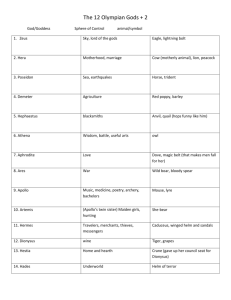
File
advertisement

Supreme Court Cases Solem V. Helm • Issue: • Was Helm’s constitutional right of freedom from cruel and unusual punishment violated? Solem V. Helm • Summarizing Facts: • Jerry helm (respondent) was convicted of 6 non violent felonies. In the state he was in, because of his history, if he committed another felony he would be subject to the maximum for a Class 1 felony. The punishment for that was life imprisonment and $25,000 fine without parole. Solem V. Helm • Summarizing facts continued… • The lower courts ruled that because he had 6 prior felonies, his sentence would stand. • The respondent appealed to governor to pardon his sentence and it was denied • Helm then filed a petition of certiori claiming his sentence violated the 8th amendment. Solem V. Helm • Decision: • The Supreme court ruled in favor of Helm stating that his 8th amendment rights were violated. Solem V. Helm • Reasoning: • Majority: “as a matter of principle that a criminal sentence must be proportionate to the crime for which defendant has been convicted” • The Court overturned the sentence on the grounds that it was "cruel and unusual". Justice Powell wrote for the five-member majority • “Finally, we compare the sentence imposed for commission of the same crime in other jurisdictions”. “It appears that Helm was treated more severely than he would have in any other State”. Solem V. Helm • Majority continued… • The language of the opinion, however, refrained from striking down state statutes setting minimum sentencing guidelines for recidivism. The majority opinion only called for exceptions to the statutes protecting the constitutional freedom from cruel and unusual punishment. Solem V. Helm • Dissenting: • The dissenting justices observed that in Rummel V. Estelle, a life sentence imposed after on a third non violent felony conviction did not constitute cruel and unusual punishment. • Further, the justices “rejected the fiction that all of Helm’s crimes were innocuous or nonviolent. Solem V. Helm • What is your opinion? Solem V. Helm • How does this case relate to Equality v. Discretion? Harmelin V. Michigan • Issue: • Does the 8th amendment of the United States Constitution contain a proportionality guarantee with regard to punishment? • Or • Were 8th amendment rights violated due to the punishment not being proportionate to the crime? Harmelin V. Michigan • Facts: • Petitioner (the party who petitioned the Supreme Court to review the case) Harmelin was convicted of possessing 672 grams of cocaine and sentenced to life in prison without parole. He claims the punishment is significantly disproportionate to the crime and violates his 8th amendment rights. • Michigan court of appeals heard case and affirmed his conviction. • Supreme court granted certiori Harmelin V. Michigan • Decision (Majority) • Original judgement affirmed. The 8th amendment “does not contain a proportionality agreement”. • “The majority’s rationale for the above holding is that if we were to allow such analysis of the proportionality principle, we would be, in effect, imposing subjective values as to what is and what is not proportional based on subjective views….” Harmelin V. Michigan • Decision (Majority) continued… • “The Court states that it is up to the legislature, and not the judiciary, to make such determinations” • (meaning: it is up to how they make or phrase the law) Harmelin V. Michigan • Dissent: • Argues that this punishment may violate 8th amendment because “is it contrary to the evolving standards of decency that mark the progress of a maturing society”. • Also, looking back at solem v. helm, they need to look at 1) harm caused, 2) sentence imposed on other criminals in same jurisdiction and the sentences imposed for same crime in other jurisdictions be used to evaluate whether statute (law) in question violates 8th amendment. Harmelin V. Michigan • Your opinion? • How does this relate to second basic choice of equality v. discretion? U.S. v. Booker • Issue: • 1. Whether imposing an enhanced sentence under the U.S. sentencing guidelines, based on judicial determination violates the 6th amendment, and if it does • 2. Whether the sentencing guidelines are unconstitutional U.S. v. Booker • Facts: • Booker’s (petitioner) sentence was enhanced (or made worse/longer) without the jury. It was based only on the judge’s determination and without Booker’s consent to a no jury trial. • In separate cases, according to sentencing guidelines, defendant could have been given enhanced sentence , but judge decided not to enhance due to supreme court case law stating it was violation of 6th amendment unless facts were presented to jury. U.S. v. Booker • Decision (Majority) • Enhanced sentences that used facts not presented to jury are a violation of the 6th amendment right to trial by jury. • Sentencing act reform was repealed by this decision. U.S. v. Booker • Dissent: • By repealing the sentencing reform act, it takes away congressional right to determine sentencing. This is allowing for courts to implement different sentences for different crimes (what is this called?) U.S v. Booker • Your opinion? • How does this relate to equality v. discretion? • (determinate sentencing – what is it?)