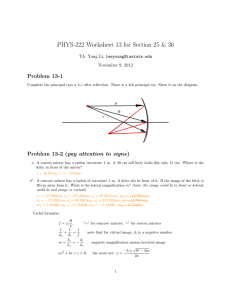
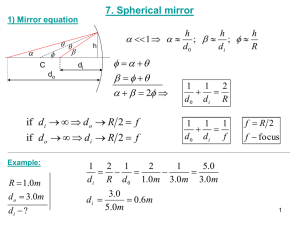
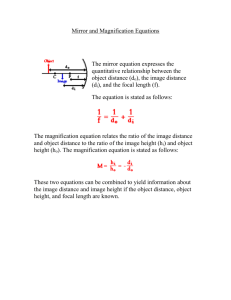
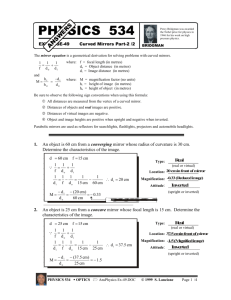
Image Characterisitics Type: Virtual or Real
advertisement

Image Characterisitics Type: Virtual or Real Orientation: Upright or Inverted Size: Same, Larger or Smaller Position: Behind the mirror or In front of the mirror Distance from mirror (same, closer or farther than object) 1 Images formed by plane mirrors 6 steps See handout last class, refer to p. 58 Make sure -the extended rays in step 2 equal the rays in step 1. -Extended rays (virtual) are dotted 2 Characteristics of images formed by plane mirrors: Images are: -virtual -upright -equal to the size of the object -the position is behind the mirror, at the same distance from the mirror as the object 3 Images formed by a pinhole camera Images are: -real -inverted -the size depends on the ratio between the do (distance of object from pinhole) and di (the distance of the screen from the pinhole) -the position is behind the pinhole 4 Magnification (size) of an image can be found mathematically M = hi/ho hi = height of image ho = height of object M = - di/do di =the distance of the image from mirror/lens do= the distance of the object from the mirror/lens If the object is inverted, the hi will be negative di is negative if the image is behind the mirror If magnification is negative it is because the image is inverted (upside down) 5 Example: A pinhole camera with a depth of 20.cm is used to take a photograph of a person standing 5.0 m away. If the height of the image is 10. cm, what is the magnification (M) of the pinhole camera and how tall is the person? List what you know and what you need to find M=? di = do = hi = ho= Write the two formulas: M = - di /do (di is positive in a pinhole camera) M = hi/ ho Plug in the values you have M = - 0.20.m/5.0m = -0.040m Now we know M = -0.040m -0.040 = hi/ho = 0.10m / ho ho = 0.10m/-0.040m = 2.5m 6 Homework: p. 70 1 ­ 6 7 Let's look at converging mirrors 8