IP address
advertisement

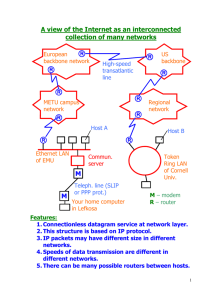
Department of Computer Science Faculty of Civil Engineering, Brno University of Technology Computer Technology Computer Networks • Networking • Internet Services Main organization for standardization ITU (International Telecommunication Union) - part of OSN - standards of (tele)connectivity http://www.itu.ch - ITU -T (CCITT original) - for computers communication (ISDN,…) ISO (International Organization for Standardization) - http://www.iso.ch IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) - 147countries - IEEE802 - standard. for LAN tech. (IEEE802.3 - for Ethernet) W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard of WWW service ČSNI (Český normalizační institut) - member of ISO ISOC - IAB - IETF, IESG - organizations in Internet IANA, NIC - IP addresses a ports support, top domain admin. (http://www.nic.com) Classification of networks • area – LAN (Local Area Network), – MAN (Metropolitan Area Network), – WAN (Wide Area Network) • topology – bus (Ethernet), – circle (Token Ring), – star (ARCnet) • access method – collision (stochastic) - CSMA/ CD - Ethernet, – non-collision (deterministic) - Token Ring • node role – peer to peer, client - server Topology of network (cabling) Bus topology: Ethernet Topology with structured cabling (star): Ethernet Circle topology: Token Ring HUB Access method - CSMA with collision detecting (CSMA/CD = Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) peer-to-peer client -server Ethernet today • Classic – 10 MBit/s – 10Base-2, 10Base-5, 10Base-T, 10Base-FL • FastEthernet – 100 MBit/s – 100Base-TX, 100Base-T4, 100Base-FX • Gigabit Ethernet – 1000 MBit/s – 1000Base-SX, 1000Base-LX, 1000Base-T Terminology •node, host = computer connected to network •internetworking = communication between networks •internet = connected networks •Internet = well-known computer network •connected service start-end of connection •non-connected service without connection (posted packet) entity entity •With acknowledge = reliable •Without acknowledge = non-reliable entity entity Architecture of networks Layer model (what and where to do) • decomposition to the tasks maintained by separated layers • layer interface definitions Protocol (how to do) • set of rules and technologies for communication • each layer has its own protocol • format of the data definition LAN Microsoft: NetBEUI (non-routable) NetWare: IPX/SPX (routable) heterogeneous networks (WAN, LAN): TCP/IP Layer • Each layer uses the service of the lower layer • offers its service to the higher layer • communication partner of the n-th layer is only the n-th layer • communication between the partners (the same layer) is controlled by the protocol Layer N+1 Layer N+1 Communication protocol Layer N Layer N Layer N-1 Layer N-1 Protocols TCP/IP Four layers TCP/IP Application - application interface Transport - direct connection Network - routing Network interface - transfer of bits TCP/IP application transport network network interface ISO/OSI application presentation relation transport network link physic Protocols TCP/IP Protocols of TCP/IP layers A HTTP HTTP FTP TELNET SMTP L 80 20/21 T L 23 POP3 DNS NFS RPC 110 53 123 111 25 other UDP TCP RTP N L P H L IP ARP RARP ICMP RIP IGMP OSPF Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, Novel, X.25, ATM, (SLIP, PPP) transfer medium TCP/IP Communication TCP/IP addresses Each node in the network has its own unique address Layers has its address format • Domain address = text address (application layer) www.seznam.cz • IP address = logic address (network layer) 32 bits - 195.119.180.19 • MAC address = physic (real) address (net inteface) 48 bits - 00-00-64-65-73-74 Domain address in TCP/IP (application layer) • DNS (Domain Name System) service domain address - IP address mapping • name servers = nodes providing DNS service • domain address example: hp832.fce.vutbr.cz node name . subdomain . subdomain . top level domain • domain – specification where node is placed – top level domain: COM, EDU, GOV, MIL, NET, ORG – v USA Non-US country code – (cz, sk, at, de, …) – subdomain Domains Hierarchy Unnamed root only USA gov mil nasa edu augustana com net novell czech org int cz vutbr fce Examples: www.atlas.cz www.rfc-editor.org www.altavista.com de www indy fee IP address IP version 4 • 32bits integer expressed as four dot separated numbers • logic (abstract) address Example of IP address: 0 7 8 1001 0011 147.229.26.10 15 16 23 24 31 1110 0101 0001 1010 0000 1010 Finite number of addresses: 2 32 • new IP protocol (IP version 6) - 128 bits address - eight hexadecimal numbers colon separated CA32:F123:C210:1234:0000:0000:0000:1A11 Structure of IP address IP address (p.q.r.s) contains two parts (for routing) - netid - hostid Example: IP network address 193.12.99.0 193 12 99 0 Classes of IP addresses and network mask: class A B C netid hostid p q.r.s p.q r.s p.q.r s nodes max 16777214 65534 254 subnet mask 255.