under the NDIS for their lifetime? 38. The test in s.24(1)(e) is whether a person is likely to require support under the NDIS for their lifetime. This requires a delegate to consider whether: a. the person is likely to require support of a kind that is funded or provided under the NDIS, and b. the support is likely to be required for the rest of the person’s lifetime. Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 7 of 19 39. It is important to note that this test can include consideration of a person’s likely need for both general supports provided under the NDIS and reasonable and necessary supports funded through the NDIS. 40. In Mulligan the AAT held that the test in s.24(1)(e) does not require a delegate to be satisfied that the supports likely to be required for the person’s lifetime meet all of the criteria for reasonable and necessary supports specified in s.34 of the NDIS Act. At the same time, where the supports likely to be required for a person’s lifetime clearly would be better met by other service systems, then the person would generally not be considered to require support under the NDIS for their lifetime. The National Disability Insurance Scheme (Supports for Participants) Rules 2013 provides guidance as to what supports the NDIS will provide. 41. If an impairment varies in intensity (for example, because the impairment is of a chronic episodic nature) the person may still be assessed as likely to require support under the NDIS for the person’s lifetime, despite the variation. See r.5.2 of the Becoming a Participant Rules and s.24(1)(e) of the NDIS Act. Use of information 42. In considering whether a person meets the disability requirements a delegate should develop a comprehensive view of the person’s circumstances including by: a. Examining all relevant available information provided by the participant (such as the selfassessment in My Access Checker and any diagnostic or assessment information provided), and b. Talking with the person and (with the person’s consent) the person’s family, or carers. 43. Diagnostic information will generally be required to determine whether a person has a disability attributable to an impairment and whether that impairment is permanent. Information about the person’s level of functioning will generally be required to determine whether the person has substantially reduced functional capacity or psychosocial functioning. 44. Information about the person’s level of functioning may be informed by a support needs assessment, usually undertaken by a suitably qualified health practitioner, to assist with the access decision. 45. Where the available information is not sufficient for a sound decision, the NDIA may request, within the limitations of s.26 of the NDIS Act, information reasonably necessary to decide whether a person meets the access criteria. Delegates can also request a prospective participant to undergo an assessment or examination. 46. Where further information is being sought from the participant the request should clearly identify what information is being sought and by when it must be provided, which must be at least 28 days after the request date. If the request is to a third party, the delegate should inform the prospective participant of the reason for the delay in making the decision. See s.26 of the NDIS Act and Operational Guideline – Information Handling –Collecting, Accessing and Recording Protected Information. General considerations for delegates 47. A decision tree designed to assist decision makers in making and recording their decisions has been developed and is attached. The decision tree should be completed for each prospective participant, except a prospective participant who: a. Has a condition listed in List A at Appendix A of this Operational Guideline, or Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 8 of 19 b. Has been found eligible for a program at Appendix C of this Operational Guideline, or c. Is a child under 6 years of age who has developmental delay, or d. Is a child under 7 years of age who has a condition listed in List C at Appendix A to Operational Guideline – Access – Early Intervention Requirement. See Operational Guideline – Access – Decision Tree Disability Requirements and Early Intervention Requirements. Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 9 of 19 Appendix A List A – Conditions which are likely to meet the disability requirements in s.24 of the NDIS Act 1. Intellectual disability diagnosed and assessed as moderate, severe or profound in accordance with current DSM criteria (e.g. IQ 55 points or less and severe deficits in adaptive functioning) 2. Autism diagnosed by a specialist multi-disciplinary team, pediatrician, psychiatrist or clinical psychologist experienced in the assessment of Pervasive Developmental Disorders, and assessed using the current Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V) diagnostic criteria as having severity of Level 2 (Requiring substantial support) or Level 3 (Requiring very substantial support) 3. Cerebral palsy diagnosed and assessed as severe (e.g. assessed as Level 3, 4 or 5 on the Gross Motor Function Classification System - GMFCS) 4. Genetic conditions that consistently result in permanent and severe intellectual and physical impairments: Angelman syndrome Coffin-Lowry syndrome in males Cornelia de Lange syndrome Cri du Chat syndrome Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18 – full form) Epidermolysis Bullosa (severe forms): o Autosomal recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa o Hallopeau-Siemens type o Herlitz Junctional Epidermolysis Dystrophica Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Leigh syndrome Leukodystrophies: o Alexander disease (infantile and neonatal forms) o Canavan disease o Krabbe disease (globoid cell leukodystrophy) – Infantile form o Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease (Connatal form) Lysosomal storage disorders resulting in severe intellectual and physical impairments: o Gaucher disease Types 2 and 3 o Niemann-Pick disease (Types A and C) o Pompe disease o Sandhoff disease (infantile form) o Schindler disease (Type 1) o Tay-Sachs disease (infantile form) Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 10 of 19 Mucopolysaccharidoses – the following forms: o MPS 1-H (Hurler syndrome) o MPS III (San Fillipo syndrome) Osteogenesis Imperfecta (severe forms): o Type II - with two or more fractures per year and significant deformities severely limiting ability to perform activities of daily living Patau syndrome Rett syndrome Spinal Muscular Atrophies of the following types: o Werdnig-Hoffmann disease (SMA Type 1- Infantile form) o Dubowitz disease (SMA Type II – Intermediate form) o X-linked spinal muscular atrophy 5. Spinal cord injury or brain injury resulting in paraplegia, quadriplegia or tetraplegia, or hemiplegia where there is severe or total loss of strength and movement in the affected limbs of the body 6. Permanent blindness in both eyes, diagnosed and assessed by an ophthalmologist as follows: a. Corrected visual acuity (extent to which an object can be brought into focus) on the Snellen Scale must be less than or equal to 6/60 in both eyes; or b. Constriction to within 10 degrees or less of arc of central fixation in the better eye, irrespective of corrected visual acuity (i.e. visual fields are reduced to a measured arc of 10 degrees or less); or c. A combination of visual defects resulting in the same degree of visual impairment as that occurring in the above points. (An optometrist report is not sufficient for NDIS purposes.) 7. Deafblindness confirmed by ophthalmologist and audiologist and assessed as resulting in permanent and severe to total impairment of visual function and hearing 8. Amputation or congenital absence of two limbs Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 11 of 19 Appendix B List B – Conditions for which permanent impairment/functional capacity are variable and further assessment of functional capacity generally is required Note: Synonyms for conditions are also shown e.g. condition/ synonym/ synonym 1. Conditions primarily resulting in Intellectual/ learning impairment Intellectual disability Pervasive developmental disorders not meeting severity criteria in List A of this Operational Guideline or List C of Operational Guideline – Access – Early Intervention Requirements: Asperger syndrome Atypical autism Childhood autism Chromosomal abnormalities resulting in permanent impairment and not specified on List A: Aicardi-Goutières syndrome CHARGE syndrome Cockayne syndrome Types I and Type II/Cerebro-oculo-faciao-skeletal (COFS) syndrome /Pena Shokeir syndrome Type II/Weber-Cockayne syndrome/Neill-Dingwall syndrome) Cohen syndrome Dandy-Walker syndrome DiGeorge syndrome /22q11.2 deletion syndrome/Velocardiofacial syndrome/ Shprintzen syndrome/Conotruncal anomaly face syndrome Down syndrome Fragile X syndrome Kabuki syndrome Menkes disease Prader-Willi syndrome Seckel syndrome /microcephalic primordial dwarfism/Harper’s syndrome/Virchow-Seckel dwarfism Smith-Lemli-Optiz syndrome Smith-Magenis syndrome Spinal muscular atrophy Types III and IV Sturge-Weber syndrome Trisomy 9 Tuberous sclerosis Turner syndrome Williams syndrome Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome 2. Conditions primarily resulting in Neurological impairment Alzheimer’s dementia Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease HIV dementia Huntington’s disease Multi-infarct dementia Parkinson’s disease Post polio syndrome Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 12 of 19 Vascular dementia Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system: Abetalipoproteinaemia Adult-onset spinal muscular atrophy/late-onset SMA type III) Fazio-Londe disease/Progressive bulbar palsy of childhood Friedrich’s ataxia Hereditary spastic paraplegia/ Infantile-onset ascending hereditary spastic paralysis/ L1 syndrome/ spastic paraplegias types 2 and 11Huntington’s disease/Huntington’s chorea Louis-Bar syndrome/Ataxia-telangiectasia Motor neuron disease/Motor neurone disease/ Lou Gehrig’s disease /Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Primary lateral sclerosis Progressive bulbar palsy Spinal muscular atrophy – all types Spinocerebellar Ataxia – all types, including Machado-Joseph disease Extrapyramidal and movement disorders Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome /Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN)/neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 1 (NBIA 1) Parkinson’s disease Shy-Drager syndrome /Multiple System Atrophy /Striatonigral degeneration (MSA-P)/ Sporadic olivopontocerebellar atrophy (MSA-C) Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome/Progressive supranuclear ophthalmoplegia Stiff-man syndrome /Stiff-person syndrome Other degenerative diseases of the nervous system Alzheimer’s disease Alpers disease/Grey-matter degeneration/Alpers syndrome/progressive sclerosing poliodystrophy/progressive infantile poliodystrophy Lewy body dementia Pick’s disease Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system Adrenoleukodystrophy Multiple sclerosis Schilder’s disease /Diffuse myelinoclastic sclerosis – non-remitting Episodic and paroxysmal disorders Brain stem stroke syndrome Cerebellar stroke syndrome Motor and sensory lacunar syndromes Lennox syndrome /Lennox-Gastaut syndrome West’s syndrome Polyneuropathies and other disorders of the peripheral nervous system Adult Refsum disease Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease/Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy/ peroneal muscular atrophy Dejerine-Sottas disease /Dejerine-Sottas syndrome/Dejerine-Sottas neuropathy/progressive hypertrophic interstitial polyneuropathy of childhood/onion bulb neuropathy Infantile Refsum disease Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 13 of 19 Other disorders of the nervous system Hydrocephalus Multiple system atrophy 3. Conditions resulting in Physical impairment Amputations Congenital absence of limb or part thereof Epidermolysis bullosa Harlequin type icthyosis Juvenile arthritis / Stills Disease (excluding monocyclic/self-limited Adult Onset Stills disease) Rheumatoid arthritis Diseases of myoneural junction and muscle Andersen-Tawil syndrome/ Periodic paralysis /myoplegia paroxysmalis familiaris Becker muscular dystrophy Congenital muscular dystrophy Distal muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy Mitochondrial myopathy Myotonic dystrophy /dystrophia myotonica Myotonic muscular dystrophy Myotubular myopathy Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy Paramyotonia Congenita Thomsens disease /Congenital myotonia/ Becker myotonia) Cerebral palsy and other paralytic syndromes not meeting severity criteria on List A Cerebral palsy Diplegia Hemiplegia Monoplegia Paraplegia Quadriplegia Tetraplegia 4. Conditions resulting in Sensory and/or Speech impairment Disorders of the choroid and retina where permanent blindness diagnostic and severity criteria on List A are not met: Behr’s syndrome Kearns-Sayre syndrome Optic atrophy Retinitis pigmentosa Retinoschisis (degenerative and hereditary types/juvenile retinoschisis) Stargardt disease Usher syndrome Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 14 of 19 Disorders resulting in hearing loss Cortical deafness Pendred syndrome Sensorineural hearing loss Stickler syndrome Usher syndrome Waardenburg syndrome 5. Conditions resulting in multiple types of impairment Aceruloplasminemia Addison-Schilder disease /Adrenoleukodystrophy Albinism Arginosuccinic aciduria Aspartylglucosaminuria Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis /cerebral cholesterosis Congenital cytomegalovirus infection Congenital iodine-deficiency syndrome /cretinism Congenital rubella syndrome Glycine encephalopathy /non-ketotic hyperglycinaemia GM1 gangliosidosis Hartnup disease Homocystinuria Lowe syndrome/ Oculocerebrorenal syndrome Mannosidosis Menkes disease Mucolipidosis II /I-cell disease Mucolipidosis III /pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy Mucolipidosis IV Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL)/ Adult type (Kuf’s or Parry’s disease)/ Juvenile (Batten disease)/ Late infantile (Jansky-Bielschowsky) Niemann-Pick disease Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency Sialidosis Sulfite oxidase deficiency The following mucopolysaccharidoses: Scheie syndrome /MPS 1-H Hurler-Scheie syndrome /MPS 1 H-S Hunter syndrome /MPS II Morquio syndrome /MPS IVA Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome /MPS VI Sly syndrome /MPS VII Congenital conditions – cases where malformations cannot be corrected by surgery or other treatment and result in permanent impairment but with variable severity: Arnold-Chiari Types 2 and 