Reconstruction 1865-1877
Reconstruction
1865-1877
Mr. Owens
Essential Questions
• To what extent were the political, economic, and social effects of the Civil War and Reconstruction revolutionary?
• What were the short-term successes and longterm failures of Republican-lead Reconstruction from 1865 to 1877?
• What constitutional changes emerged due to the
Civil War and how were American identity, national purpose, and definitions of citizenship altered?
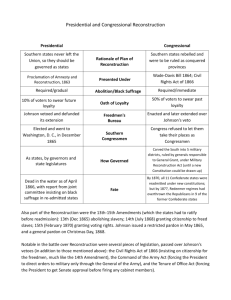
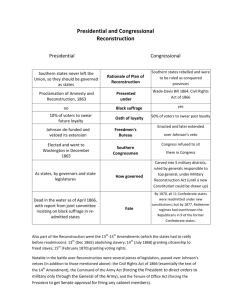
Lincoln’s Reconstruction
*
•
Lincoln’s 10% Plan :
“ Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction ”
(December 1863)
Presidential Pardons to: 1) took loyalty oath to the
Union and Constitution & 2) agreed to emancipation.
* When 10% of the voting pop. in the 1860 election were “ loyal ” the state could be reestablished.
Wade-Davis Bill (1864 ) Benjamin Wade (OH) & James Davis (MD)
• 50% of the number of 1860 voters to take oath
• “ Iron-clad Oath ” only non-Confederates could vote only if never voluntarily aided the rebellion.
• Enacted specific safeguards of freedmen ’ s liberties.
• Lincoln “ pocket ” vetoed it.
Freedmen’s Bureau (March 1865) welfare agency providing food, shelter, & medical aid for former slaves (& homeless whites)
– Led by General Oliver Howard
– Created 3,000 schools that educated 200,000 freedmen
– Attempts to settle blacks on confiscated lands blocked (“40 acres and a mule”)
Johnson’s Reconstruction
• Andrew Johnson (TN) Jacksonian Democrat, added to
Lincoln’s ticket in ‘64 to lure pro-Union Democrats, white supremacist who clashed with Republican goals
Presidential Reconstruction :
• Similar to Lincoln’s plan
• Disenfranchised Confederate civil and military officers
& wealthy ($20,000 or more) States had to ratify 13th
Amendment.
• Johnson granted 13,500 special pardons.
• None of the new state constitutions extended voting rights to blacks - result?
• 1866 Northern Republicans refused to seat ex-
Confederates including former VP Alexander Stephens
Black Codes : restricted rights of former slaves Including:
1. couldn’t rent land or borrow $ 2. Forced “vagrants” into contract-labor 3. Couldn’t testify against whites in court
Johnson Vetoes: Freedmen’s Bureau re-charter & Civil
Rights Act to nullify black codes, but Congress overrides both in 1866
- 29 vetoes but 15 overridden by Republican Congress
“Radical” Republicans
• Radical Republicans led by Charles Sumner in Senate &
Thaddeus Stevens in House wanted to punish the
South & extend rights to former slaves
• Civil Rights Act of 1866 – all blacks were citizens & attempted to eliminate black codes
• 14 th Amendment (June 1866 – ratified by states 1868)
*
Citizenship Clause: All persons born or naturalized in
*
U.S. are citizens (including former slaves)
Due Process & Equal Protection Clause: States can ’ t deny rights, “ equal protection ” or “ due process ” to any U.S. citizen
*
Disqualified former Confederate political leaders from holding state or fed. office.
*
*
Confederate states must pay off debts.
Punished states that denied black suffrage by reducing members of Congress & electoral college
Radical Reconstruction & Impeachment
• Johnson’s “ Swing Around the Circle ” 1866 midterm campaign backfired – Republicans gained 3 to 1 majority in Congress
Reconstruction Acts of 1867
* Required new state constitutions, including black suffrage and ratification of the 13 th and 14 th
*
Amendments.
Divide the 10 “ unreconstructed states ” into 5 military districts “Military Reconstruction”
Johnson Impeachment:
• Command of the Army Act & Tenure of Office
Act : Pres. couldn’t remove Generals or officials [esp. Cabinet] without the Senate ’ s consent.
• Johnson fires Sec. of War Edwin Stanton claiming laws unconstitutional
• Johnson Impeached in 1868 but 1 vote shy of removal in 3 month Senate trial
Election of 1868 & Grant
Election of 1868: Ulysses S. Grant victory over
Horatio Seymour in ugly campaign “waving the bloody shirt” due to in part victory in
South – lesson?
15 th Amendment :
• Passed in 1869 - Ratified in 1870.
• The right to vote can ’ t be denied by the fed or state government “ on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude.
• Congress shall enforce it.
”
• Women ’ s rights groups were furious – why?
Civil Rights Act of 1875
• Guaranteed equal accommodations in public places & forbid courts from banning blacks from juries
• Law was poorly enforced & ignored
• No significant Civil Rights legislation for 89 years
Reconstruction in the South
• Republican government dominated South during Military occupation
• Democrats attempted to undermine
Republicans as “ Carpetbaggers ” & “ Scalawags”
• African American legislators: Freedmen controlled lower house in South Carolina & 2 black senators from Mississippi: Hiram Revels (1870) &
Blanche Bruce (1875) & 20 blacks served in House of Reps – Next black Senator from South?
• Myth of “Colored Rule” – undermined support
Building Black Communities:
• Reunited with families, many moved to cities.
• Rise of Negro Baptist and American Methodists
Episcopal (AME) churches
• New black colleges - Howard, Atlanta, Fisk,
Morehouse - train black ministers & teachers
• Rise of Sharecropping (tenant farming) landlord seed & supplies in exchange for ½ of the harvest, by 1880 less than 5% were landowners
The North During Reconstruction
• Rise of “Spoilsmen” – Republican leadership shifted from reformers to Party Bosses like
Sen. Roscoe Conkling & James Blaine
• Corruption:
– Jay Gould & James Fisk corner the Gold Market in
1869
– Credit Mobilier Scandal – profiteering & graft from transcontinental railroad
– Whiskey Ring – Fed agents & distillers defrauded gov. of millions
– “Grantism”
– Boss Tweed Ring of Tammany Hall urban politcal machine corruption in NYC
• Election of 1872: despite scandals Grant defeats reform-minded Horace Greeley editor of NY Tribune
• Panic of 1873 : overspeculation & overbuilding by railroads led to high bankruptcy, unemployment & debt
End of Reconstruction
• Radical Republicans in decline & northern focus on economic issues
• White supremacy reigns in South
– Ku Klux Klan “invisible empire” founded in 1867 by Nathan Bedford Forrest lynchings & violence to suppress black votes
– Force Acts in 1870 & 1871 use of federal military to crush Klan operations
• Amnesty Act of 1872 : pardon all Confederates except top leaders. Led to white Southern Democrat
“ Redeemers ” regaining control of South
• Election of 1876 : Republican moderate Rutherford
B. Hayes of OH vs. NY reform governor Dem Samuel
Tilden. Disputed result but Tilden appeared in lead.
• Compromise of 1877 :
1.
Hayes gets the presidency
2.
Immediate end of military Reconstruction in South
3.
Support for Southern transcontinental railroad “Ruther-fraud Hayes”
“His Fraudulency”