File
advertisement

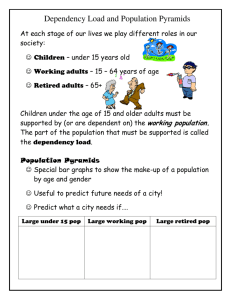
Give an example of a map that would have a ‘large scale’ What map projection distorts the size of land masses close to the poles? If a city is found at: Latitude: 43° 40' 0 N, Longitude: 79° 25' 0 W, what continent is it on? Another word for Perceptual Region is? Give an example of distance decay: Give an example of hierarchal diffusion: Give an example of relocation diffusion: Where is the world’s population distributed? More people today than ever before (7.3 billion) World’s population increased at a faster rate in the 2nd half of the 20th century than ever before in history Almost all pop. Growth is in LDCs Generally has meant growth (global scale) Regional examples of pop. decline usually short term (war, disease, famine) These 2 trends generally still hold true today with a couple exceptions Can you think of any? Fig. 2-1: This cartogram displays countries by the size of their population rather than their land area. (Only countries with 50 million or more people are named.) Population Concentrations Similarities around world: •live near ocean/river •low-lying •fertile soi •temperate climate •10°N - 55°N 2/3rds of people are clustered in 4 regions East Asia (E China, Japan, Korea, Taiwan) South Asia (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka) Southeast Asia (Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines) (Western) Europe (includes 48 countries) 1/3 of world lives in India or China! NE United States & SE Canada - Bosnywash West Africa (Nigeria) Even though population distribution is uneven, it is far from irrational Ecumene – permanently inhabited areas of earth’s surface Fig. 2-2: World population is very unevenly distributed across the Earth’s surface and it can be compared to climate distribution. 75% of world’s population lives on 5% of Earth’s surface (environmental determinism) Dry Lands – deserts, unable to grow crops Wet Lands – near equator Cold Lands – near poles High Lands – mountains Humans have always been spread very unevenly across the E’s surface Even as pop. exploded from 1.5 billion to 6.5 billion in only 100 yrs the areas of pop. concentration simply became more highly concentrated (denser) & most of the uninhabited land remained uninhabited Arithmetic Density (pop. or crude): total # of people divided by total land area Physiological Density: # of people supported by a unit of arable land ▪ Higher the #, more ppl need to be fed on the crops grown Agricultural Density: ratio of # of farmers to the amount of arable land ▪ MDCs have low #’s b/c of technology & finance Egypt Population: 73.3 million Pop. Density: 190/sq.mile Physiological Density: 6319/sq.mile 98% of Egyptians live on 3% of the country’s land Switzerland Population: 7.4 million Pop. Density: 465/sq.mile Physiological Density: 4710/sq.mile Mountainous landscape Ukraine Population: 46.7 million Pop. Density: 200/sq.mile Physiologic density: 381/sq.mile Vast farmlands 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. China 1,372,200,000 India 1,277,440,000 USA 321,867,000 Indonesia 252,164,000 Brazil 204,930,000 Pakistan 190,969,000 Nigeria 173,615,000 Bangladesh 159,061,000 Russia 146,068,000 Japan 127,130,000 Canada’s current population = 35,482,000 (0.5% of world population!)