Why Might the World Face an Overpopulation

Why Might the World Face an
Overpopulation Problem?
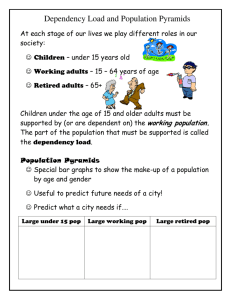
• Malthus:
– Pop. Growing faster than food supply
• Today: 1 person, 1 unit of food
• 25 years: 2 person, 2 units of food
• 50 years: 4 persons, 3 units of food
• 75 years: 8 persons, 4 units of food
• 100 years: 16 persons, 5 units of food
Neo-Malthusians
• Recent pop. Grown (20 th century)
– 2 arguments
1. Gap b/t pop. Growth and resources is wider in some countries
2. World pop. Growth is exceeding lots of resources
Malthus’s Critics
• Unrealistic
• Pop. Growth does not equal problems
• Sufficient resources if distributed equally
• More people = greater power
World Health Threats
• Epidemiologic transition- distinctive causes of death
Epidemiological Transition
• Stages 1 & 2
– Stage of famine
– Black Plague
– Cholera
Figure 2-23. Cholera in Soho, London, 1854. Dr. John Snow mapped the distribution of cholera victims and water pumps to prove that the cause of the infection was contamination of the pump near the corner of Broad and
Lexington streets.
Epidemiologic Transition Stage 3 &
4
• Degenerative and human created diseases
– Decrease in infectious disease deaths
– Increase in chronic disorders
• Polio
• Cancer
Epidemiological Transition Stage 5
• Re-emergence of infectious diseases
– Why? Evolution
• Become resistant to drugs and insecticides
• malaria
– Why? Poverty
• TB
– Why? Travel
• Traveling more/easier