Earth Science Regents Review
advertisement
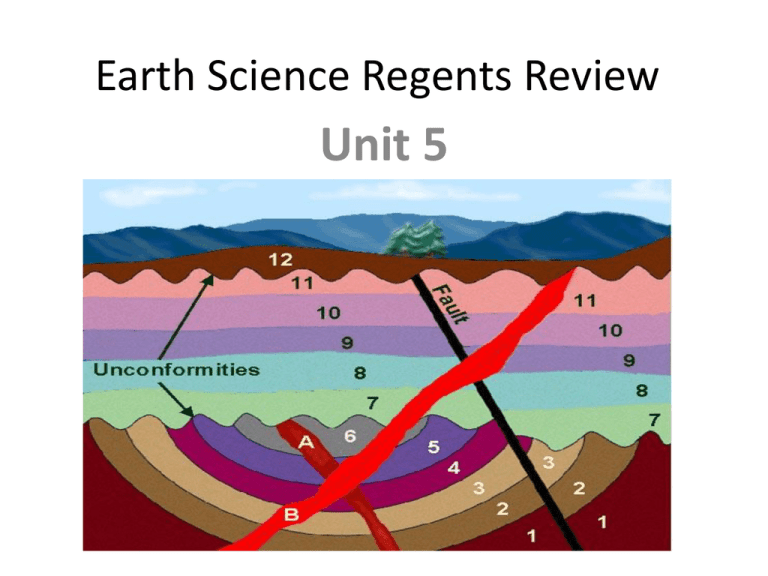
Earth Science Regents Review Unit 5 Sequence of Events • Principle of Superposition: older layers are on the bottom • Law of Original Horizontality: sedimentary layers are all horizontal before crustal movement • Law of Cross Cutting Relationships: whatever cuts across a layer is younger than the layer • Principle of Uniformitarianism: the way geologic events happened in the past happen in the same way today. An unconformity is a buried erosional surface. It is usually represented by a squiggly line in between layers. The steps are as follows: • uplift and emergence •weathering and erosion •subsidence and submergence •deposition of _______________ How did this form? 1) _________________is the matching of strata through fossils or characteristics of the layers to prove that they were once part of the same outcrop. What are index fossils? These are fossils found in many locations but only existed for one geologic time period. They are excellent time markers. Volcanic Ash Useful because volcanic ash could cover large areas in a very small period of time (days to weeks) and each volcano has a mineral “fingerprint” it is very useful in correlation 7 The diagram below shows a fossil found in the surface bedrock of New York State. Which other fossil is most likely to be found in the same age bedrock? 1.Phacops 2.condor 3.Coelophysis 4.Tetragraptus Which fossil may be found in the surface bedrock near Ithaca, NY? 1. 2. 3. 4. 3) Define radioactive decay: The breakdown of an unstable atom into a more stable atom which is a completely different element. 5) Parts of radioactive decay Parent isotope Daughter isotope The unstable isotope Decreases during decay The stable isotope Increases during decay A.k.a. decay product 5) Define half life: It is the time needed for half of a substance to decay into its stable form. 6) Why is the half life so useful for accurate dating? Nothing can change the half life. 7) Which isotope should we use? Carbon- 14 Potassium-40 Short half-life Dates living things Recent events of less than 50,000 years (Pleistocene to Holocene) Looooong half-life Can be used on rocks Dates very old events # of half- # of years passed lives 0 1 2 3 4 fraction remaining amount of C-14 amount of N-14 How old is a How old is a fossil that substance that has contains 25g of 100g of Carbon-14 Potassium-40 and and 100 g of Nitrogen- 175 g of Argon-40? 14?