Mirrors Study guide ANSWER KEY Vocabulary: see notes Law of
advertisement
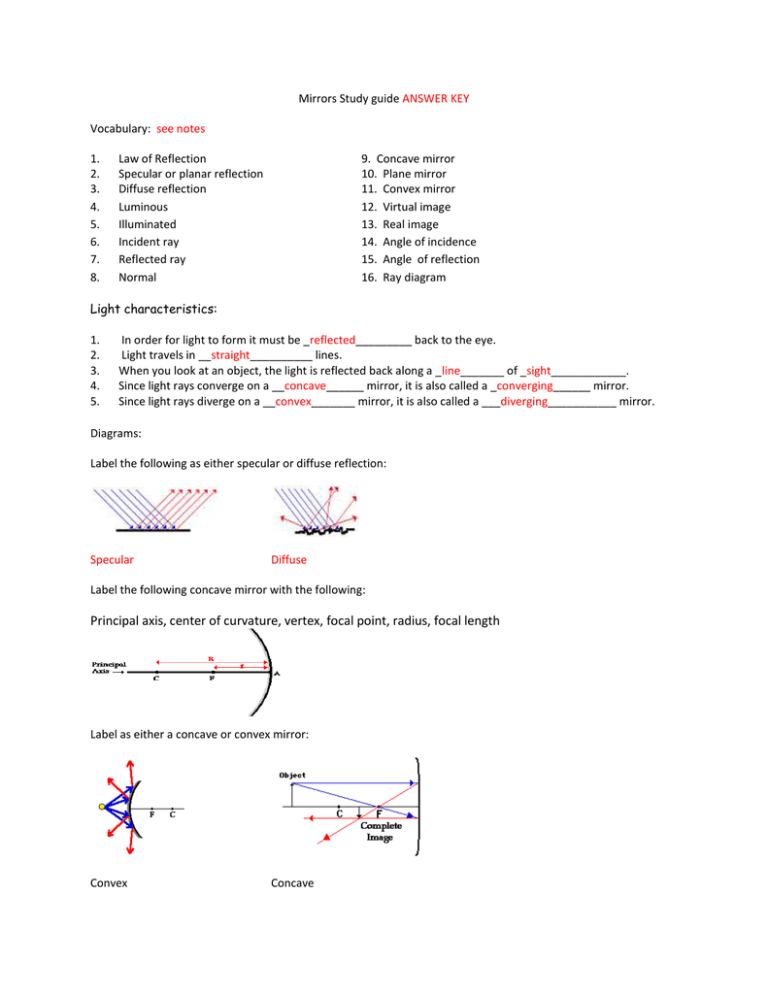
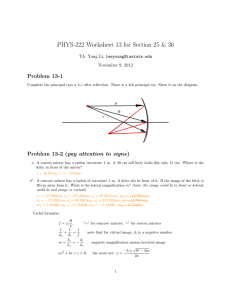
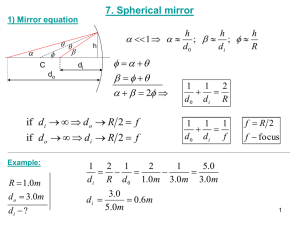
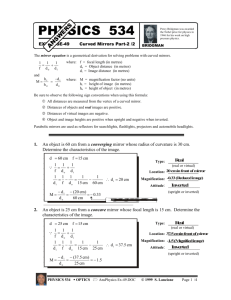
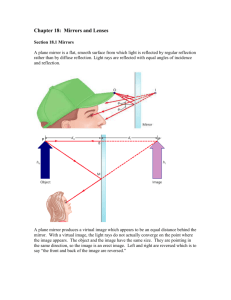
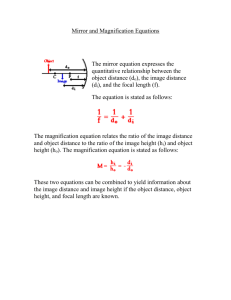
Mirrors Study guide ANSWER KEY Vocabulary: see notes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Law of Reflection Specular or planar reflection Diffuse reflection Luminous Illuminated Incident ray Reflected ray Normal 9. Concave mirror 10. Plane mirror 11. Convex mirror 12. Virtual image 13. Real image 14. Angle of incidence 15. Angle of reflection 16. Ray diagram Light characteristics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. In order for light to form it must be _reflected_________ back to the eye. Light travels in __straight__________ lines. When you look at an object, the light is reflected back along a _line_______ of _sight____________. Since light rays converge on a __concave______ mirror, it is also called a _converging______ mirror. Since light rays diverge on a __convex_______ mirror, it is also called a ___diverging___________ mirror. Diagrams: Label the following as either specular or diffuse reflection: Specular Diffuse Label the following concave mirror with the following: Principal axis, center of curvature, vertex, focal point, radius, focal length Label as either a concave or convex mirror: Convex Concave Real (R) vs. Virtual Images (V) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. _V____ Are upright _R____ Are inverted _V____ Are behind the mirror __R___ Are on the same side of the mirror as object _R, V____ Are formed by concave mirrors _V____ Are formed by convex mirrors _R____ Can be projected onto a screen _R____ Rays of light actually converge and pass through the image _V____ Rays of light do not actually pass through the image _R____ Can be larger, smaller, or the same size as the object Plane, Concave, or Convex Mirrors 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. concave_____ Form real or virtual images plane, convex_____ Form only virtual images plane_____ Form images that are the same size only convex_____ Form images that are always reduced concave_____ Form images that are either smaller/same size/larger than the object concave_____ Form images that are either real or virtual plane, convex_____ Form images that are only virtual plane, convex_____ Form images that are behind the mirror concave_____ Form images that are either behind the mirror or on the