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 255.255.255.0 Subnetting - dividing of the network • goals: more nodes in the net load balancing • hostid of IP address is divided to the two parts - subnet num - node num • subnet mask • 32 bits integer expressed as four dot separated numbers • first continuous part of bits contain 1 - defines network part of the IP address C Classes of IP addresses A B C 0 0 7 8 15 16 net 23 24 31 node 10 net 110 node net node Subnet mask net node Subnet mask net subnet node Examples: determining of net and node parts of IP address IP address = 193.12.99.18, subnet mask = 255.255.255.0 193.12.99.18 = 11000001 00001100 01100011 00010010 255.255.255.0 = 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000 193.12.99.0 = 11000001 00001100 01100011 00000000 network part of IP address = 193.12.99.0 IP address = 195.229.26.10, subnet mask = 255.255.255.224 195.229.26.10 = 11000011 11100101 00011010 11101010 255.255.255.224 = 11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000 195.229.26.224 = 11000011 11100101 00011010 11100000 network part of IP address = 195. 229.26.224 Examples: determining of net and node parts of IP address IP address = 147.229.22.85 subnet mask = 255.255.255.192 147.229.22.85 255.255.255.192 = 1001 0011 1110 0101 0001 0110 0101 0101 = 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1100 0000 147.229.22.64 = 1001 0011 1110 0101 0001 0110 0100 0000 network part of IP address = 147.229.22.64 Special IP addresses subnet address - symbolic address of the subnet - hostid contains only 0 bits: 136.229.26.0 broadcast - message to all nodes in LAN - group IP address (hostid contains only 1 bits) example: 195.229.26.255 = 11000011 11100101 00011010 11111111 multicast - message to some group of nodes in LAN Subnetting 193.12.2.1 net 193.12.x.x 193.12.2.2 net 193.12.1.x Gateway net 193.12.2.x One net representation 193.12.2.3 193.12.2.4 TCP/IP Communication Node X Each submitting layer adds its header (or removes it in receiving case) Applicat. layer Application data message Transport layer TCP header packet Network layer Physic interface layer TCP data IP header Frame header IP data datagram Frame data frame physic transport Node Y Applicat. layer Transport layer Network layer Physic interface layer Network connecting - active elements Passive elements (connectors, cabling, …) Active elements - electronic equipment for network connection (signal amplifying and transformation) node X node Y Applic. Applic. Transport gateway Transport Network router Network Link bridge repeater physic transport Link V. síťového rozhraní Internet (IP) Layer • Realized by IP protocol • Provides •unified addresses – logic IP addresses •unified format of transferred data (IP datagrams) •routing between the LANs via routers •address mapping: B ARP, RARP protocols A •non-connected, non-reliable Router 1 service Router 2 C Router 3 D E Data transfer between two nodes in different networks node knows - source (its) and target IP address, - source (its) and target MAC address (ARP) - IP address of router of its network • node send packet to the router if the net part is different • router send packet to the router or direct to the target node • IP routing table - subnet mask, target network, gateway (router) Network layer protocols IP Internet Protocol - packet transfer, without acknowledge, routing support ARP Address Resolution Protocol - ARP table determining physic address from IP address RARP Reverse Address Resolution Protocol - automatic allocation of IP address to the connected node ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol transfer of reserved service information Transport Layer TCP Layer • Data transfer between the applications • TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - provides: - connected service - makes connections between the nodes - acknowledging of successful data receiving • UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - provides: - non-connected, non-reliable data transfer Port = number of the service Socket = IP address + port • Ports of well-known services (WWW - port no. 80) • Other services - dynamic generated ports Ports and protocols of some services HTTP FTP HTTP 80 20/21 TELNET SMTP 23 25 POP3 DNS NFS RPC 110 53 123 111 TCP UDP IP Network interface Transport medium Application Layer • Applications and services communicate directly with the transport layer • Application implements needed mechanisms not supported in used transport layer • The main model of TCP/IP communication: client-server. Client actively requests the service and starts the communication Server provides the service passively at the client request. Protocols of applikation layer FTP (File Transfer Protocol) rfc 959 Telnet - rfc 854 SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) rfc 821 POP3 (Post Office Protocol) rfc1939 HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) rfc 2616 DNS (Domain Name System) rfc1035 DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) From 1969 all information about Internet published in RFC (Request for Comments) web accessible (http://www.rfc-editor.org). Useful commands Network is inaccessible ipconfig ping to IP address - default gateway determining - answer of gateway nslookup address tracert address domain and IP address resolving prop. of the trace to the node