Foods – Nutritional Needs Name ° The following information can be
advertisement

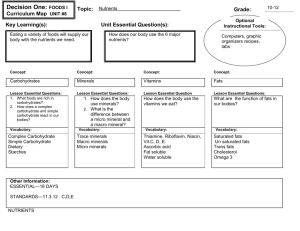
Foods – Nutritional Needs The following information can be found in Guide to Good Food. 1. Pg. 34 – Define the following: Nutrient – Nutrition – Malnutrition – How many nutrients are needed for good health? List the 6 nutrient groups: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 2. Carbohydrates – pg. 35-36 Carbohydrates can be divided into three categories: 1. 2. 3. What makes up simple carbohydrates? What makes up complex carbohydrates? Define fiber – Functions of carbohydrates (sugars and starches) 1. Name ° 2. 3. 4. Sources of carbohydrates- 3. Fats – pg 37-38 Fats include both & . Sources of fatsExamples of visible fat – Examples of invisible fat – Functions of fat 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 4. Proteins pg. 39-40 Proteins are made up of small units called . What is complete protein? Complete protein can be found in & . What does it mean when two or more incomplete proteins complement each other? Functions of proteins 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Vitamins pg. 40 Vitamins are needed in small amounts for . Water soluble vitamins include Fat soluble vitamins include 6. Minerals pg. 47 Why are minerals needed? At least how many minerals are needed for good health? 7. Water pg. 53-54 Functions of water 1. 2. 3. 4. . . 5. Foods – Nutritional Needs Name The following information can be found in Guide to Good Food. 1. Pg. 34 – Define the following: Nutrient – a chemical substance in food that helps maintain the body Nutrition – the study of how the body uses nutrients Malnutrition – a lack of the right proportions of nutrients to maintain a healthy body How many nutrients are needed for good health? More than 50 List the 6 nutrient groups: 1. carbohydrates 2. fats 3. protein 4. vitamins 5. minerals 6. water 2. Carbohydrates – pg. 35-36 Carbohydrates can be divided into three categories: 1. simple 2. complex 3. fiber What makes up simple carbohydrates? 6 types of sugar What makes up complex carbohydrates? starch & fiber Define fiber – a form of complex carbohydrates from plants that humans can’t diget ° Functions of carbohydrates (sugars and starches) 1. provides energy 2. helps the body digest fats 3. allows body to use proteins for growth & maintenance instead of energy 4. provides bulk (fiber) to aid in digestion, reduce cholesterol & lower blood pressure Sources of carbohydrates- plant foods 3. Fats – pg 37-38 Fats include both fats & oils . Sources of fatsExamples of visible fat – oil, margarine, butter, fat on meat Examples of invisible fat – eggs, whipped cream, baked goods Functions of fat 1. supplies energy/ stores energy in form of fat 2. carry fat-soluble vitamins through body 3. insulates the body from shock and temperature change 4. protects vital organs 5. makes meat and baked good more tender 6. adds flavor to food 7. source of essential fatty acids (surrounds nerves and cells) 4. Proteins pg. 39-40 Proteins are made up of small units called What is complete protein? amino acids . Protein that includes all 9 essential amino acids Complete protein can be found in meats & soybeans . What does it mean when two or more incomplete proteins complement each other? When each food has incomplete protein, but when combined, they provide all 9 amino acids (together they make a complete protein) Functions of proteins 1. provide energy 2. build and repair tissues 3. help make antibodies, enzymes, hormones & some vitamins 4. regulates fluid balance in cells and body processes 5. Vitamins pg. 40 Vitamins are needed in small amounts for normal growth, maintenance & reproduction Water soluble vitamins include C & B complex (thiamin, niacin, ribroflavin, B 6, Folate Fat soluble vitamins include A, D, E, & K 6. Minerals pg. 47 Why are minerals needed? Become part of bones, soft tissues, and body fluids At least how many minerals are needed for good health? 7. Water pg. 53-54 Functions of water 1. found inside and outside all cells 2. aids digestion, cell growth, and maintenance 3. lubricates joints and body cells 4. helps regulate body temperature 21 . . 5. all chemical reactions rely on water