same side as the object plane_____ Form images that are always the same distance from the mirror as the object plane_____ Form images that have left to right reversal plane, convex_____ Form images that are always upright concave_____ Form images that are upright or inverted plane_____ Are flat, smooth mirrors concave, convex_____ Are curved mirrors Ray Diagrams: Image Characteristics: LOST The goal of drawing Ray diagrams is to find the following: L: _location O: _orientation (upright or inverted) S: _size (same, enlarged, reduced) T: _type (real, virtual) Complete each Ray Diagram and complete the LOST image characteristics to be expected: Plane Mirror – Draw each reflected ray according to the Law of Reflection. Extend the rays on the other side of the mirror to indicate where the image will be located. behind mirror, upright, same size, virtual Concave Mirrors – 5 cases Convex Mirror Behind mirror, upright, smaller, virtual Concave mirror summary: Case # Object Location Image location Orientation Size Type 1 Beyond C Between C & F Inverted Smaller Real 2 At C At c Inverted Same size Real 3 Between C and F Behind C Inverted Larger Real 4 At F No image Na Na Na 5 In front of F Behind mirror Upright Larger virtual Mirror Math Mag = - di/do 1. Determine the image distance and image height for a 5.00-cm tall object placed 30.0 cm from a concave mirror having a focal length of 15.0 cm. a. What is the magnification? –di/do -30/30 = -1 b. What case is this? Answer: di = 30.0 cm and hi = -5.0 cm 1/15 = 1/30 + 1/di to solve for di then, hi = -30 5 30 NOTE: this is "Case 2" because the image is inverted, real, same size as object 2. Determine the image distance and image height for a 5.00-cm tall object placed 20.0 cm from a concave mirror having a focal length of 15.0 cm. a. What is the magnification? –di/do -60/20 = -3 b. What case is this? Answer: di = 60.0 cm and hi = -15.0 cm 1/15 = 1/20 + 1/di to solve for di then, hi = - 60 5 20 NOTE: this is "Case 3" because the image is inverted, real and larger 3. Determine the image distance and image height for a 5.00-cm tall object placed 10.0 cm from a concave mirror having a focal length of 15.0 cm. a. What is the magnification? –di/do = 30/10 = 3 b. What case is this? Answer: di = -30.0 cm and hi = +15.0 cm 1/15 = 1/10 + 1/di to solve for di then, hi = 30 5 10 NOTE: this is "Case 5" because the image is upright, virtual and larger Sign Conventions f is NEGATIVE = if mirror is convex____________ di is NEGATIVE = if image is virtual_____________ hi is NEGATIVE = if image is inverted_____________