The Cell
advertisement
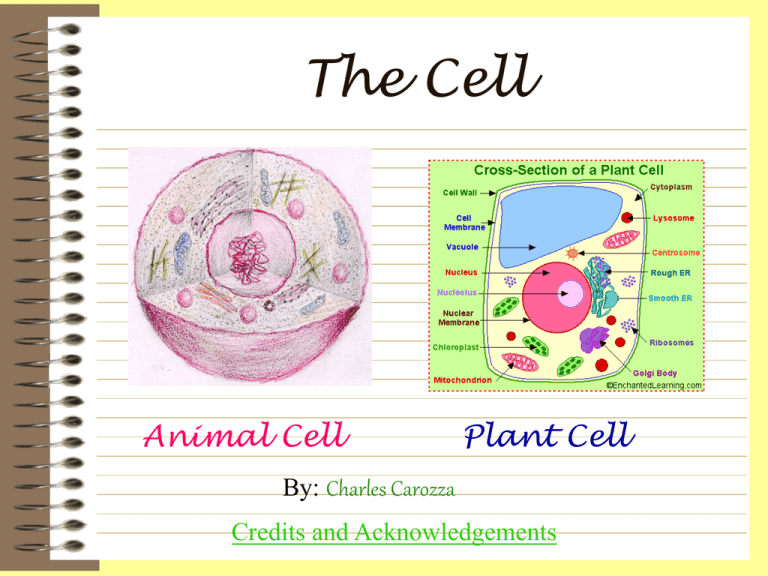
The Cell Animal Cell Plant Cell By: Charles Carozza Credits and Acknowledgements Cell Wall - Most commonly found in plant cells - Controls turgity -Extracellular structure surrounding plasma membrane -Primary cell wall: extremely elastic - Secondary cell wall: forms around primary cell wall after growth is complete Cell Membrane - Outer membrane of cell that controls cellular traffic - Contains proteins (left, gray) that span through the membrane and allow passage of materials - Proteins are surrounded by a phospholipid bi-layer. Nucleus The Nucleus consists of these various parts. Nucleolus The Nuclear membrane - Spherical shape - Surrounds nucleus - Composed of two layers - Numerous openings - Visible when cell is not dividing - Contains RNA for protein manufacture for nuclear traffic Chromosomes - Usually in the form of chromatin - Contains genetic information - Composed of DNA - Thicken for cellular division - Set number per species (i.e. 23 pairs for human) Mitochondria - Second largest organelle with unique genetic structure - Double-layered outer membrane with inner folds called cristae - Energy-producing chemical reactions take place on cristae - Controls level of water and other materials in cell - Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, and forms urea Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum(ER) is a network of folded membranes that extend through the cytoplasm to the nuclear membrane. There are two kinds of ER, rough and smooth. Rough has ribosomes associated with it, smooth has no ribosomes. ER is involved in the transport of materials through the cell. Ribosomes - Each cell contains thousands - Miniature 'protein factories' - Composes 25% of cell's mass - Stationary type: embedded in rough endoplasmic reticulum - Mobile type: injects proteins directly into cytoplasm Chloroplast - A plastid usually found in plant cells - Contain green chlorophyll where photosynthesis takes place Golgi Bodies Golgi apparatus(sometimes called the Golgi body) is similar to endoplasmic reticulum(ER). Golgi apparatus consists of sacs (with a single membrane) which are stacked like pancakes. Closely associated with the edges of the flattened sacs you will see vesicles which have pinched off from the Golgi. Vacuole Vacuoles have the simple structure of a sac, a single membrane surrounding solid or liquid contents. There are a wide variety of vacuoles, containing a wide variety of substances. Many plant cells contain a large central vacuole filled with water. Credits/References References Used Biology". Student Handbook, vol. 2. Nashville: Southwestern Company, 1995 Clark, John. The Cell: A Small Wonder. New York: Torstar Books, Inc., 1985 de Duve, Christian. A Guided Tour of the Living Cell, vol. 1-2. New York: Scientific American Books, Inc., 1984 Swanson, Carl P. and Peter L. Webster. The Cell, 4th ed. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice hall, Inc., 1977 Chromosome picture (index.html, structure.html) courtesy of Krishna Creinsa. All illustrations done by Noreen Khalid. All graphic work done by Robert Pongsajapan. Refer to Webliography for Internet sites. Click here to go back to the beginning.







