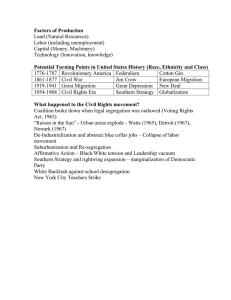
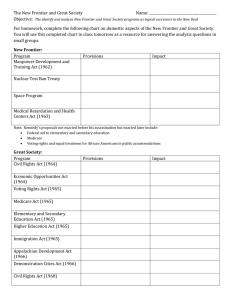
7.01: The Great Society: The Big Ideas What did LBJ think made a
advertisement
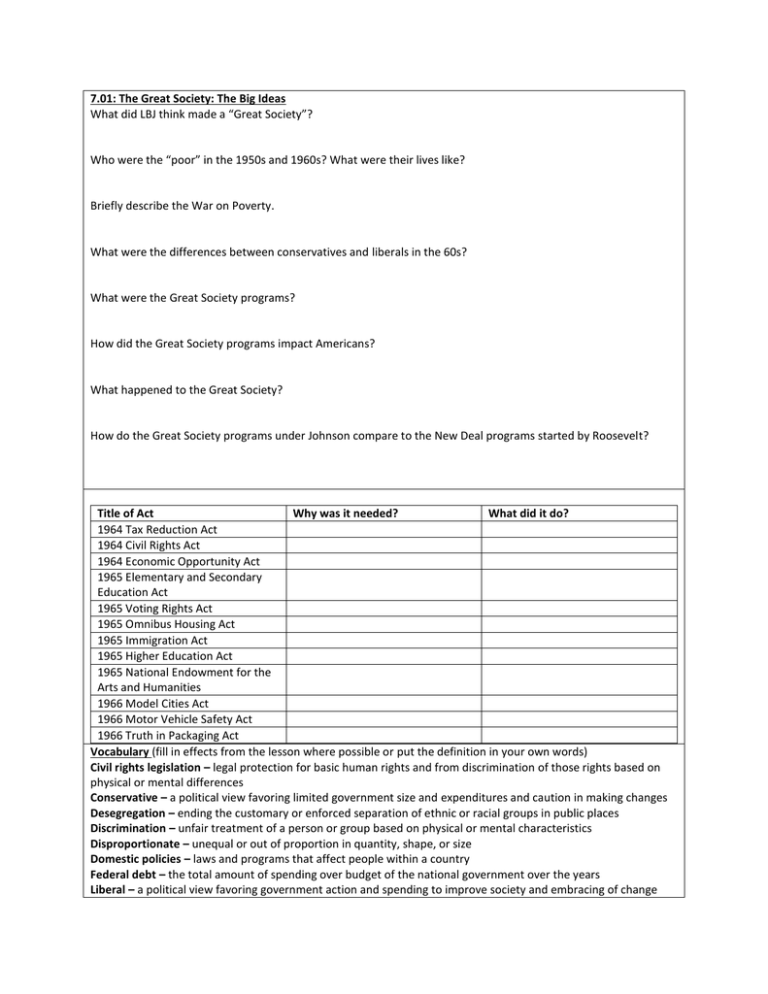
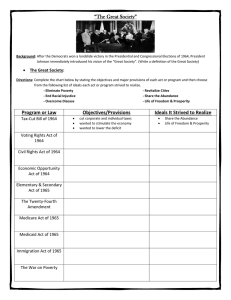
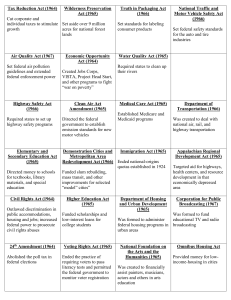
7.01: The Great Society: The Big Ideas What did LBJ think made a “Great Society”? Who were the “poor” in the 1950s and 1960s? What were their lives like? Briefly describe the War on Poverty. What were the differences between conservatives and liberals in the 60s? What were the Great Society programs? How did the Great Society programs impact Americans? What happened to the Great Society? How do the Great Society programs under Johnson compare to the New Deal programs started by Roosevelt? Title of Act Why was it needed? What did it do? 1964 Tax Reduction Act 1964 Civil Rights Act 1964 Economic Opportunity Act 1965 Elementary and Secondary Education Act 1965 Voting Rights Act 1965 Omnibus Housing Act 1965 Immigration Act 1965 Higher Education Act 1965 National Endowment for the Arts and Humanities 1966 Model Cities Act 1966 Motor Vehicle Safety Act 1966 Truth in Packaging Act Vocabulary (fill in effects from the lesson where possible or put the definition in your own words) Civil rights legislation – legal protection for basic human rights and from discrimination of those rights based on physical or mental differences Conservative – a political view favoring limited government size and expenditures and caution in making changes Desegregation – ending the customary or enforced separation of ethnic or racial groups in public places Discrimination – unfair treatment of a person or group based on physical or mental characteristics Disproportionate – unequal or out of proportion in quantity, shape, or size Domestic policies – laws and programs that affect people within a country Federal debt – the total amount of spending over budget of the national government over the years Liberal – a political view favoring government action and spending to improve society and embracing of change Migrant laborer – a worker who moves from place to place seeking work, usually referring to movement according to the seasons in farming work Poverty rate – the portion of a population living below an official level of income determined to be necessary for meeting basic needs Social welfare programs – a government initiative designed to protect citizens from economic risk and insecurity Unconstitutional – not allowed by or against the ideas and principles of the Constitution