3/Chiari malformation Microcephaly Fetal alcohol syndrome Fetal hydantoin syndrome Spina bifida VATER syndrome /VACTERL association Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 15 of 19 Appendix C People who are eligible for certain state, territory or Commonwealth schemes Note: Where a prospective participant falls within one of the following schemes the delegate is not required to refer to the Operational Guideline - Access - Decision Tree for Disability and Early Intervention Requirements in relation to their assessment of that prospective participant. a. Victoria Clients of the following Victorian schemes will generally be considered to satisfy the disability requirements without further evidence being required: Individual Support Package (ISP) Disability Support Register (DSR) Futures for Young Adults Supported Accommodation Residential Institutions Community Respite Facility Based Respite Therapy (complex therapy meeting guidelines under the Disability Act 2006 (Vic) Behaviour Intervention Services Flexible Support Packages Outreach Support Independent Living Training Case Management (Case Management meeting guidelines under the Disability Act 2006 (Vic) ECIS ECIS Waitlist MHCSS – Adult Residential Rehab Services MHCSS – Individualised Client Support Packages MHCSS – Supported Accommodation Services Program for Students with Disability (PSD) – Vision Impairment Program for Students with Disability (PSD) – Students enrolled in special schools for students with moderate to profound intellectual disability Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 16 of 19 b. Queensland Clients of the following Queensland schemes will generally be considered to satisfy the disability requirements without further evidence being required: Service Access Team Assessed Individual Funding AS and RS (Accommodation Support and Respite Support) Supported Accommodation (large/small residential, group homes, attendant care/personal care, in home accommodation support and other accommodation support) Centre Based Respite Registration of Need Database c. Northern Territory Clients of the following Northern Territory schemes will generally be considered to satisfy the disability requirements without further evidence being required: Supported Accommodation Respite Accommodation Support Community Access d. South Australia Clients of the following South Australian schemes will generally be considered to satisfy the disability requirements without further evidence being required: SA Child and Youth Services Individual Support Packages RCR Stage 1 Individual Support Packages RCR Stage 2 Individual Support Packages RCR Stage 3 Individual Support Packages RCR Stage 3 - Sensory Supported Residential Facilities (SRF) Unmet Needs Register Supported Accommodation – Residential Institutions Supported Accommodation – Group Homes Therapy Services – Therapy Support Positive Behaviour Support Community Access Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 17 of 19 e. Tasmania Clients of the following Tasmanian schemes will generally be considered to satisfy the disability requirements without further evidence being required: f. Individual Support Program Young People in Residential Aged Care Self directed funding Accommodation Support – Group Home Accommodation Support – Small/Large Resi/Hostel Centre Based Respite Community Access (including Recreation Programs) Disability Assessment Advisory Teams Severe Disability Register (Department of Education) New South Wales People currently accessing the following New South Wales schemes will generally be considered to satisfy the disability requirements without further evidence being required: Large Residential / Institution Small Residential / Institution Group Homes Hostels Attendant Care In-home Accommodation Support Alternative Family Placement Other Accommodation Support Therapy Services for Individuals Early Childhood Intervention Behaviour / Specialist Intervention Counselling Regional Resource and Support Teams Case Management, Local Coordination and Development Other Community Support Learning and Life Skills Development Recreation / Holiday Programs Other Community Access Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 18 of 19 Own Home Respite Centre-based Respite/Respite Homes Host Family Respite/Peer Support Respite Flexible / Combination Respite g. Commonwealth Clients of the following Commonwealth schemes will generally be considered to satisfy the disability requirements without further evidence being required: Better Start for Children with Disability Disability Employment Assistance : Australian Disability Enterprises Helping Children with Autism Younger Onset Dementia Key Worker Program Outside School Hours Care for Teenagers with Disability Remote Vision and Hearing Services Operational Guideline – Access – Disability Requirements (v 3.2) Publication date: 1 September 2014; appendix C updated December 2015 Page 19 of 19