Environmental Stress: Plant Adaptations with Jill Van Winkle Name
advertisement

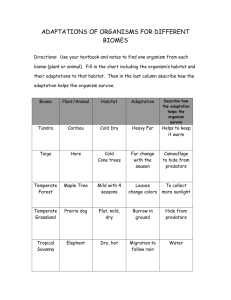
Environmental Stress: Plant Adaptations with Jill Van Winkle Name: _____________ _Period:__ 1. What is an adaptation? 2. What is plasticity in plants? Why do they need it? Instructions 1 – Observe and describe the plants at your lab bench. Decide which habitat the plant is best adapted. 2 – List at least 3 adaptations each plant has made to its habitat. Describe how they help the plant succeed. 3 – Compare and contrast the plants based upon their habitats. 4 – Select a habitat and create a plant to succeed in this environment. 5 – Draw and describe adaptations you would give the plant to succeed. You have limited resources, so you will have to choose wisely and defend your choices! Describe and compare your plants by filling out the table below: Plant 1: Plant 2: Habitat Adaptation 1 Adaptation 2 Adaptation 3 Weaknesses? 3. If the plants traded habitats, would they succeed? Which would do better? Why? 4. Select a habitat from the attached sheet. Descriptions of some of the environmental conditions for each habitat are listed on this sheet. My Habitat Is: __________________________________ 5. Adapt a plant for your habitat! You have 5 resource points. Some plant adaptations are more costly to the plant to produce. Within each category (see Adaptation Table!), you can decide how your adaptation looks or functions (e.g. size and shape of thorns, location on the plant). If you have an idea for a plant adaptation not within the categories, ask Ms. Crowell or Jill to approve it and determine the resource cost. *Remember, no more than 5 points total! So you could have as many as 5 or as few at 2 adaptations. Plant Adaptations: Points 1. __________________________________________________________ ______ 2. __________________________________________________________ ______ 3. __________________________________________________________ ______ 4. __________________________________________________________ ______ 5. __________________________________________________________ ______ TOTAL 6. Draw your plant. Label the adaptations and describe how they would make the plant more successful in its habitat. HABITAT TABLE Environmental Conditions Habitat Temperature Moisture Light Competition Predators Soil Nutrients Soil pH Desert High Low High Low Small mammals Neutral NW Forest Moderate Summer: low Winter: high Low-moderate Moderate Deer, insects Acidic Lowmoderate NE Forest Summer: high Winter: low Moderate-high year-round Low-moderate Moderate Deer, insects Neutral Moderate Bog/ Swamp Moderate High Low Low Insects Acidic Low Tropical Rain Forest High High Variable Very high All kinds Acidic Low Alpine Low! Low High Low Small mammals Alkaline High High ADAPTATION TABLE Adaptation Response to: Leaf shape & size Leaf coating Leaf toxins Leaf movement Light, temperature, moisture, competition Light, temperature, moisture Moisture, predation Predation Light Evergreen leaves Nutrients or pH 1 Vines or tendrils Light, competition 1 Spines or thorns Carbohydrate storage Predation Temperature, moisture 2 2 Stem shape or color Light, temperature, moisture Light, competition Moisture, stability, competition Light, competition, height, predation Moisture Leaf color Rapid growth Tap root Woody stems Water storage, succulent Digestive structures (carnivorous) Saprophytic or parasitic Cost (points) 1 Example Surface area for light (energy!) and gas exchange 1 Dark green = increased chlorophyll 1 2 1 2 Waxy, tough, thick leaves Bitter or poisonous compounds Move to increase or decrease light as needed (e.g. Mimosa trees) New leaves require nutrients. Useful in low nutrient environments to keep leaves. Use other plants as “scaffolds” to seek light, compete Modified leaves – cactus spines, rose thorns Energy storage, typically below ground: fleshy roots, tubers, etc. For photosynthesis, storage, etc. 2 2 Can climb above other plants to seek light Access scarce water, stability. 2 Can grow taller than other plants – more light 3 thickened stems or leaves Nutrients 4 Costly, only used in very nutrient poor conditions Light, competition, nutrients, decomposition 4 Limited light and/or nutrients. Allow growth without light!